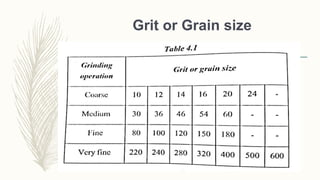
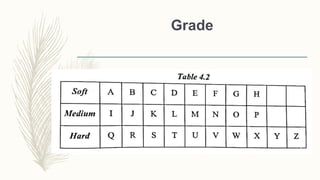
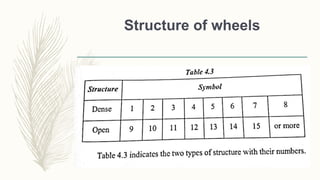
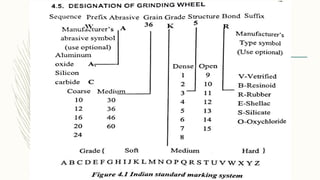
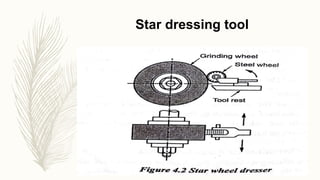
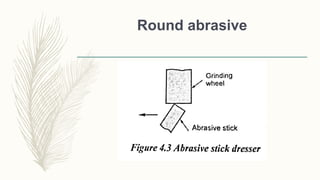
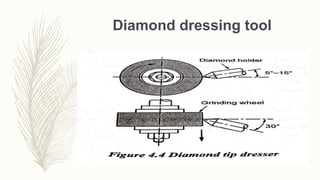
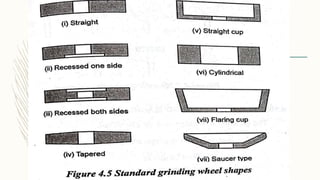
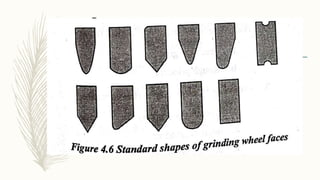
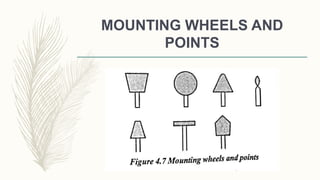
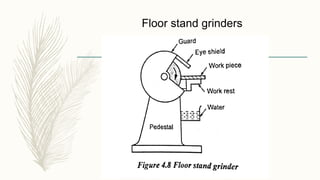
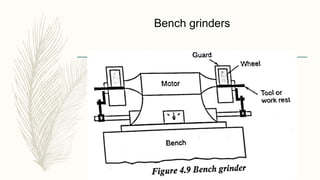
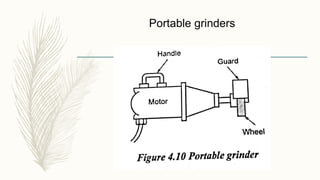
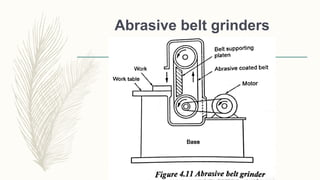
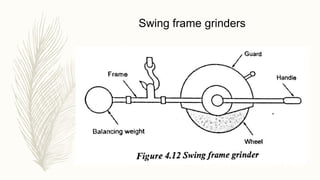
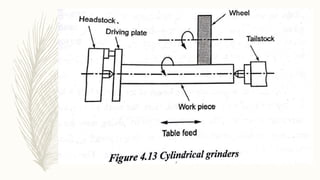
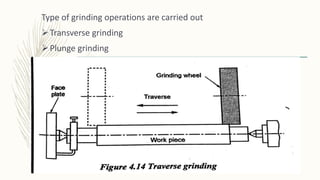
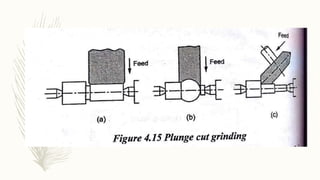
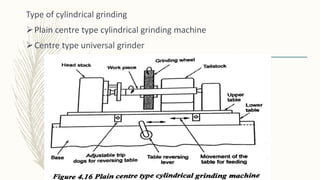
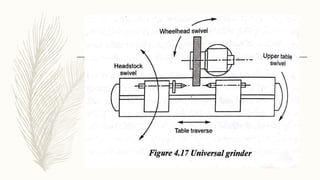
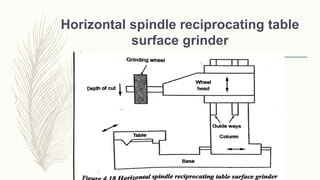
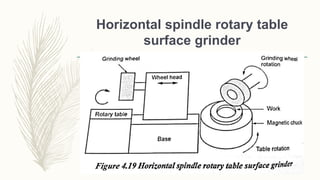
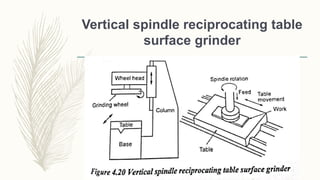
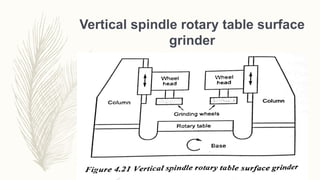
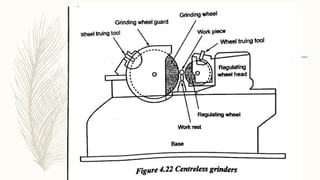
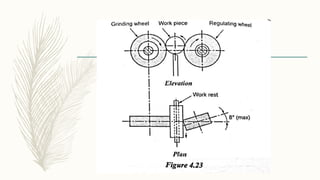
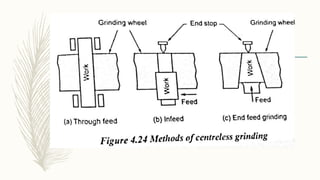
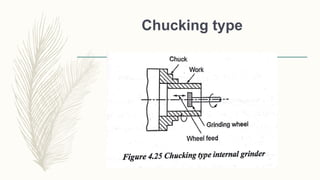
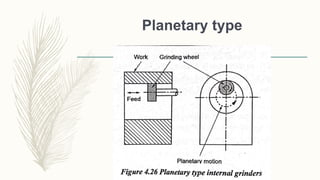
