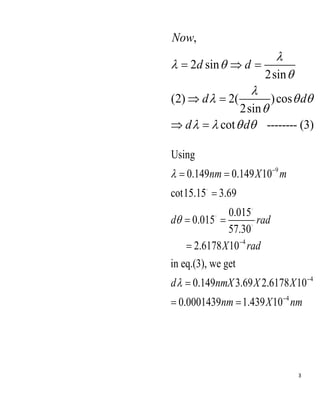Embed presentation
Download to read offline

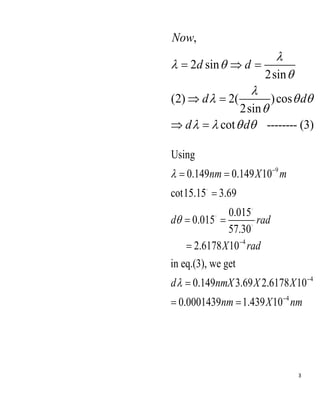

This document discusses using Bragg's law to calculate the wavelength range passing through an analyzer device. Bragg's law relates the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation to the diffraction angle when scattered from a crystal. The document gives that for a wavelength of 0.149 nm, the first-order Bragg peak occurs at an angle of 15.15 degrees. Using Bragg's law and taking the derivative with respect to angle, the document calculates that for an angular range of the analyzer of 0.015 degrees, the corresponding wavelength range passing through is 1.439 x 10^-4 nm.