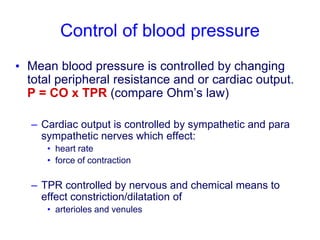
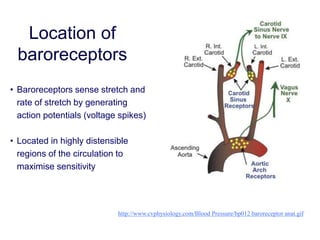
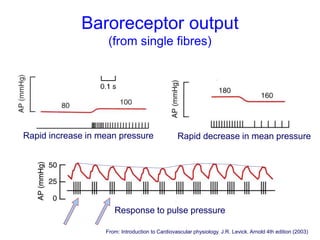
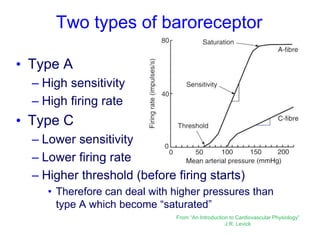
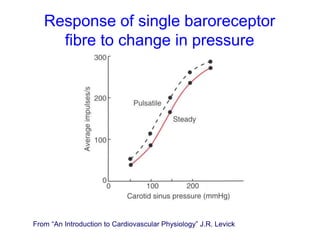
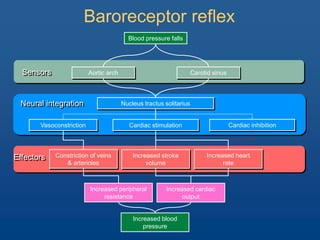
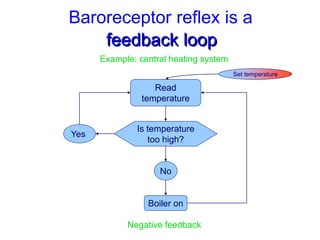
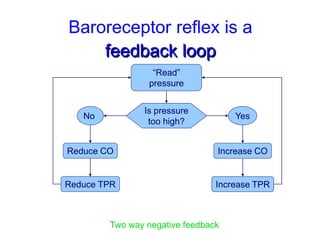
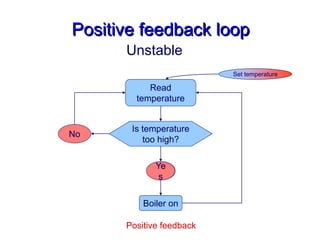
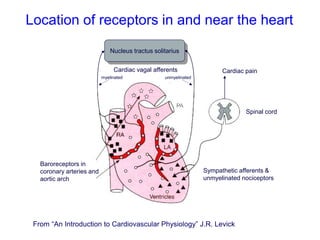
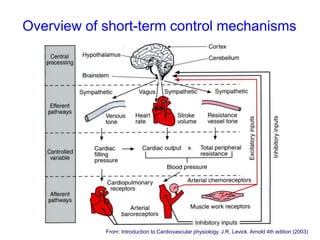
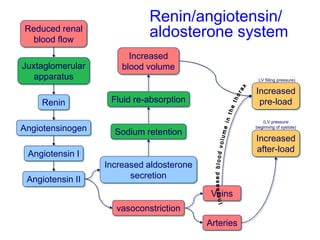
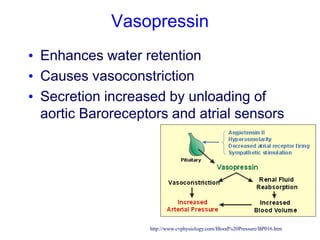
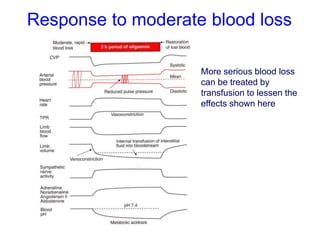
The document discusses the control of blood pressure through short-term and long-term mechanisms. Short-term control is mediated by baroreceptors located in the aorta and carotid arteries that detect changes in blood pressure and initiate reflex responses to maintain pressure. Long-term control involves renal regulation of fluid volume and sodium balance through hormones like renin, angiotensin, aldosterone, vasopressin, and atrial natriuretic peptide. The document also describes the body's response to blood loss and the types of shock that can occur from inadequate tissue perfusion.