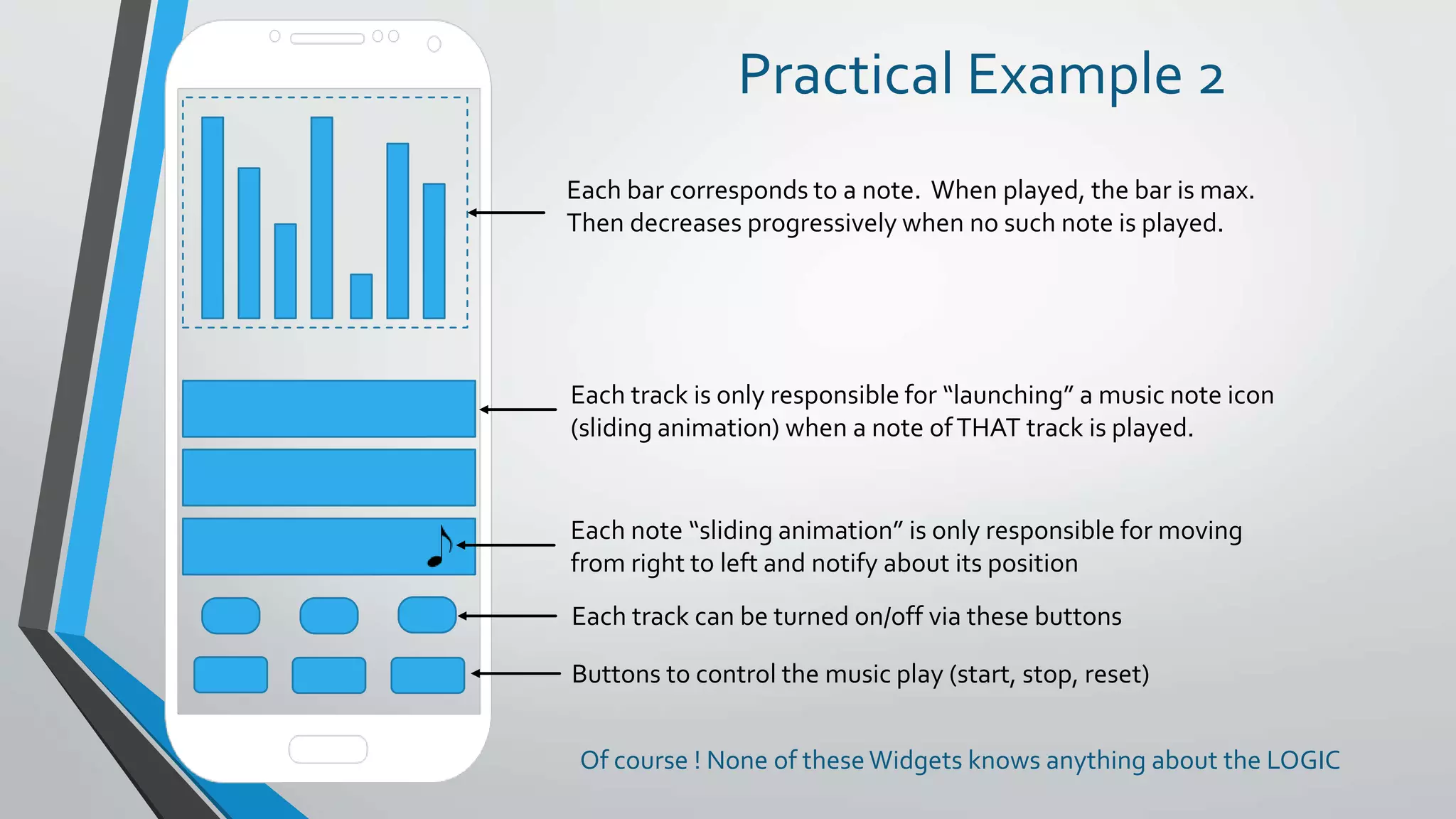
