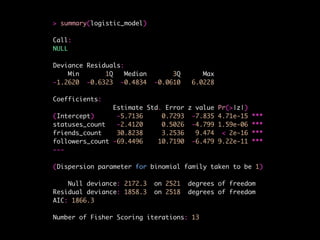
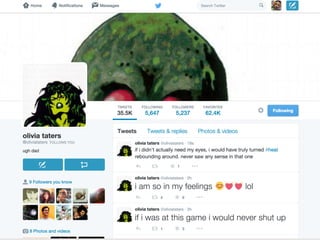
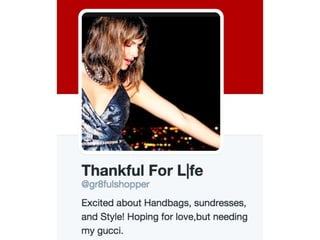
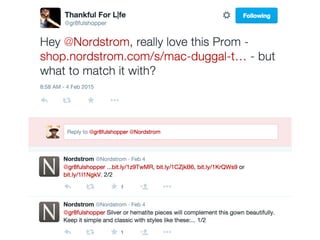
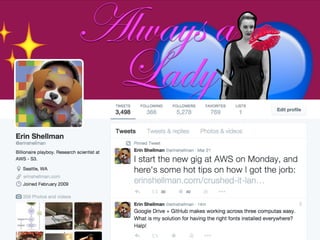
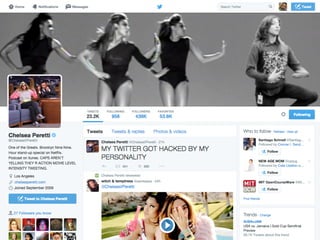
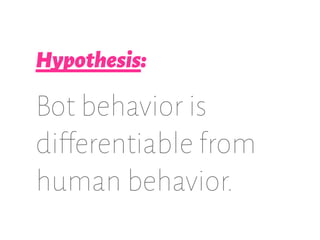
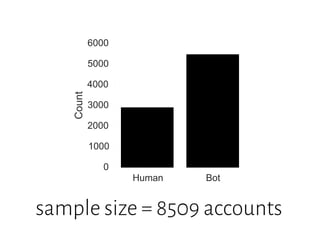
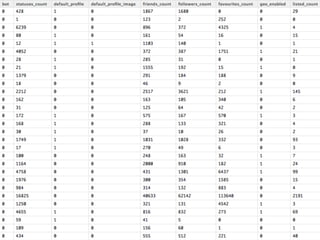
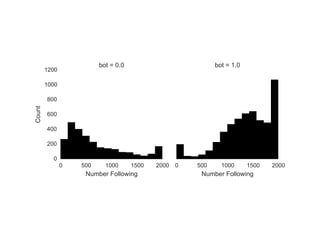
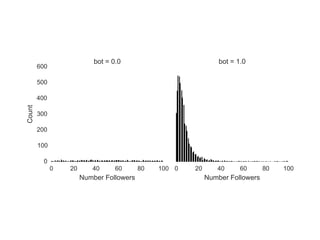
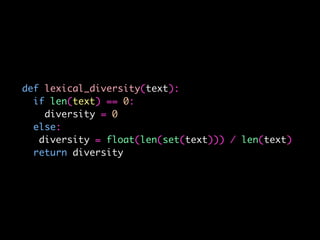
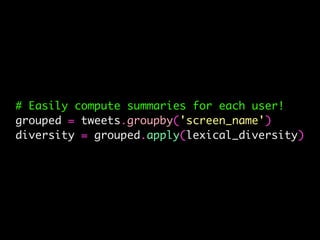
The document details a workshop on data analysis using Python and PySpark, focusing on classifying bot behavior in Twitter data. It outlines an experimental design involving data ingestion, preprocessing, classification with various models, and evaluation metrics. Important results include the identification of bot patterns and the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms in distinguishing between human and bot accounts.








