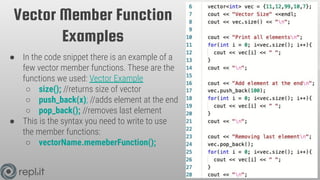
The document provides an overview of data structures in C++, focusing on vectors, stacks, and queues. It includes syntax for declaring and utilizing these structures, key member functions, and examples of their usage. Additionally, it presents a homework assignment to determine the appropriate data structure for different problems.


![What is a Vector?
● Vector - collects a sequence of values, just like an array does, but its size can
change.
● Before using a vector there is one important thing to take in mind. You need to
use the Vector Library. On the top of your program you need to call the library
#include <vector>, this syntax will let your program know that you can use
vectors and their member functions.
● Vector Syntax
○ vector<type> vectorName; //example
○ vector<double> values; //empty vector of type double
○ vector<double> values(10); //vector with a size of 10
○ vector<double> values = {32,22.5,6,11,33}; //specifying initial values
○ vector[0] = 5; //updating value in vector (similar to arrays)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clesson6-datastructures-241021111751-5e89585a/85/C-Lesson-6-Data-Structures-vector-queue-stack-pdf-4-320.jpg)