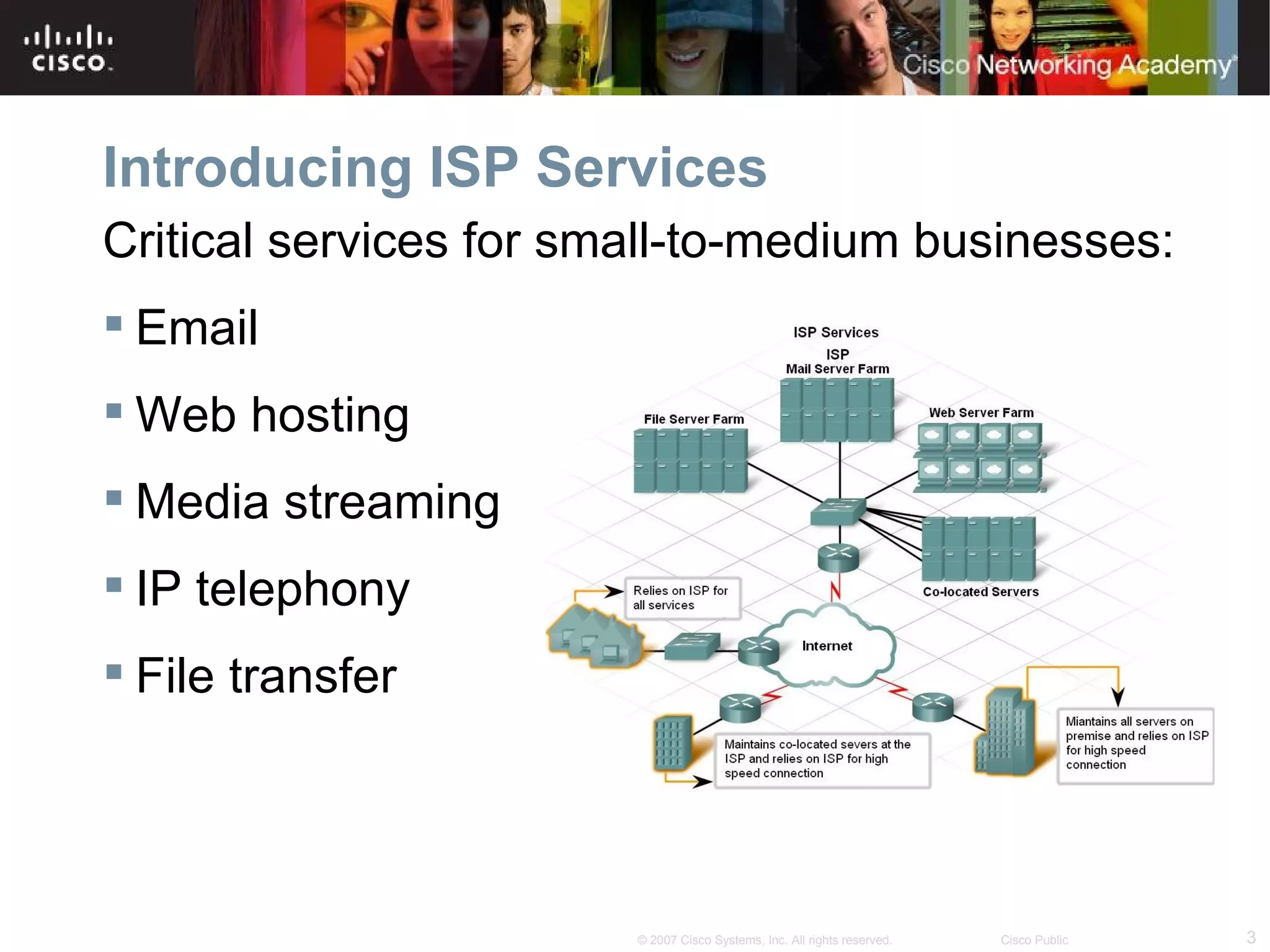
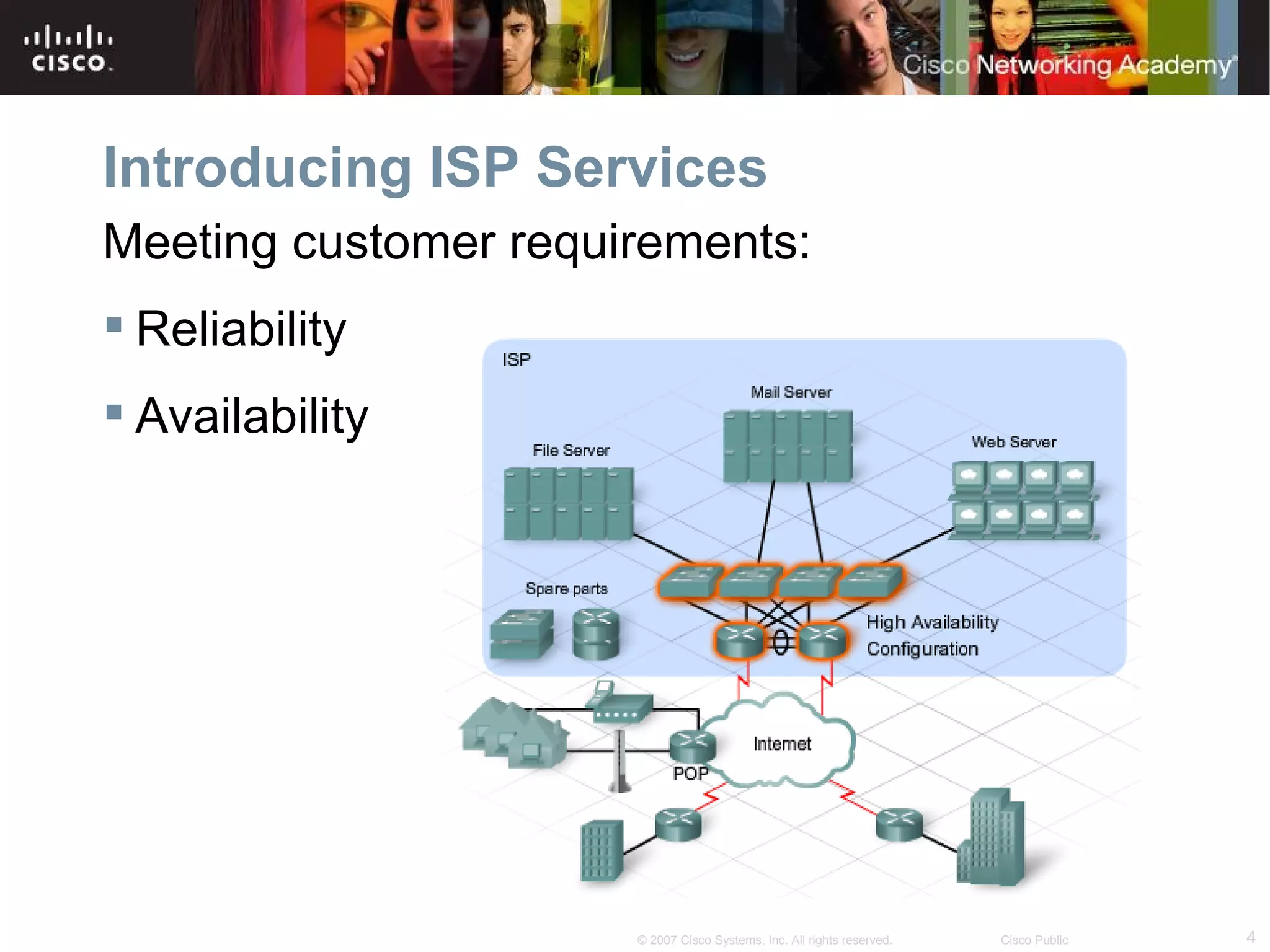
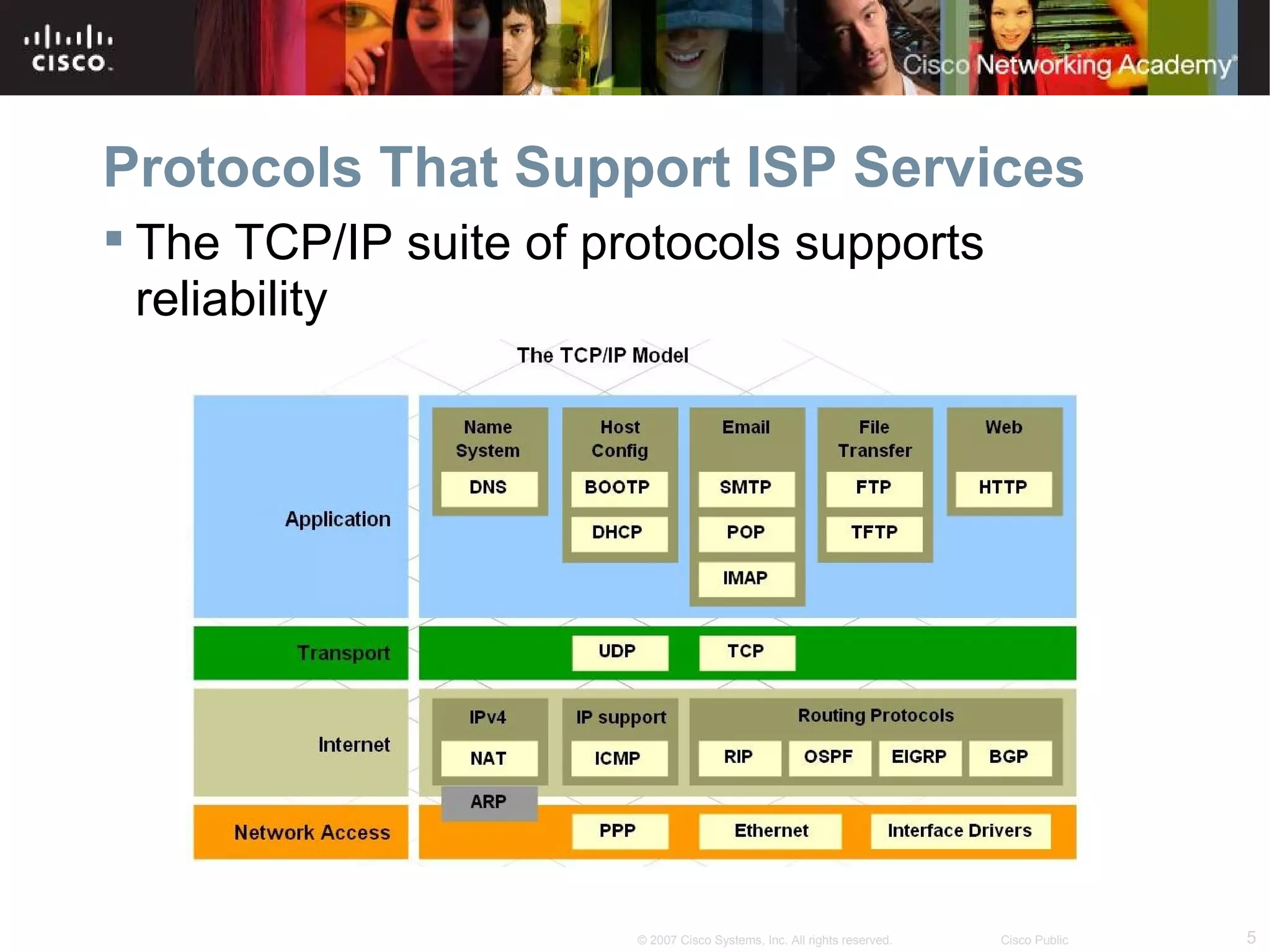
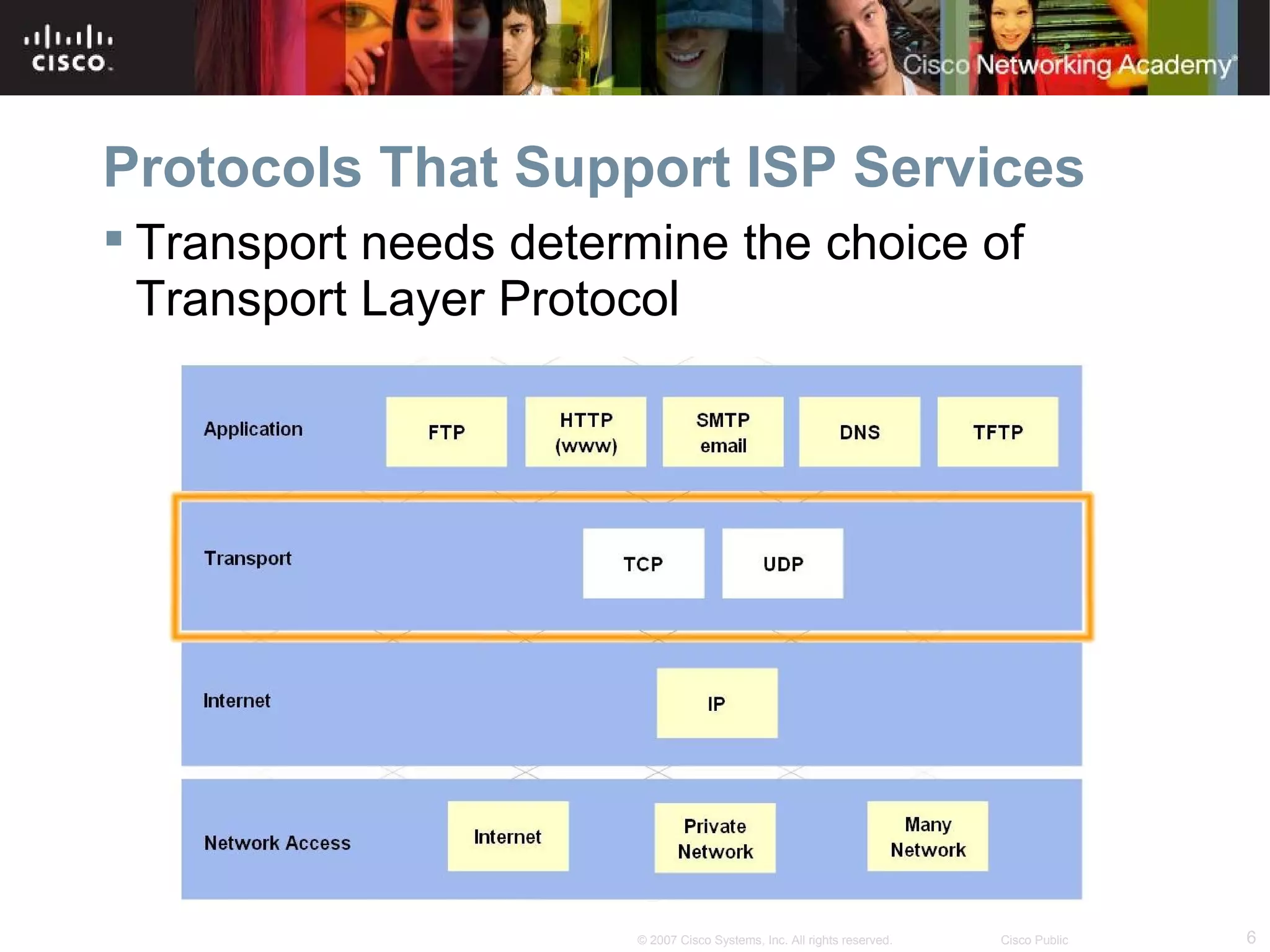
