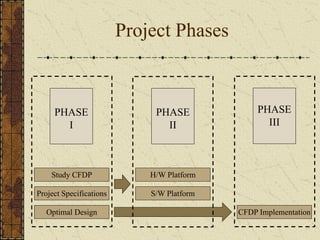
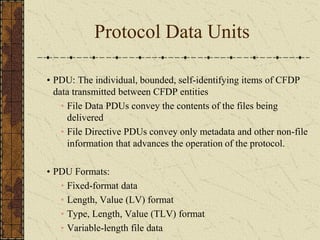
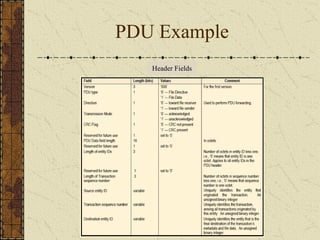
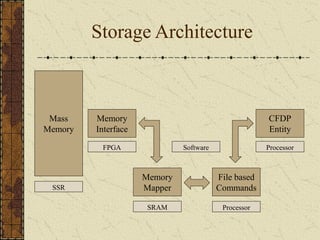
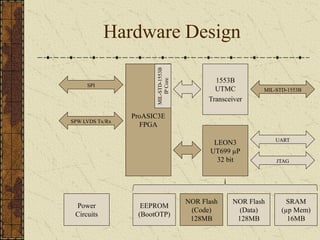
This document discusses implementing the CCSDS File Delivery Protocol (CFDP) for future Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) small satellites. It involves studying CFDP features, specifying a design for CFDP implementation, and developing both hardware and software platforms. The goals are to port an existing real-time operating system to a field programmable gate array with file management and implement a basic version of the CFDP standard for data storage and transmission.