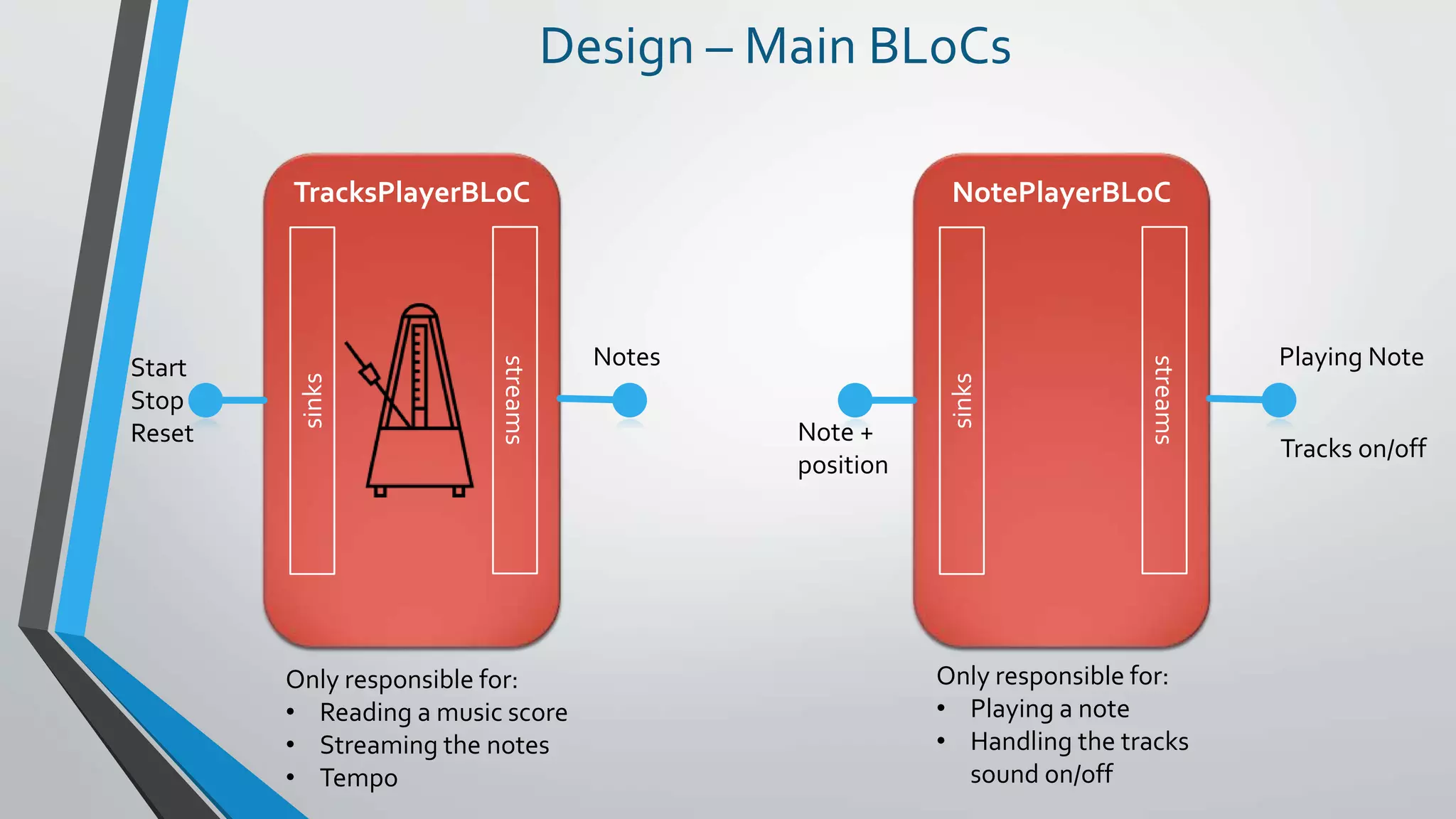
