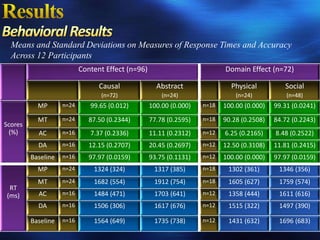
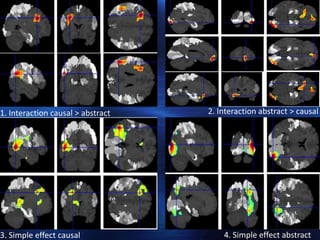
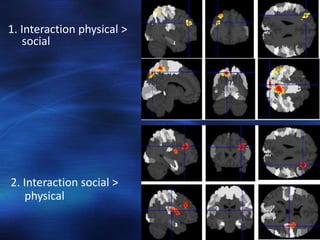
The study examined the neural substrates of conditional reasoning using fMRI. It found:
1. Conditional reasoning engaged bilateral fronto-temporo-parietal regions for integrating syntactic and visuospatial processing.
2. Causal conditional reasoning specifically activated the left fronto-parietal cortex for syntactic/semantic processing.
3. Causal reasoning relied more on left lateral frontal and temporo-parietal junction regions for linguistic processing. Abstract reasoning engaged right occipito-parieto-temporal regions for spatial manipulation.
4. Social reasoning activated right inferior frontal and insular regions for social cognition. Physical reasoning engaged left fronto-parietal regions for non-social