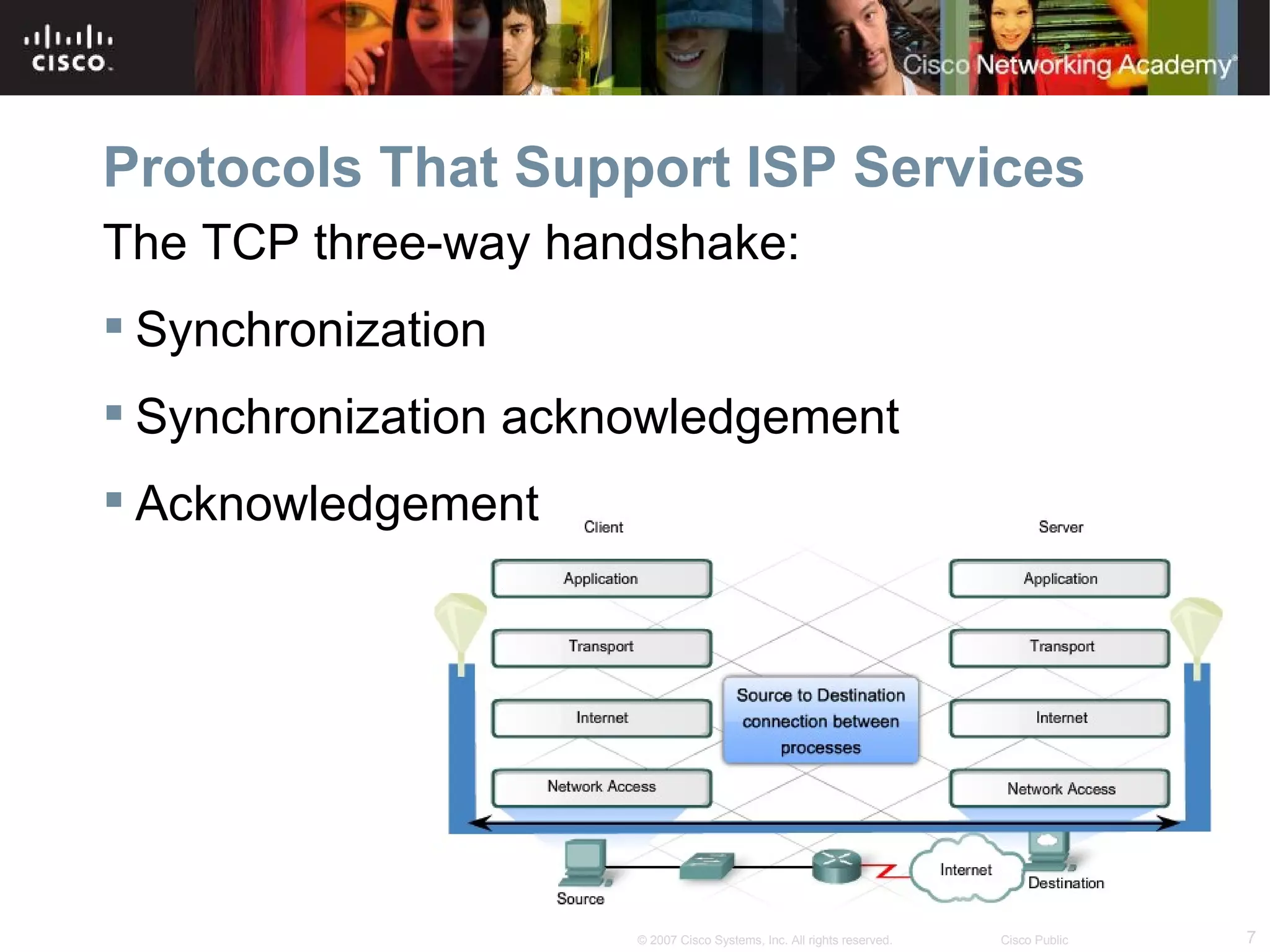
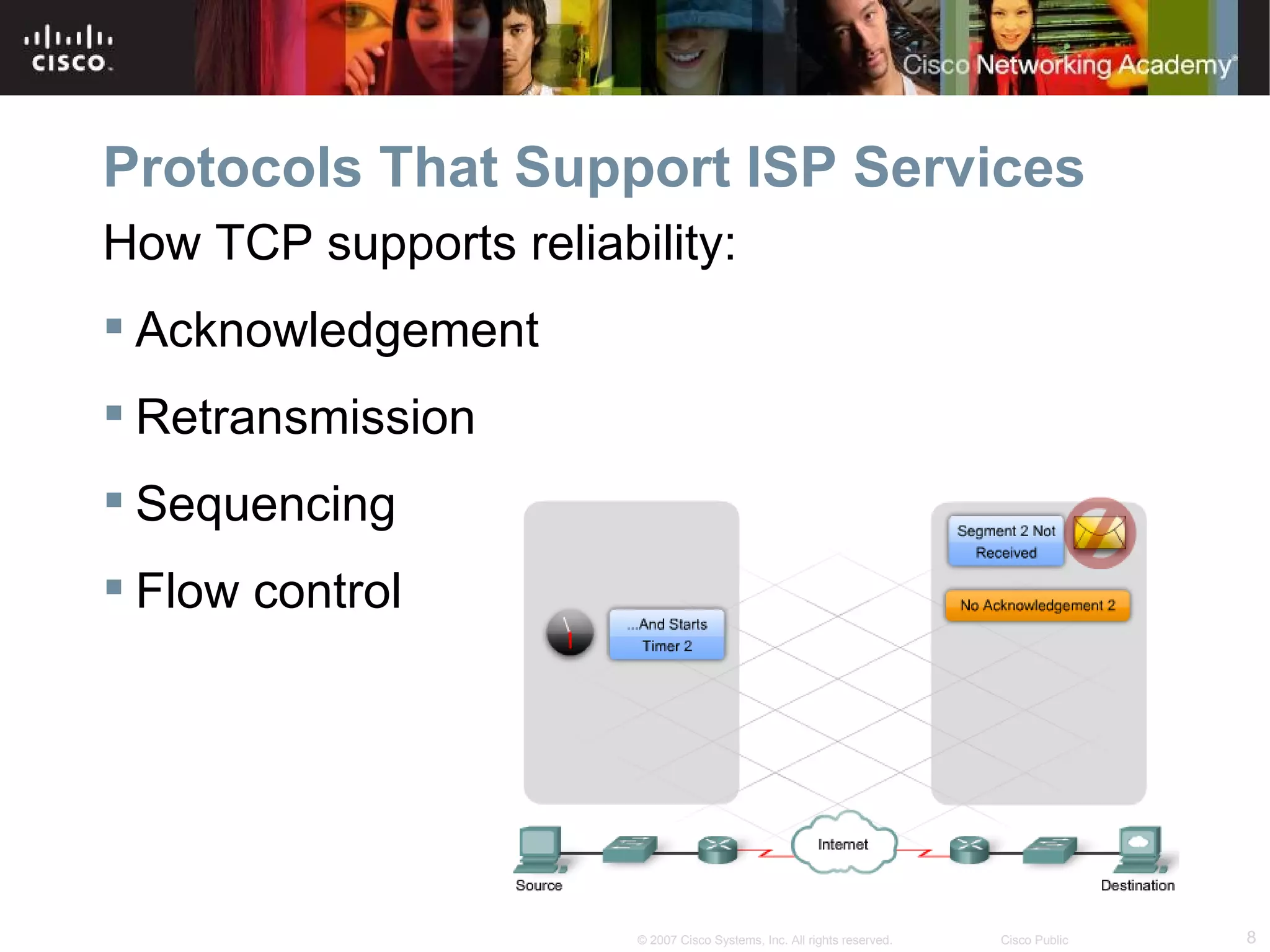
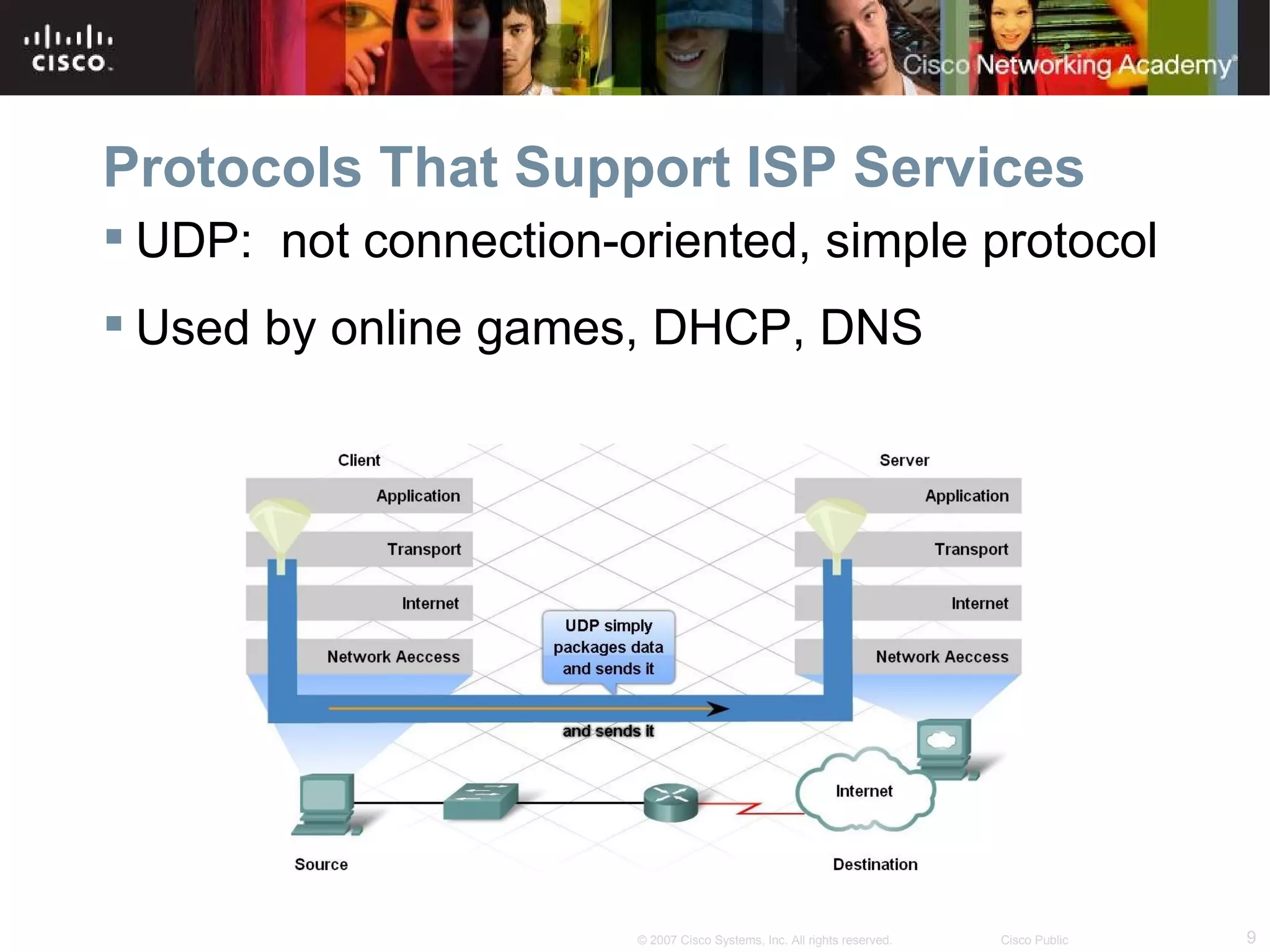
