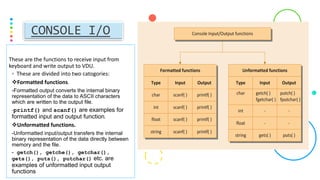
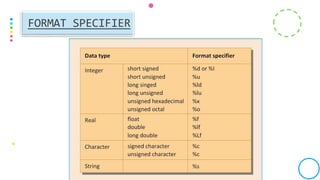
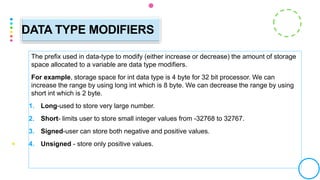
This document discusses formatted and unformatted input/output functions in C programming. Formatted functions like printf() and scanf() convert data to ASCII characters for output or expect formatted input. Unformatted functions transfer raw binary data directly. Common formatted functions are printf(), scanf(), while unformatted include getch(), putchar(). Format specifiers in formatted functions determine input/output format, and data type modifiers change variable storage size.