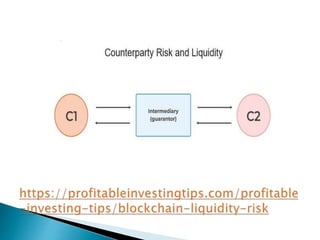
The document discusses liquidity and counterparty risk associated with distributed ledger technology and blockchains. It explains that while blockchains allow for peer-to-peer value transfer without intermediaries, there is no entity within the blockchain to handle disputes or insure against losses from default. To manage these risks, background checks on counterparties are recommended and it's best to avoid deals that seem too good to be true, as common sense is often the best guide for blockchain-based transactions.