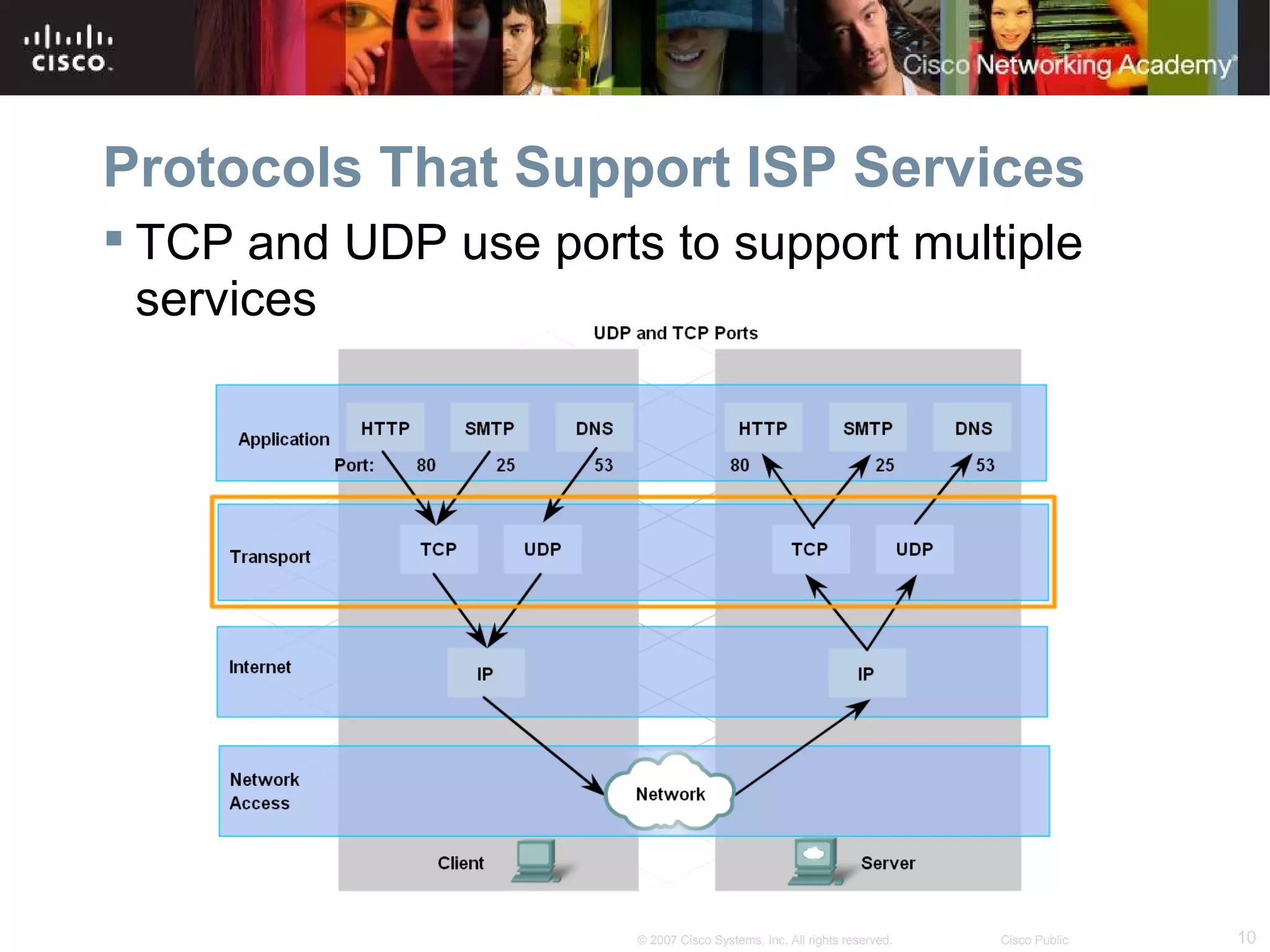
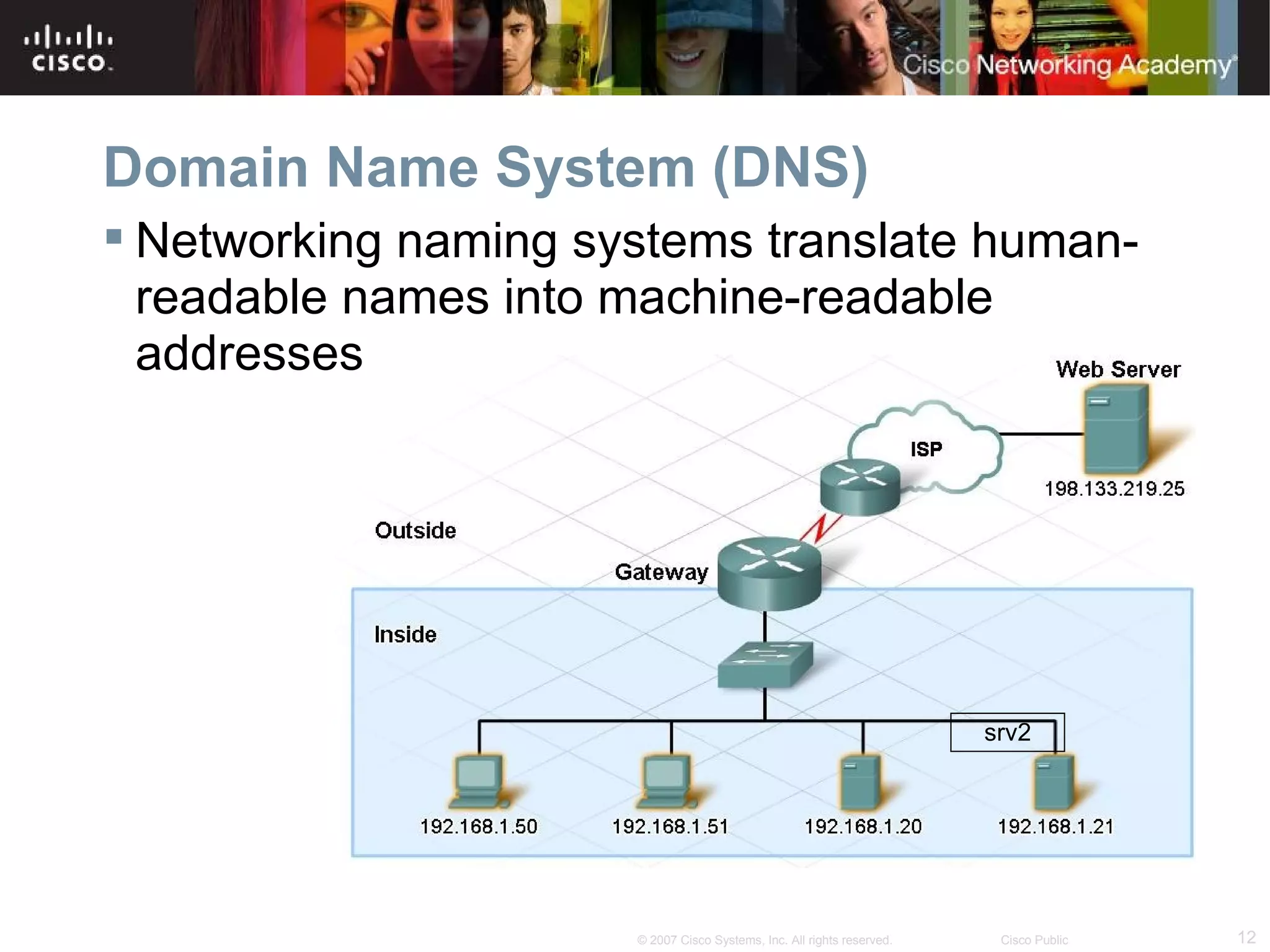
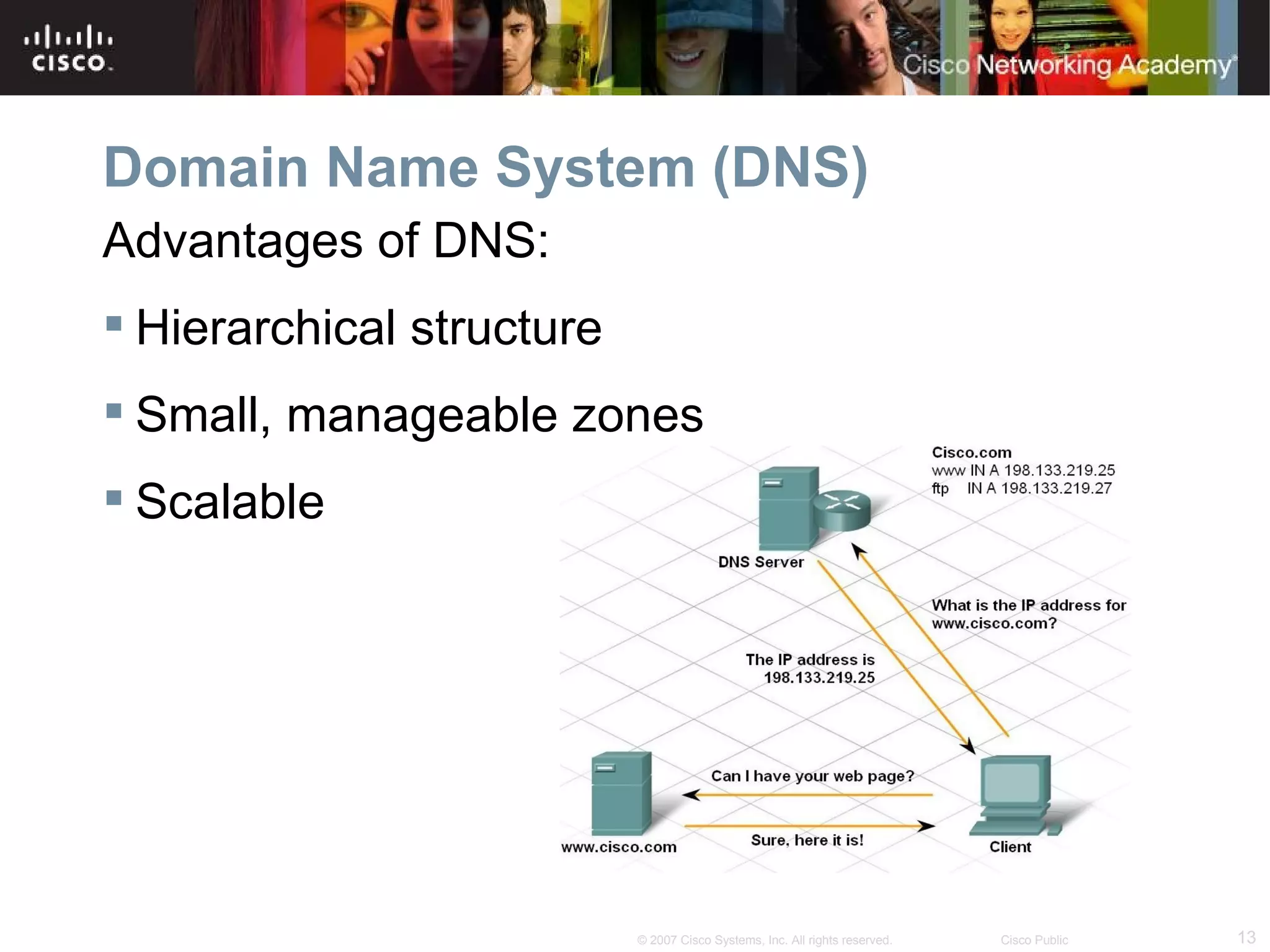
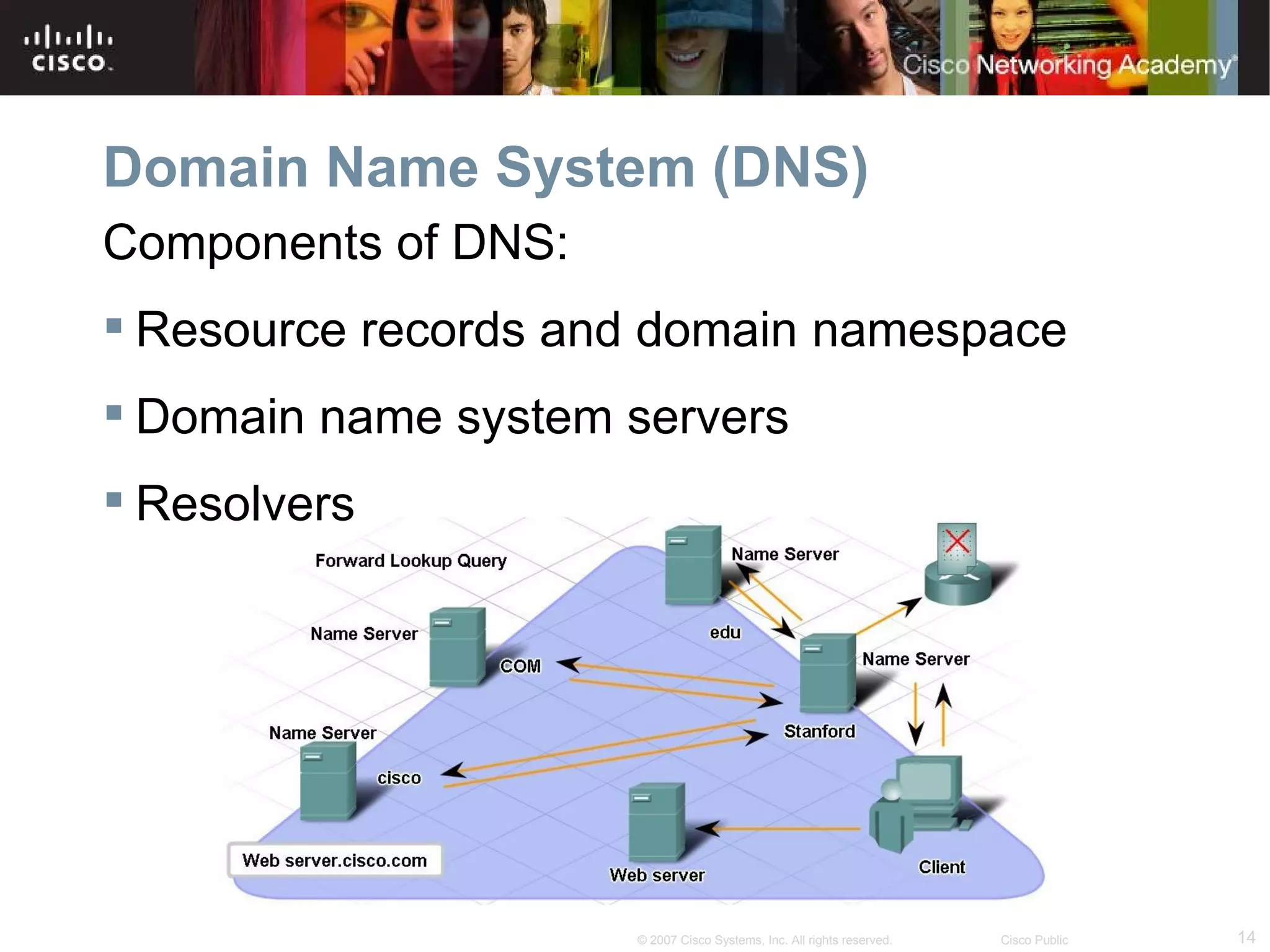
