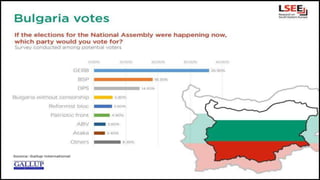
Bulgaria is a parliamentary republic with a multi-party system. The president is the head of state elected to a five-year term, while the prime minister is the head of government. The unicameral National Assembly consists of 240 members elected to four-year terms who pass laws and elect the prime minister. Local governments are led by township councils elected to four-year terms. Major political parties include GERB, the Bulgarian Socialist Party, and the Movement for Rights and Freedoms.