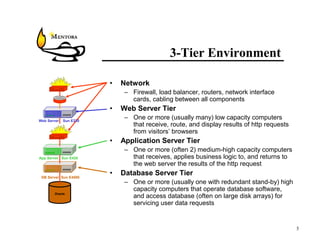
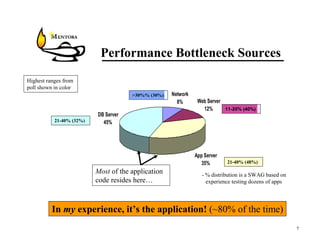
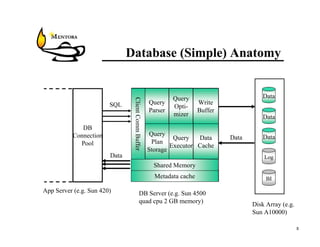
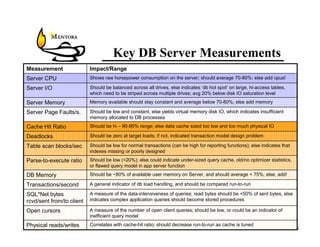
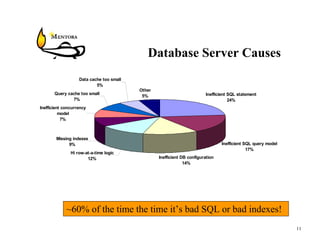
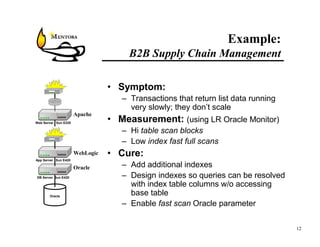
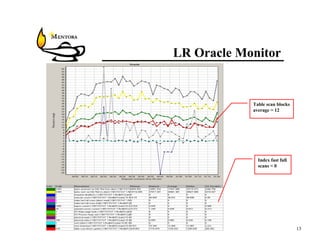
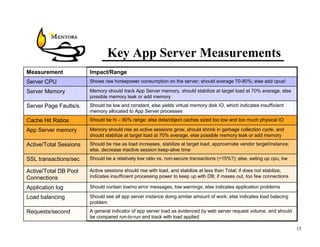
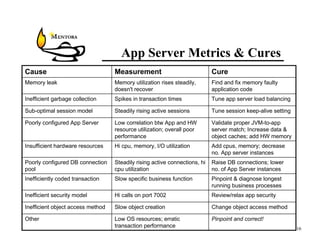
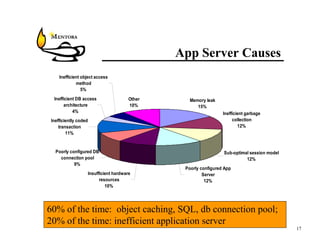
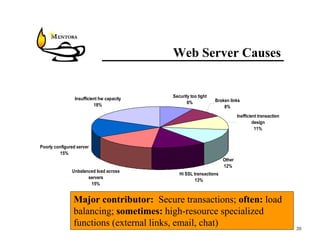
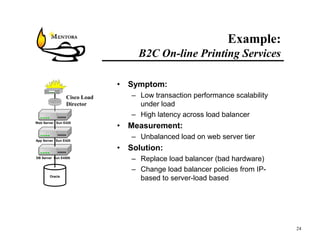
This document identifies common website performance bottlenecks and how to diagnose and address them. It begins by outlining the objectives of identifying the source, symptom, cause, measurements, and cures for bottlenecks. It then provides terms and concepts in application performance testing. The rest of the document discusses specific bottlenecks that can occur in the web server, application server, database server, and network tiers and provides examples of measurements and cures for each.