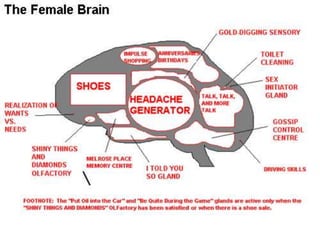
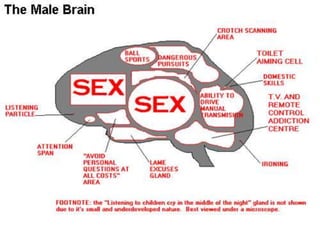
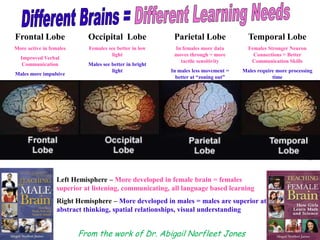
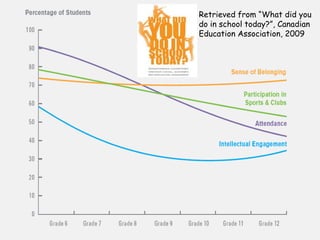
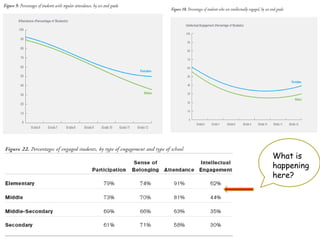
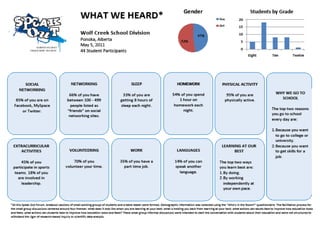
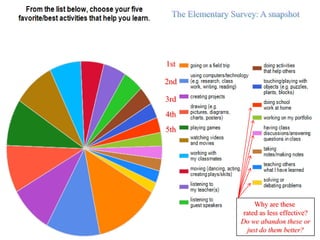
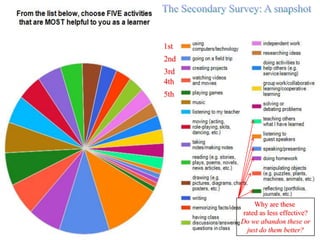
The document discusses how boys experience learning in grade 7 based on interviews with two grade 7 boys, Joe Student and Elijah Green. The boys indicated that they like school when engaged through active and hands-on learning, but get bored with passive activities like note-taking. They prefer learning later in the day and having choice in activities. The document reflects on expectations that boys would dislike school, but found that these boys enjoyed learning when their needs were met through interactive approaches. It calls for using integrated, interactive curricula to better meet the needs of male adolescent learners.