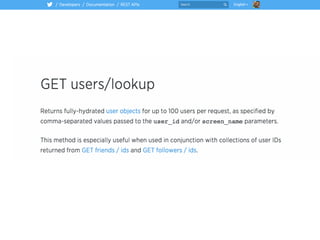

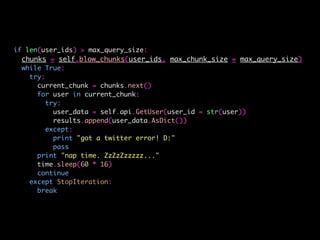
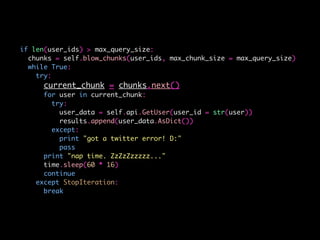
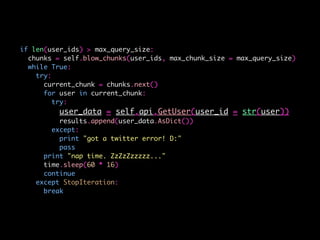
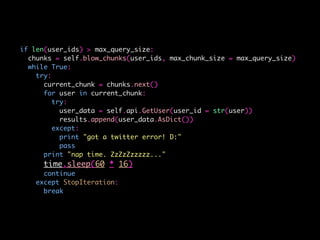
![# break query into bite-size chunks 🍔
def blow_chunks(self, data, max_chunk_size):
for i in range(0, len(data), max_chunk_size):
yield data[i:i + max_chunk_size]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bot-or-not-print-150806213436-lva1-app6891/85/Bot-or-Not-23-320.jpg)






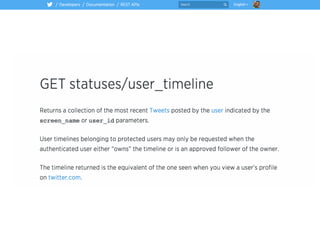
![# Naive Bayes
bayes = GaussianNB().fit(train[features], y)
bayes_predict = bayes.predict(test[features])
# Logistic regression
logistic = LogisticRegression().fit(train[features], y)
logistic_predict = logistic.predict(test[features])
# Random Forest
rf = RandomForestClassifier().fit(train[features], y)
rf_predict = rf.predict(test[features])
# Classification Metrics
print(metrics.classification_report(test.bot, bayes_predict))
print(metrics.classification_report(test.bot, logistic_predict))
print(metrics.classification_report(test.bot, rf_predict))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bot-or-not-print-150806213436-lva1-app6891/85/Bot-or-Not-43-320.jpg)

![# construct parameter grid
param_grid = {'max_depth': [1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, None],
'max_features': [1, 3, 6, 9, 12],
'min_samples_split': [1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15],
'min_samples_leaf': [1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15],
'bootstrap': [True, False],
'criterion': ['gini', 'entropy']}
# fit best classifier
grid_search = GridSearchCV(RandomForestClassifier(), param_grid = param_grid).fit(train[features], y)
# assess predictive accuracy
predict = grid_search.predict(test[features])
print(metrics.classification_report(test.bot, predict))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bot-or-not-print-150806213436-lva1-app6891/85/Bot-or-Not-45-320.jpg)


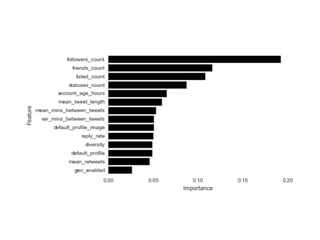

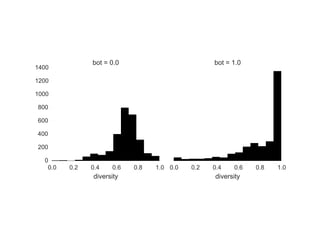
![> confusionMatrix(logistic_predictions, test$bot)
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction 0 1
0 394 22
1 144 70
Accuracy : 0.7365
95% CI : (0.7003, 0.7705)
No Information Rate : 0.854
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 1
Kappa : 0.3183
Mcnemars Test P-Value : <2e-16
Sensitivity : 0.7323
Specificity : 0.7609
Pos Pred Value : 0.9471
Neg Pred Value : 0.3271
Prevalence : 0.8540
Detection Rate : 0.6254
Detection Prevalence : 0.6603
Balanced Accuracy : 0.7466
'Positive' Class : 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bot-or-not-print-150806213436-lva1-app6891/85/Bot-or-Not-51-320.jpg)