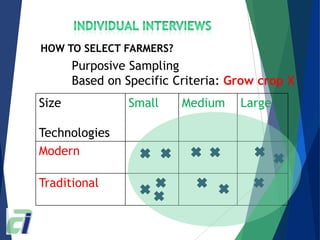
The document outlines a training guide for conducting focus group discussions and individual farm surveys related to agriculture in Cambodia. It details the preparation steps for facilitators, including team selection, participant selection, and discussion management techniques to ensure effective communication. The guide also emphasizes the importance of quality control for data collection and the need for a suitable environment for discussions.