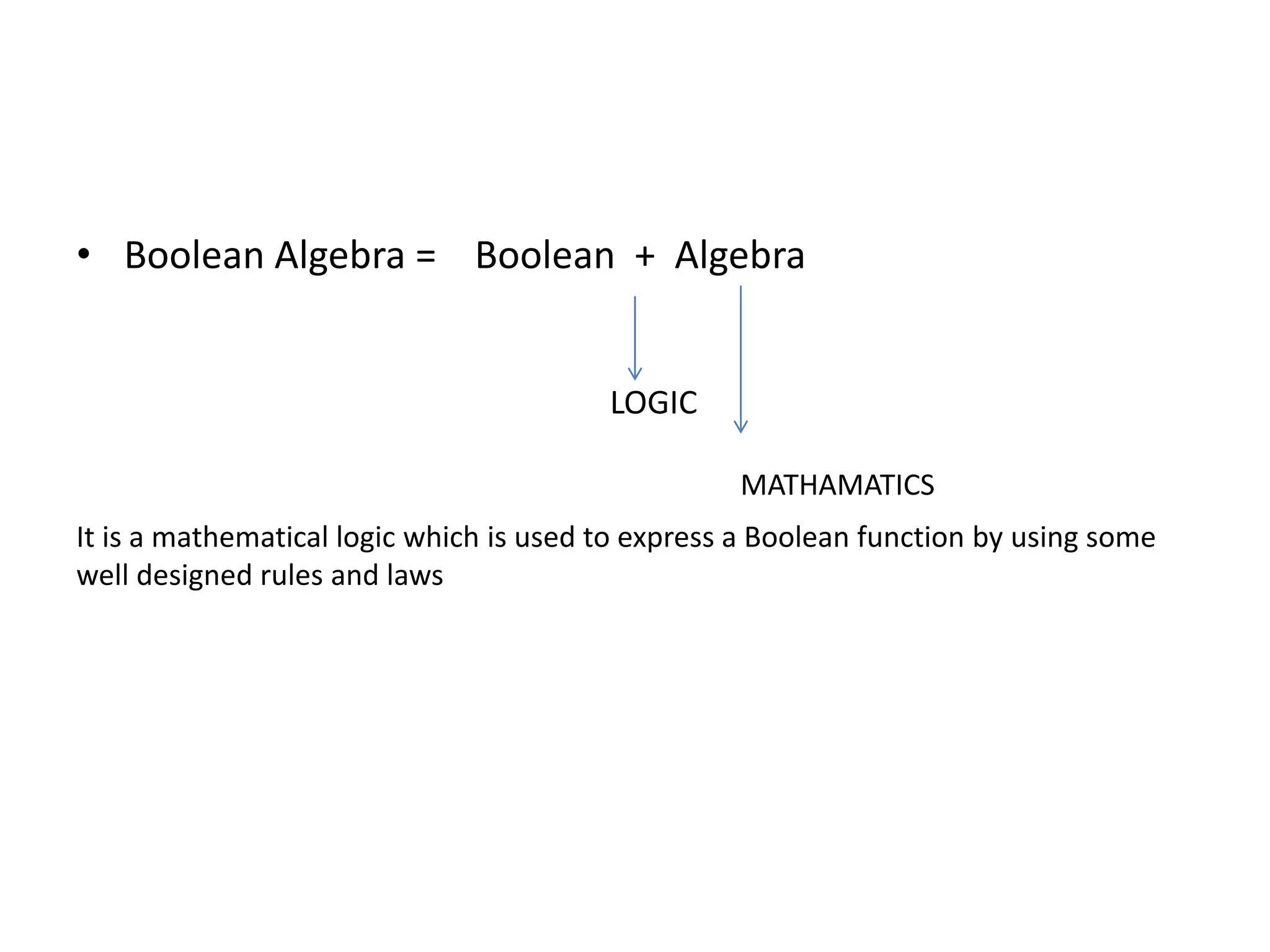
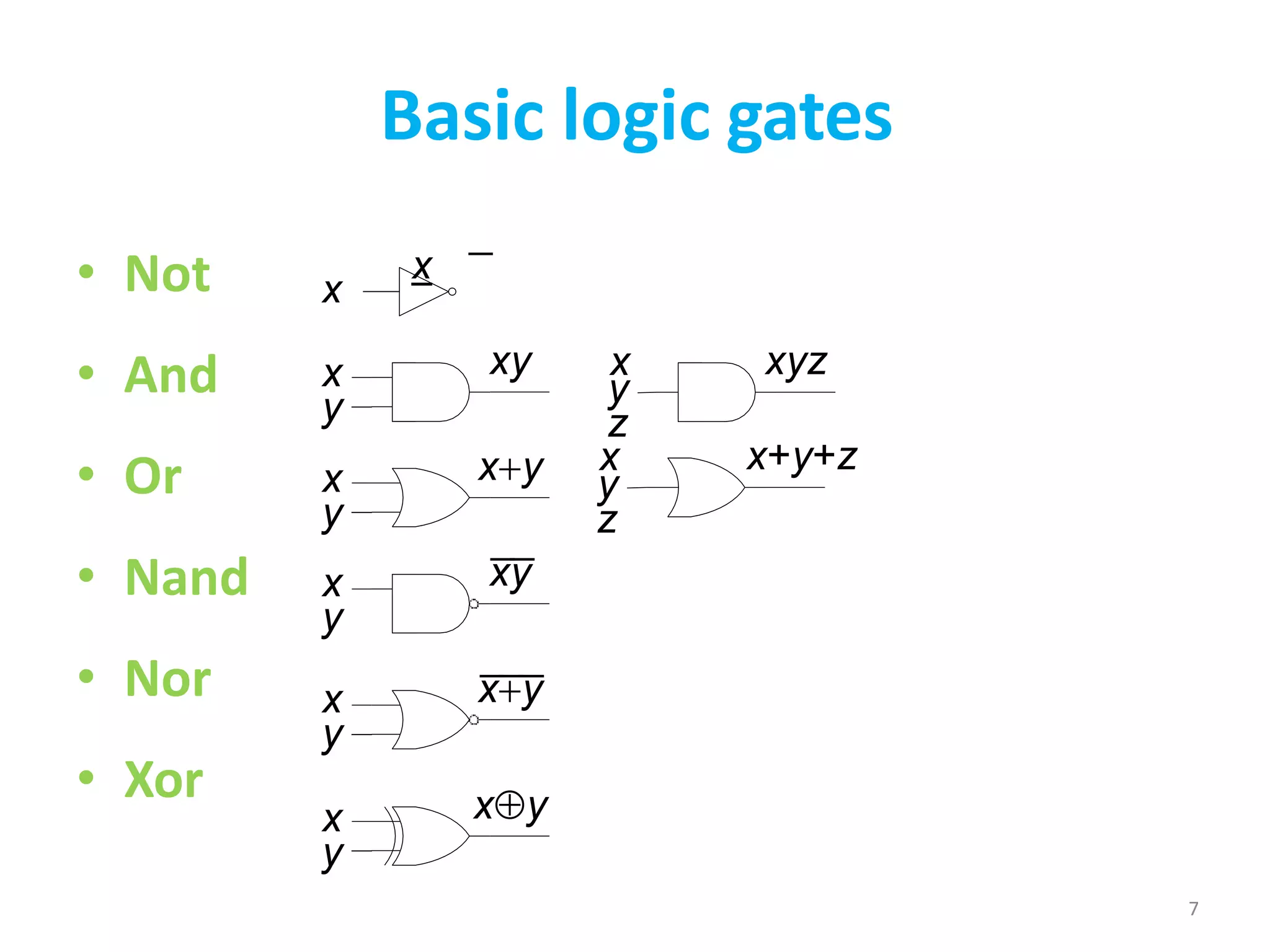
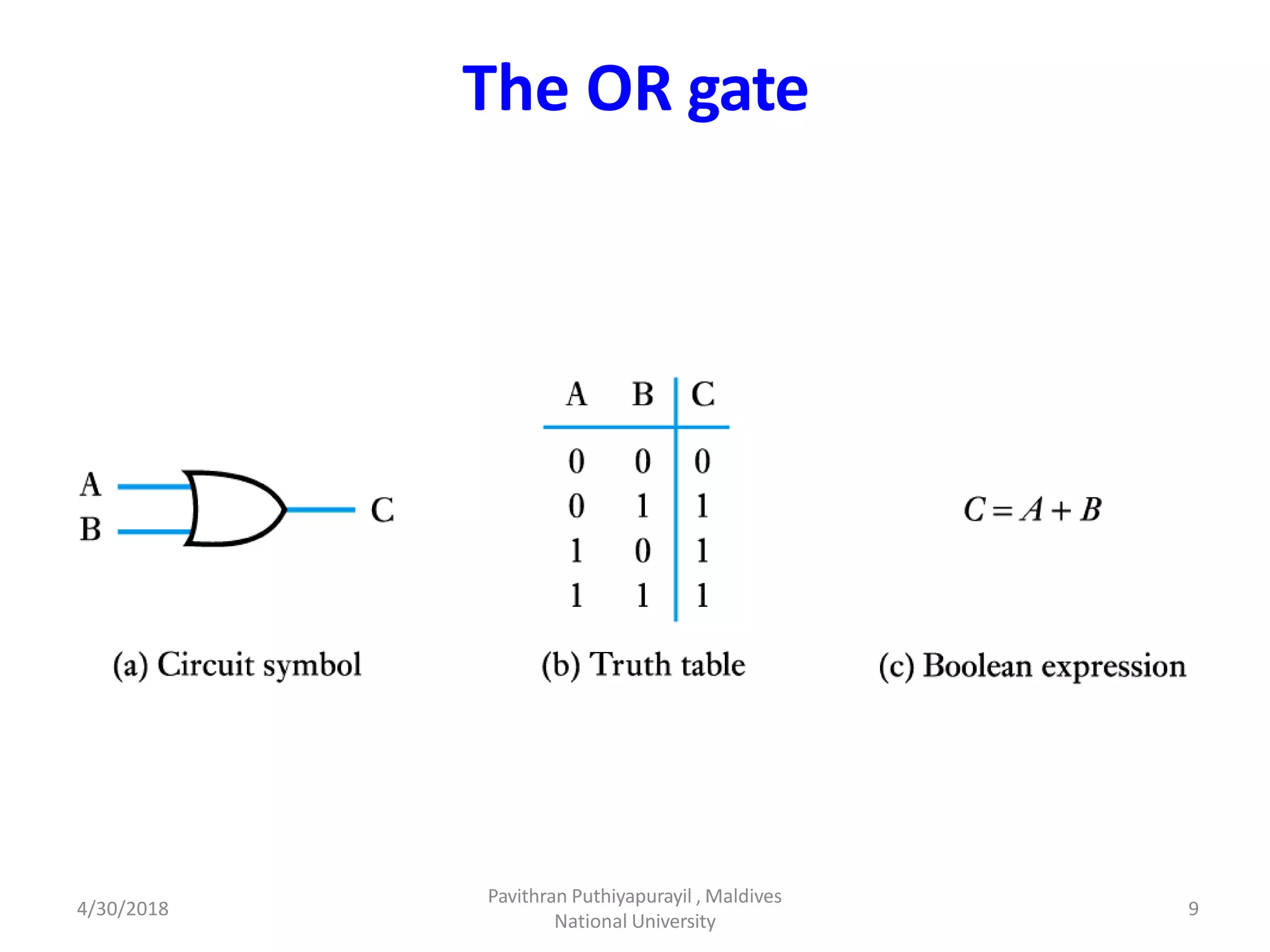
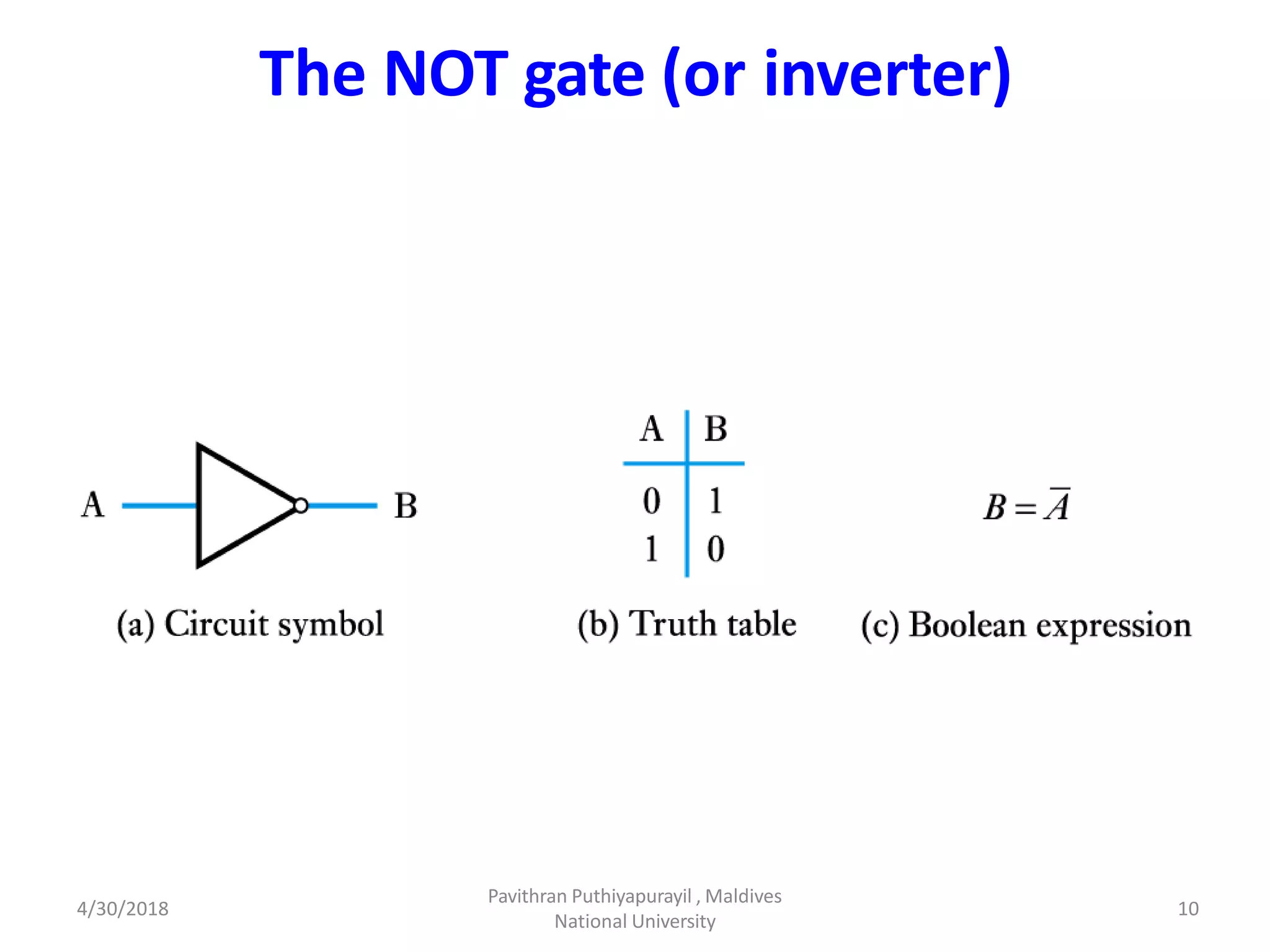
