Embed presentation
Download to read offline



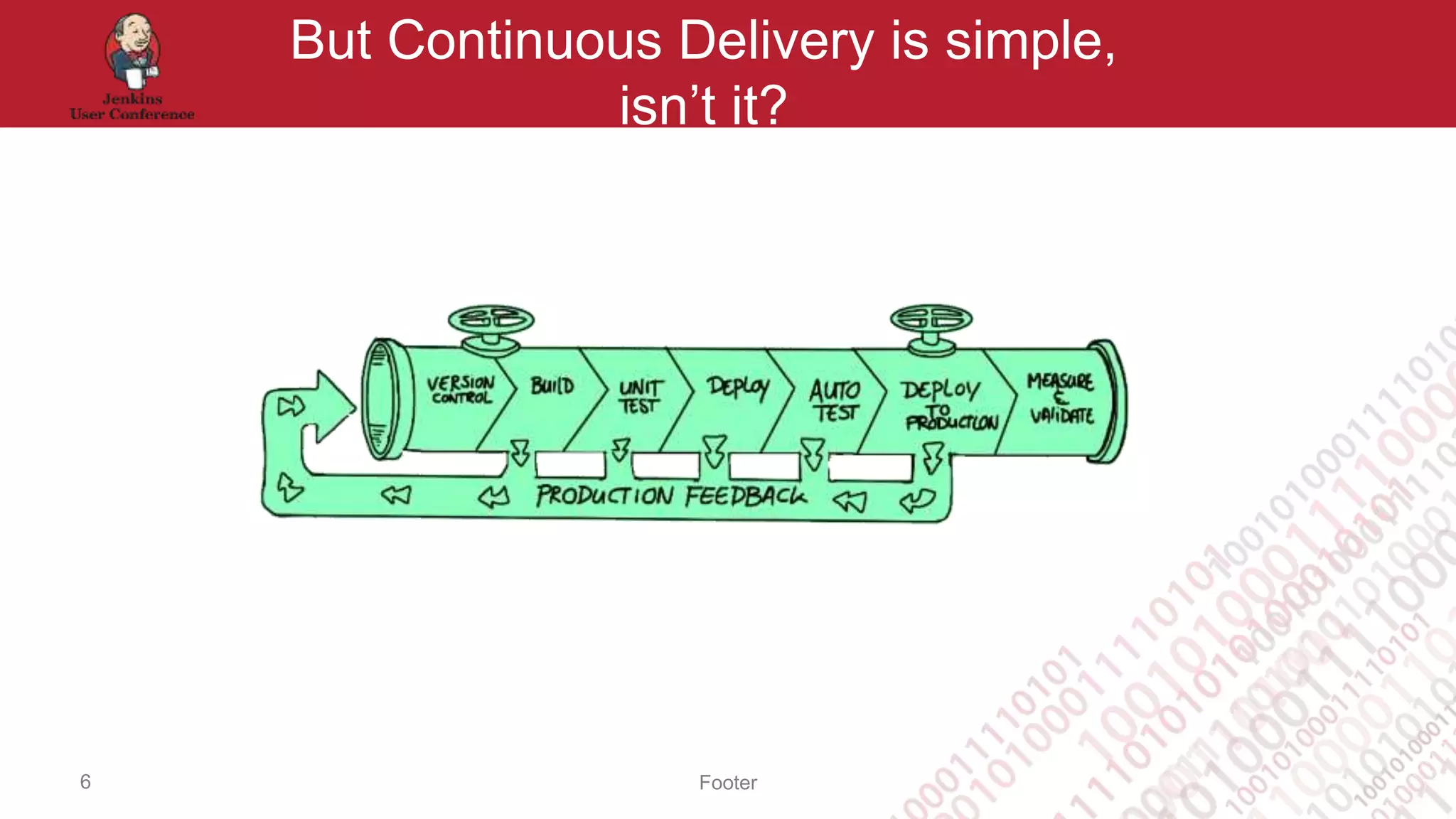






Continuous Delivery is not a commodity because no two Continuous Delivery pipelines are exactly the same. Continuous Delivery requires integration with multiple tools and frameworks, support for multiple operating systems, and customizable flows, dashboards, and reporting. While the principles of Continuous Delivery can be learned from others, each organization's Continuous Delivery process is unique and cannot simply be copied from another. Continuous Delivery is more of an art than a science that depends on people, not just technology.