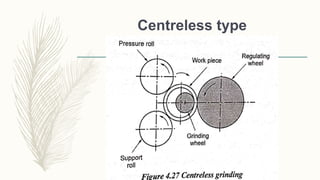
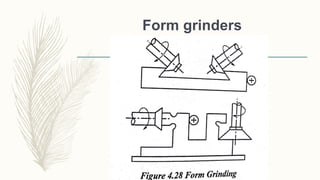
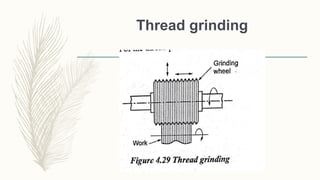
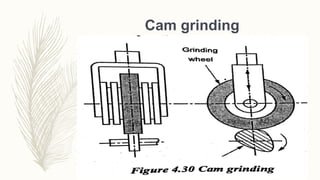
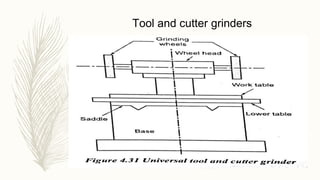
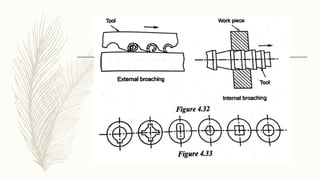
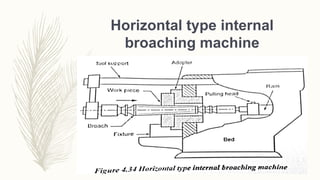
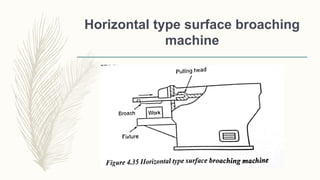
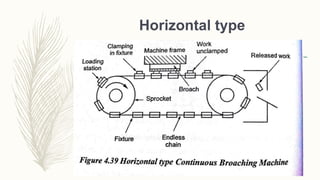
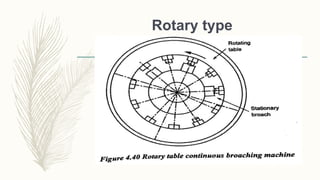
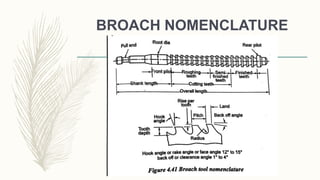
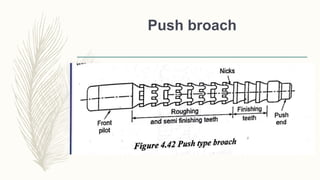
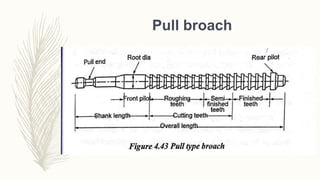
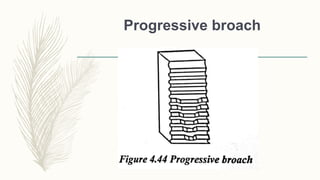
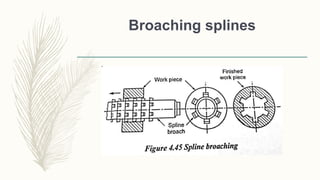
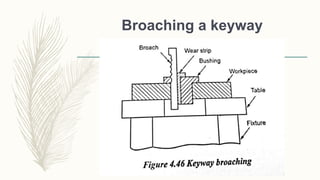
The document discusses abrasive processes and broaching. It describes various grinding wheel specifications and types of grinding machines. The key types of grinding machines are cylindrical grinding machines, surface grinding machines, and internal grinding machines. It also discusses broaching machines, broach construction, and different types of broaching such as push, pull, surface, and continuous broaching. Broaching is used to machine surfaces using a special cutting tool called a broach.