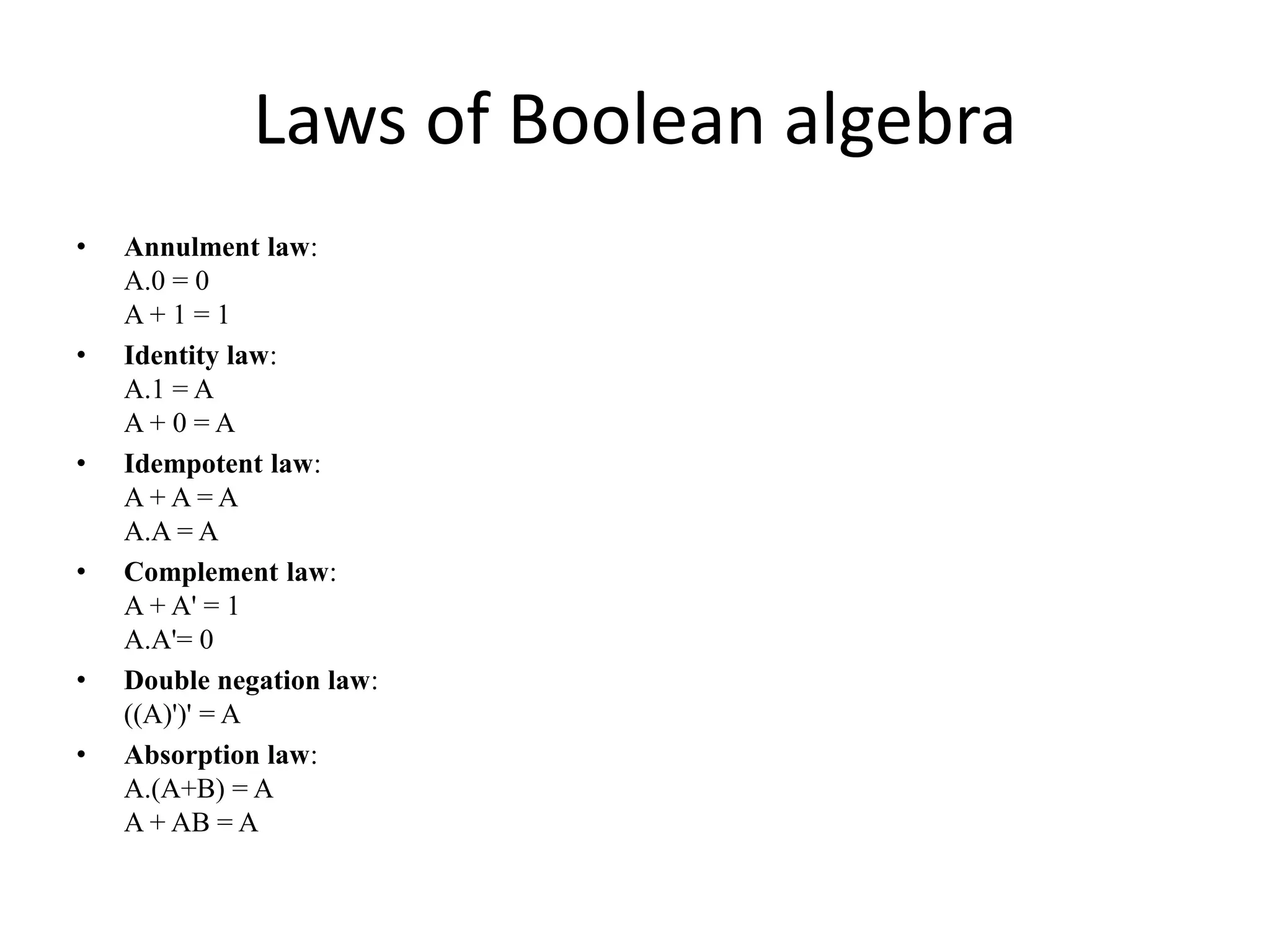
This document discusses computer organization and architecture. It defines organization as the physical aspects of a computer and architecture as the logical aspects. It then provides an overview of Boolean logic, which uses true and false values. The basic logic gates such as AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, and XOR are described. Laws of Boolean algebra are also outlined, including commutative, associative, distributive, annulment, identity, idempotent, complement, double negation, and absorption laws.