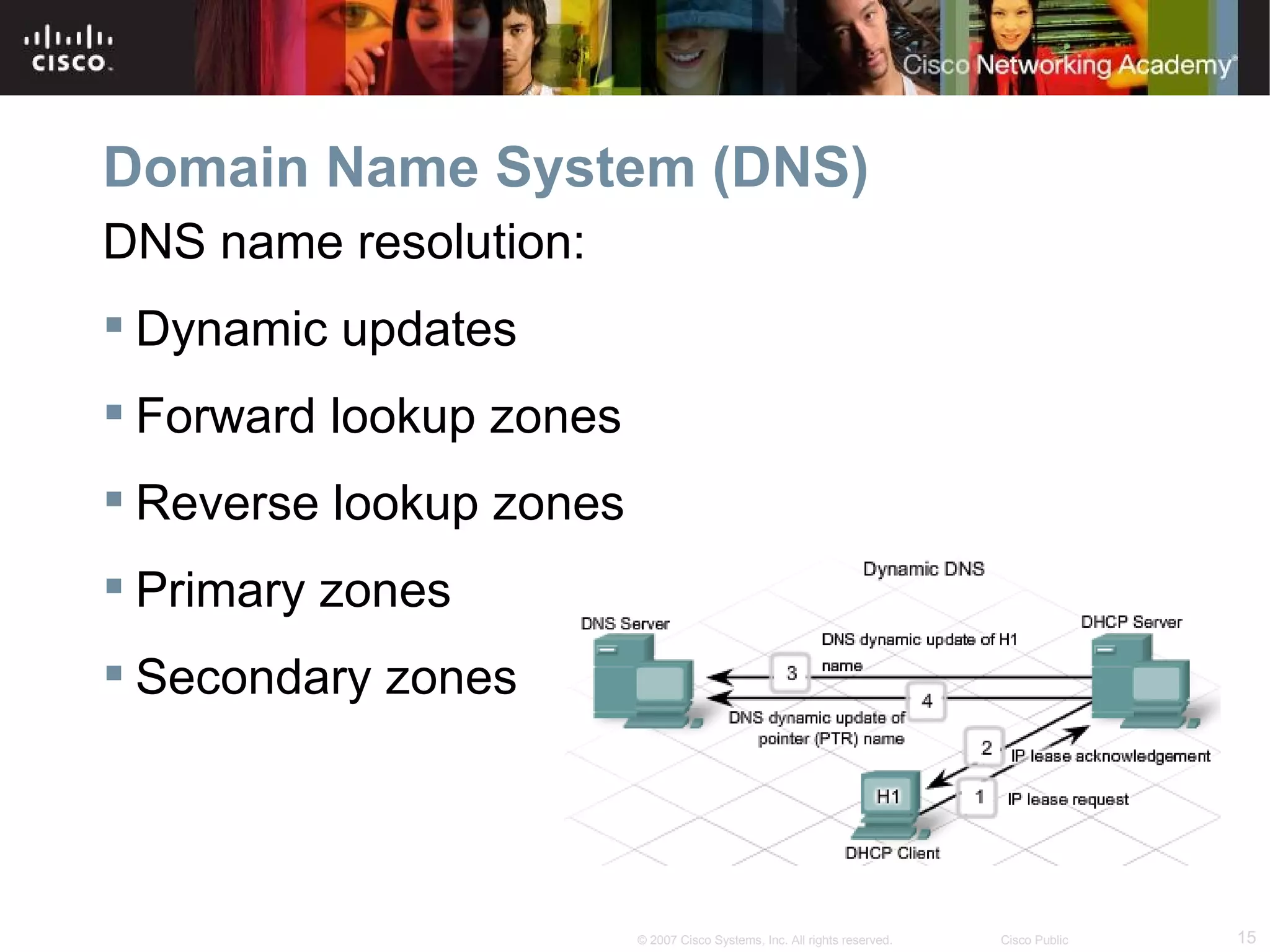
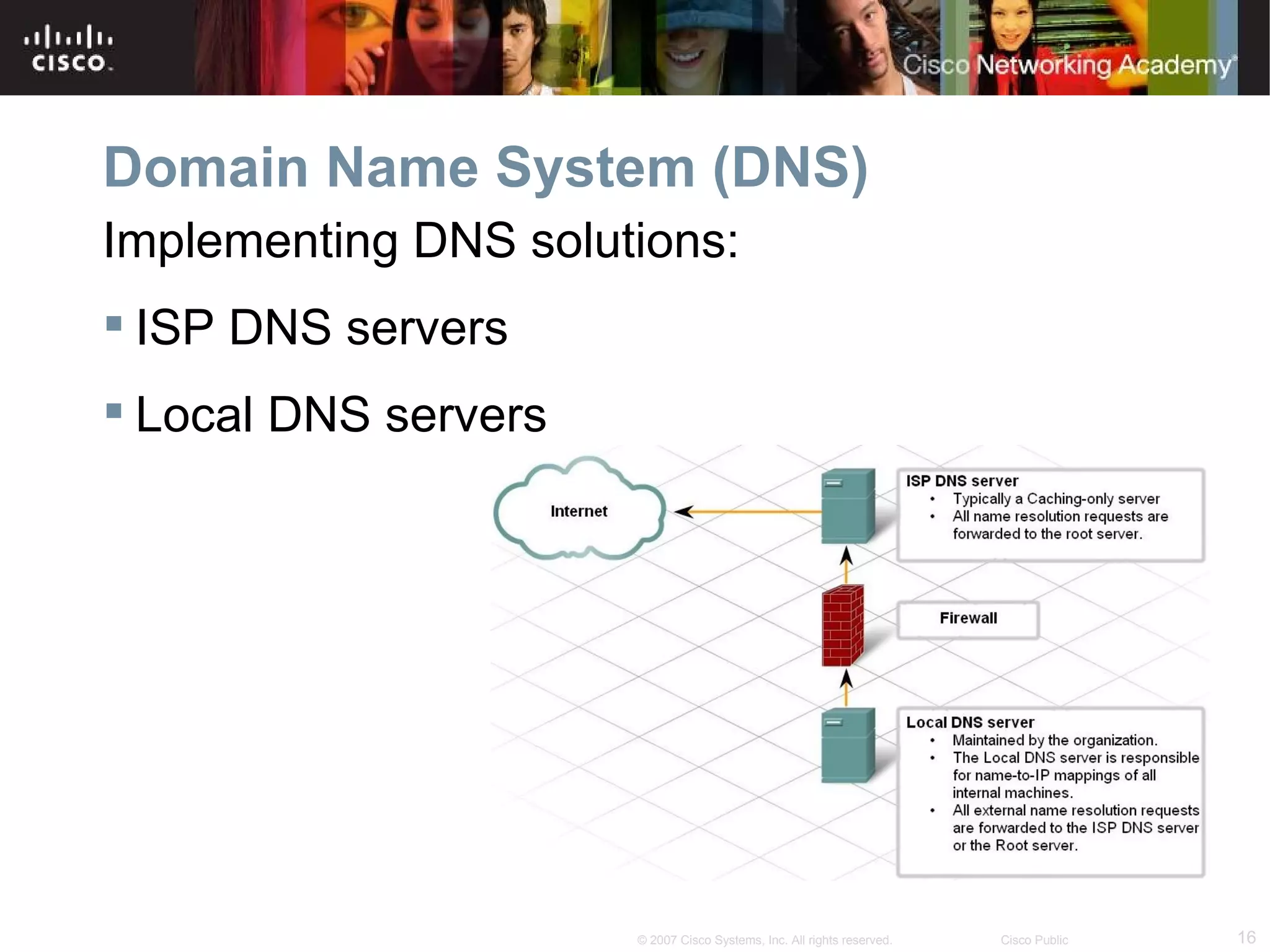
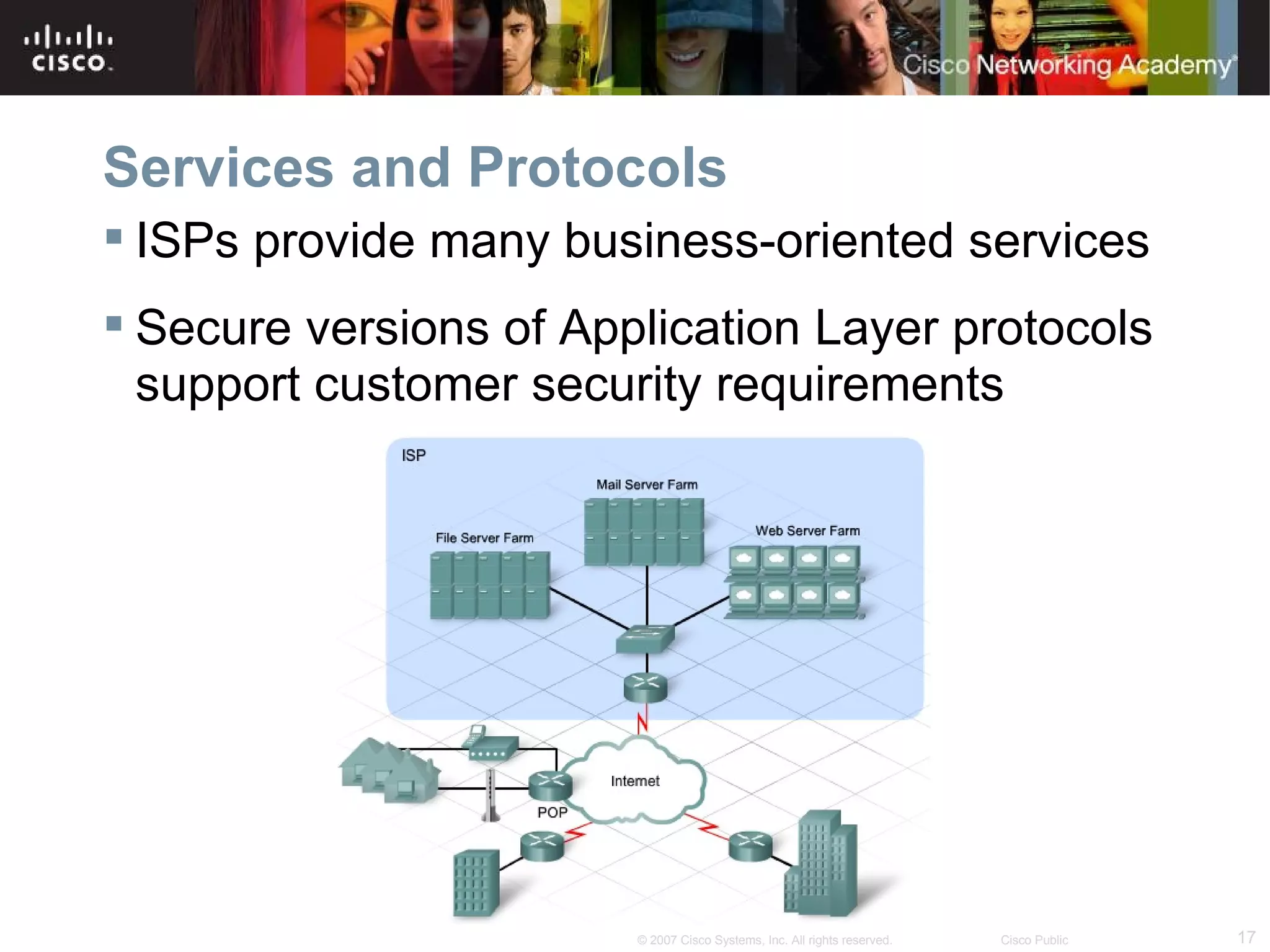
