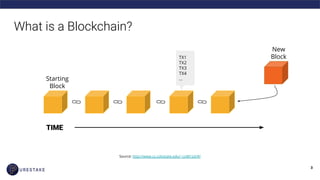
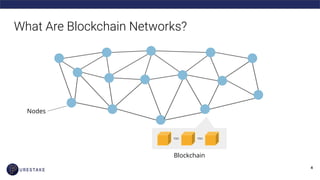
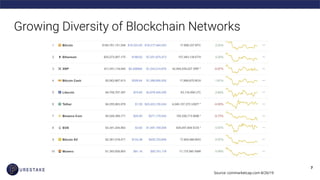
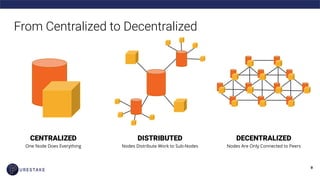
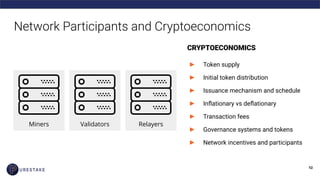
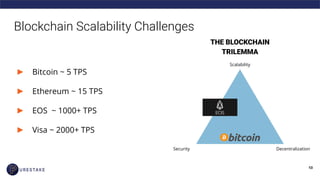
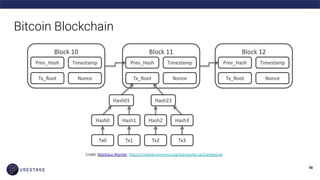
The document provides an introduction to blockchain technology, covering its definition, key use cases, and various types of blockchain networks, including public and private ones. It discusses scalability challenges faced by blockchain systems and highlights solutions like Layer 2 technologies, along with the concept of cryptoeconomics related to token supply and governance. The author, Derek Yoo, shares his background and insights into the growing diversity and applications of blockchain in sectors such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare.