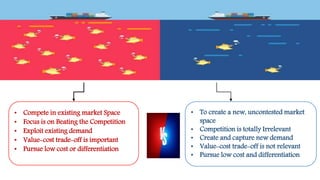
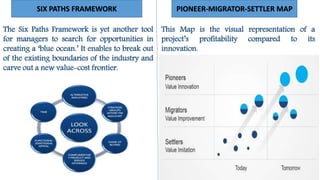
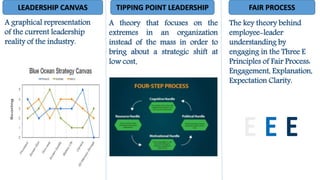
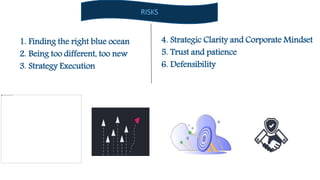
This document provides an overview of blue ocean strategy, a marketing theory that focuses on exploring untapped markets rather than competing in existing markets. It describes blue ocean strategy versus red ocean strategy, tools used in blue ocean strategy like the value innovation model and strategy canvas, strengths like being grounded in data and providing a process, risks like finding the right market and strategy execution, examples of companies that used it like Cirque du Soleil and Netflix, and discusses whether it can be a blessing or curse in developing countries.