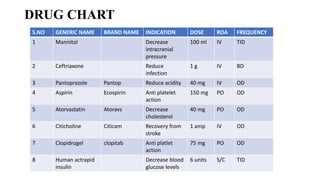
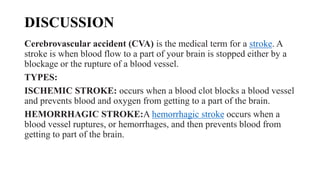
The patient, a 63-year old male, presented with weakness on the left side of his body, slurred speech, and nasal regurgitation. CT brain showed an acute infarct in the right fronto-parieto-temporal-occipital lobe, consistent with an ischemic stroke. He was diagnosed with cerebrovascular accident with ischemic stroke and treated with medications to reduce swelling, prevent infections, reduce acidity and cholesterol, and blood thinners to prevent another stroke. He was also counseled on lifestyle changes to prevent future strokes.