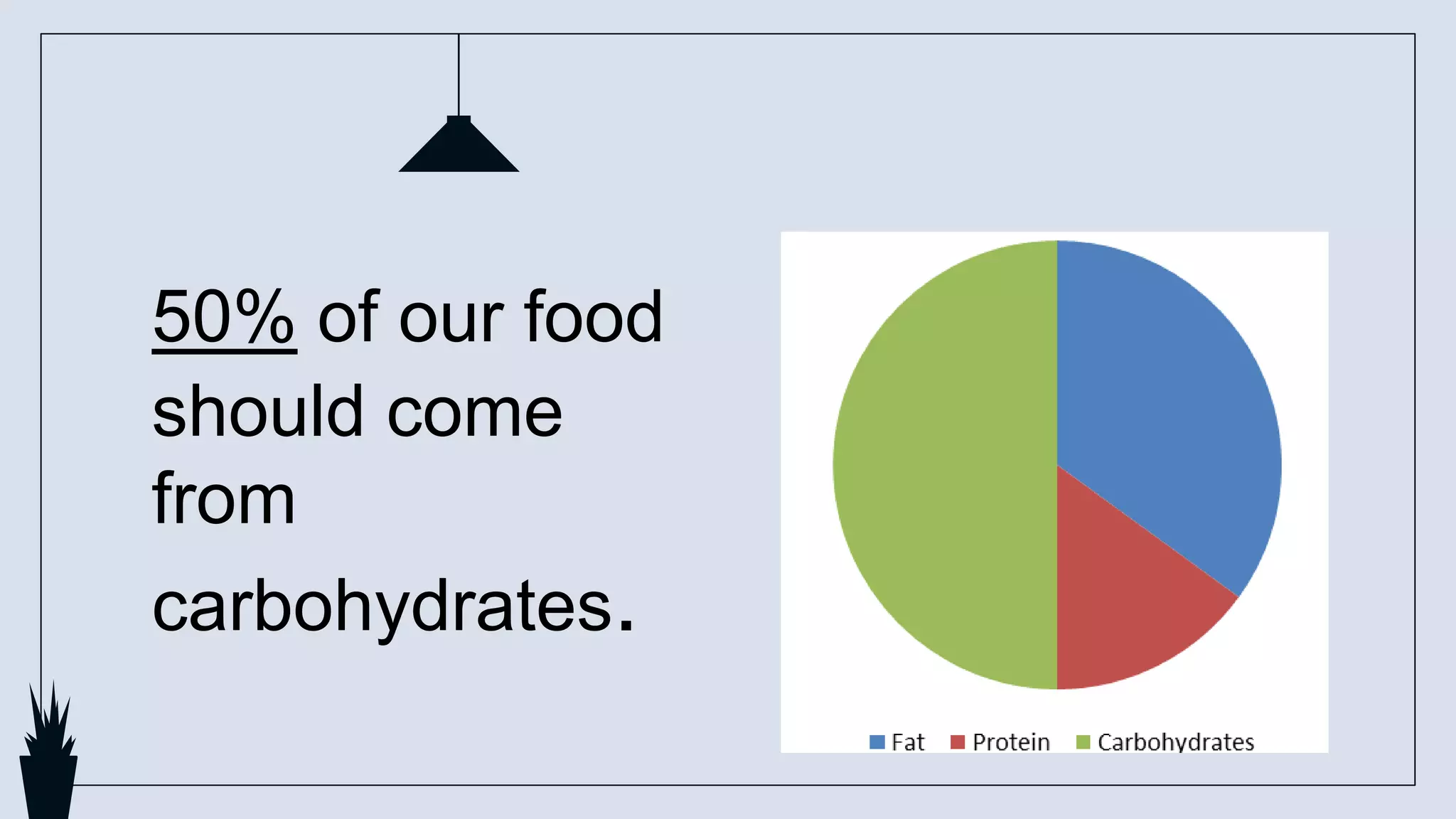
Carbohydrates perform various functions in food products. They can help cause browning reactions through the Maillard reaction when sugars react with proteins under heat. Dextrinization breaks starch down into smaller molecules called dextrins through dry heat, contributing to surface browning. Caramelization occurs when sucrose is heated above its melting point, used in confectionery for color and flavor. Gelatinization involves starch granules swelling and thickening mixtures when heated in water then cooled to form gels. These reactions impact color, flavor, and texture in many baked and cooked foods.