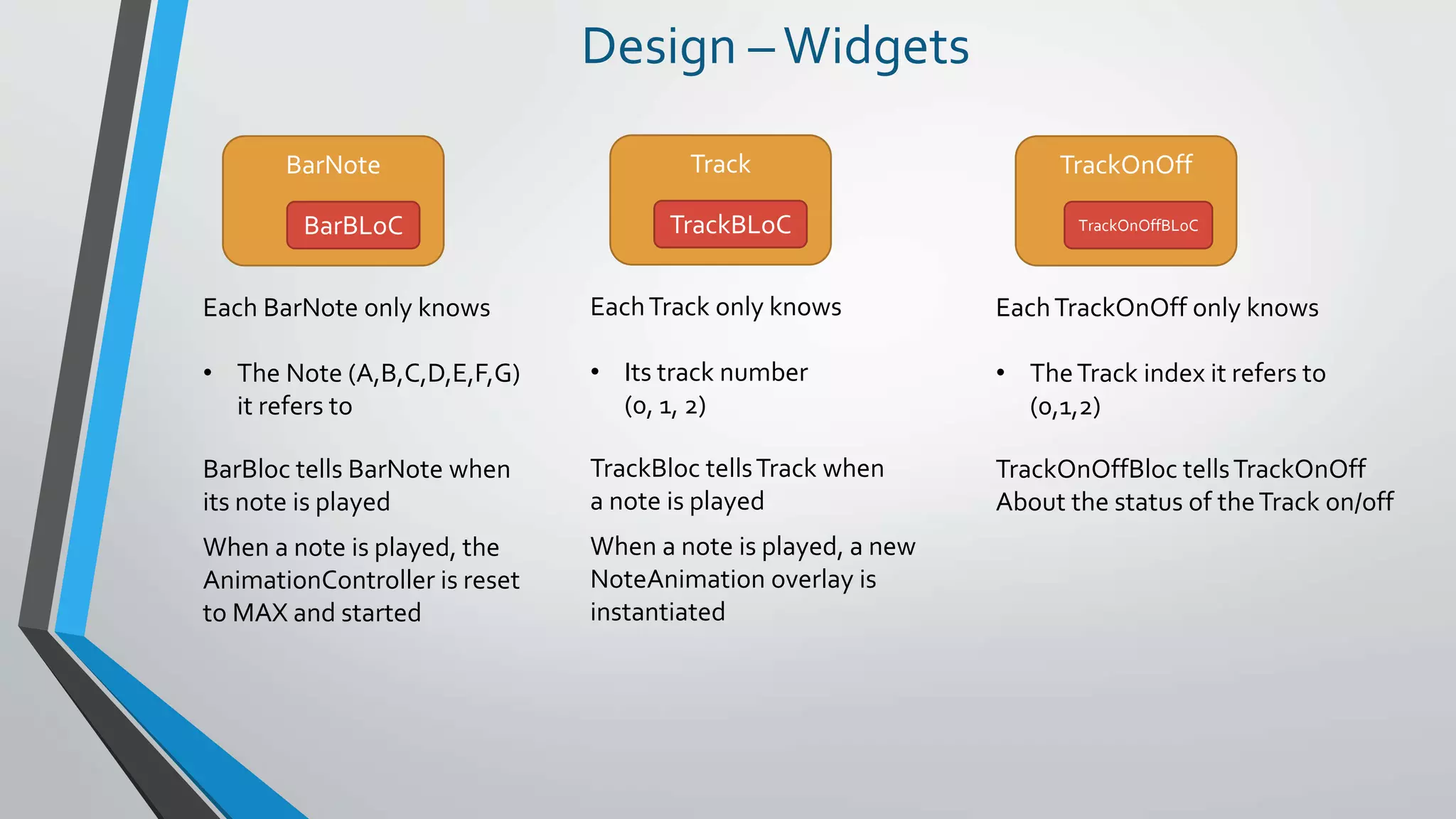