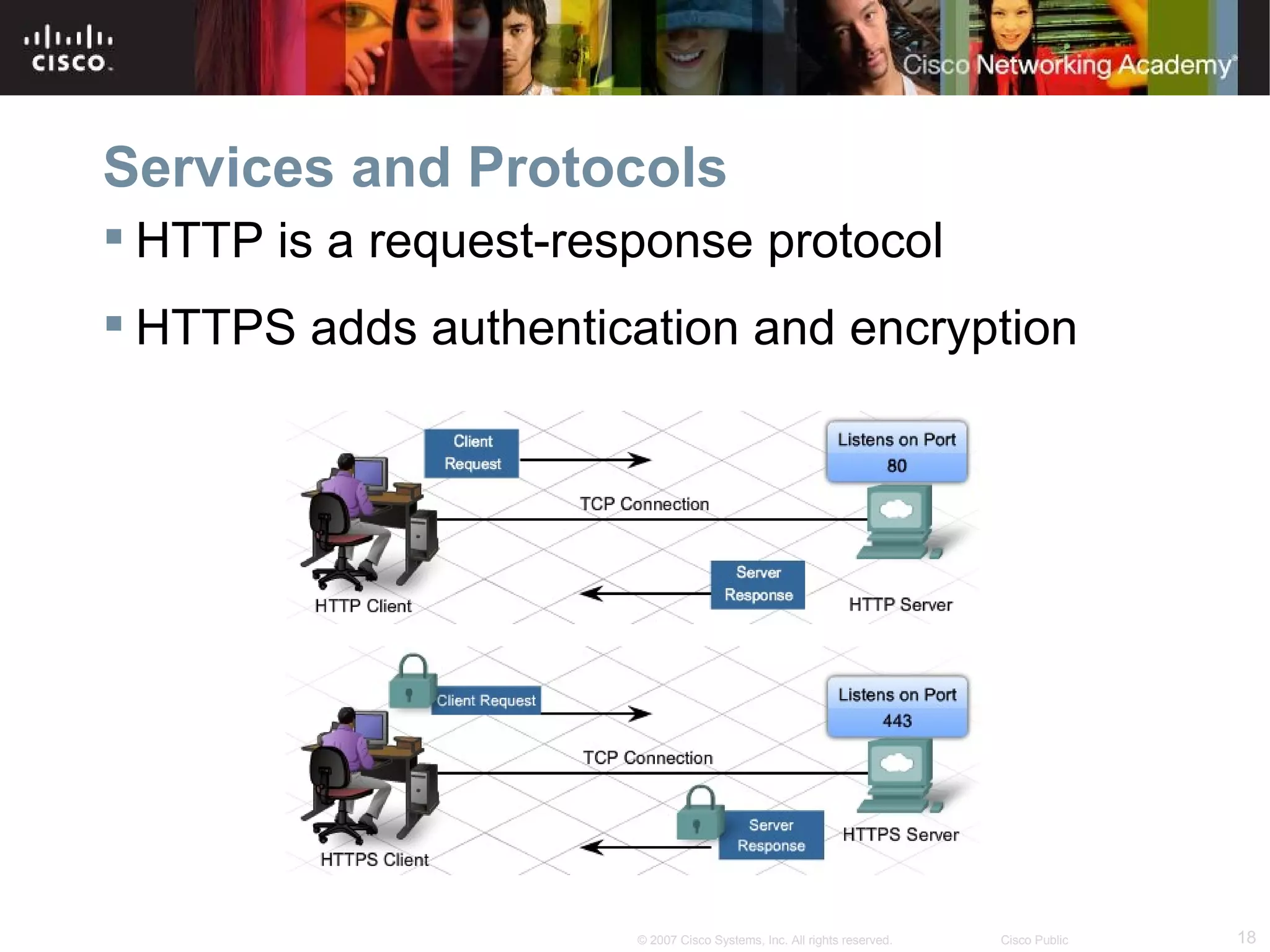
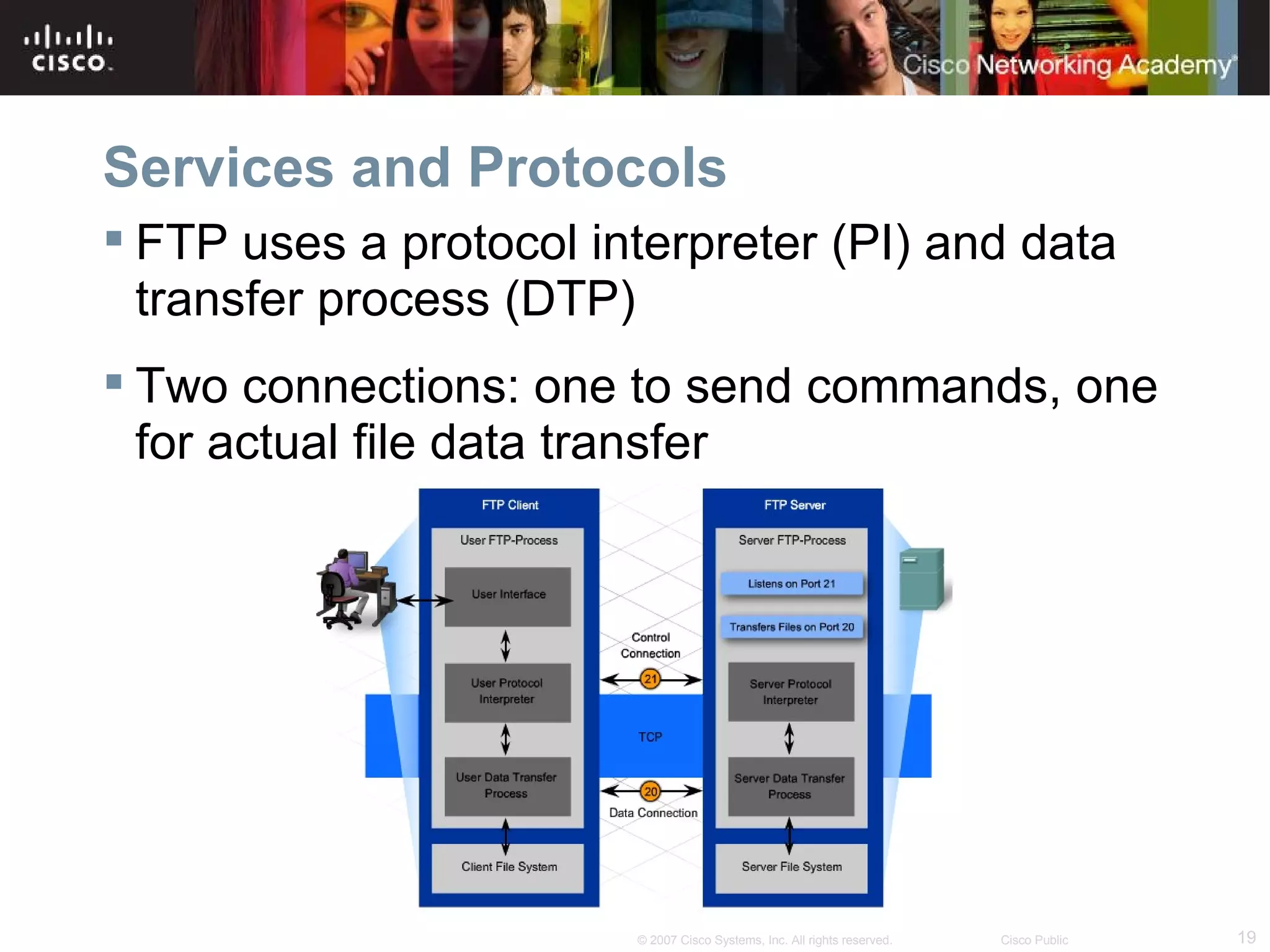
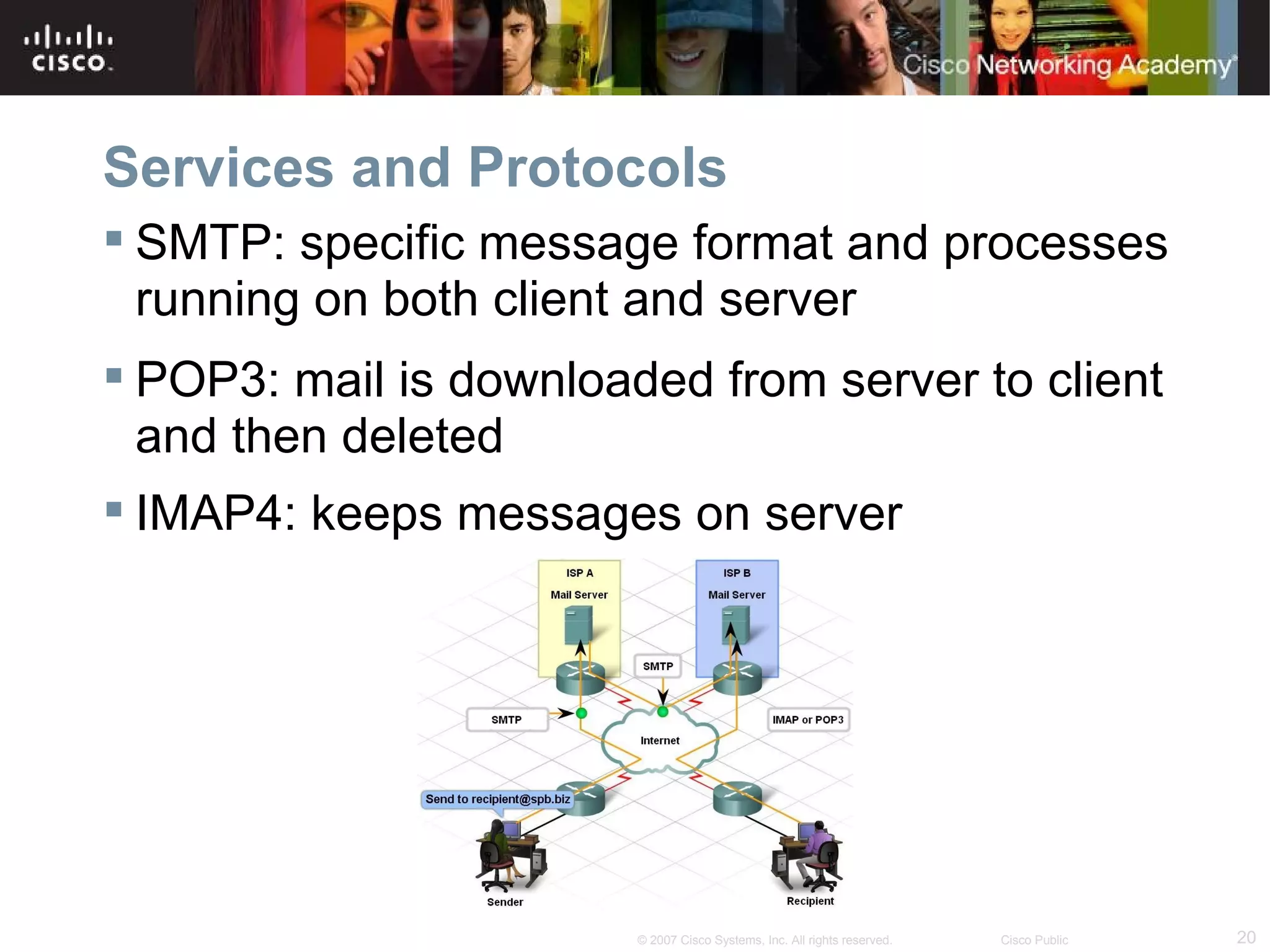
The document discusses services provided by internet service providers (ISPs) including email, web hosting, media streaming, IP telephony, and file transfer. It describes how protocols like TCP/IP, UDP, and DNS support these services and ensure reliability and availability for customers. Key protocols and services covered include HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, and DNS for translating names to IP addresses in a hierarchical system.