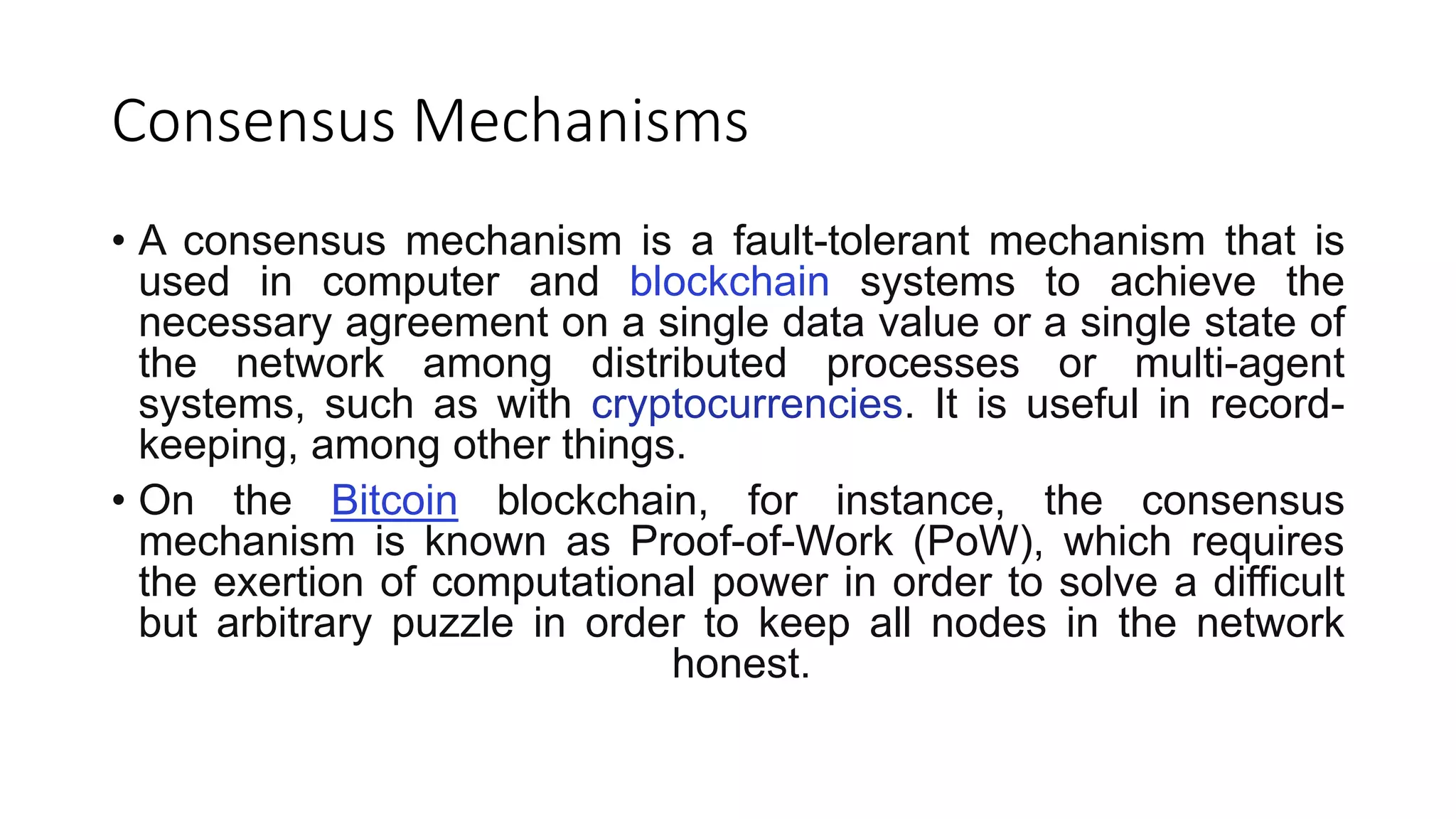
Blockchain technology has several important uses including facilitating secure transactions, lowering compliance costs, and accelerating data processing. It can be applied to smart contracts, money transfers, digital media, IoT, and more. Specific companies in each sector are utilizing blockchain, such as BurstIQ for healthcare data sharing, Propy for real estate transactions, and Circle for cryptocurrency investments and exchanges. Blockchain works by recording transactions in distributed ledgers called blocks that are verified across a network.