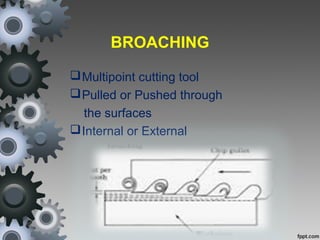
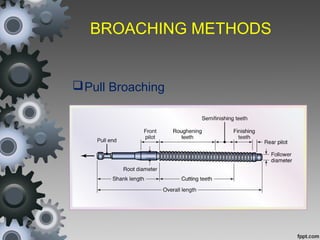
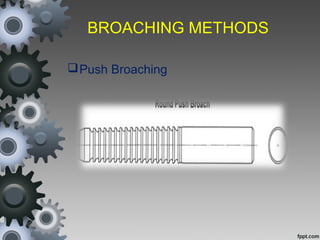
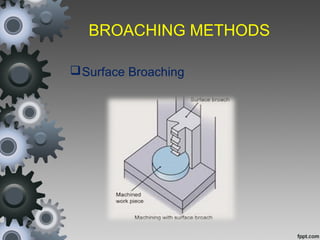
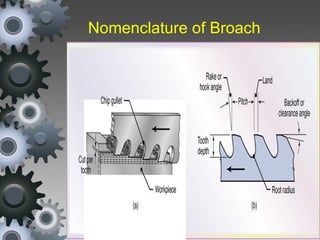
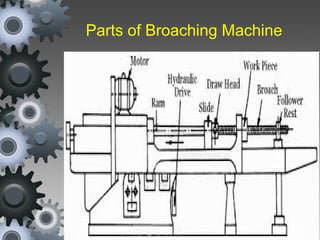
Broaching is a machining process that uses a broach tool to remove material. There are different types of broaches and broaching methods depending on the operation. Broaching provides high production rates and accuracy for machining holes, slots and surfaces. It is well-suited for mass production but requires expensive broach tools and fixtures.