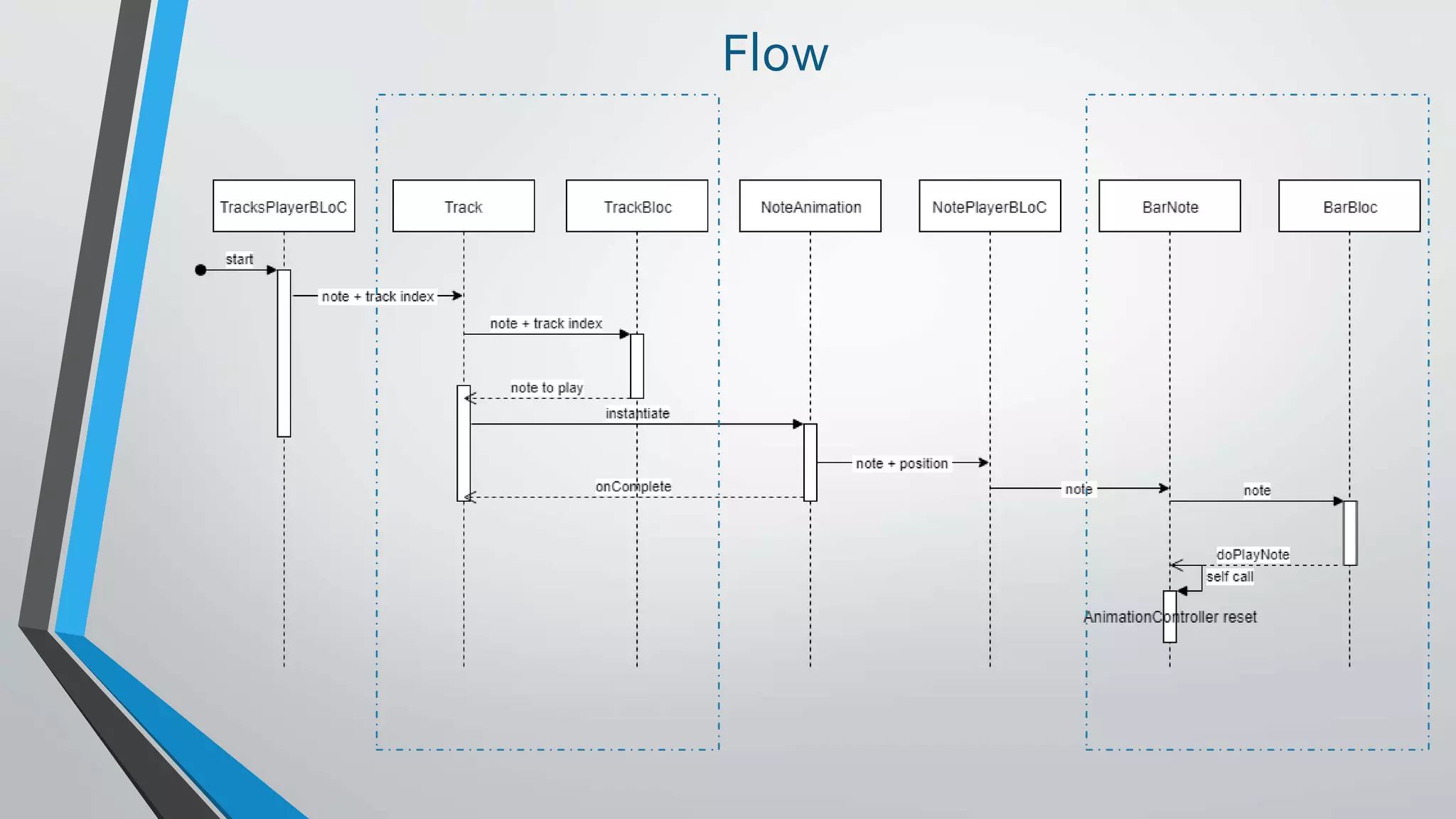
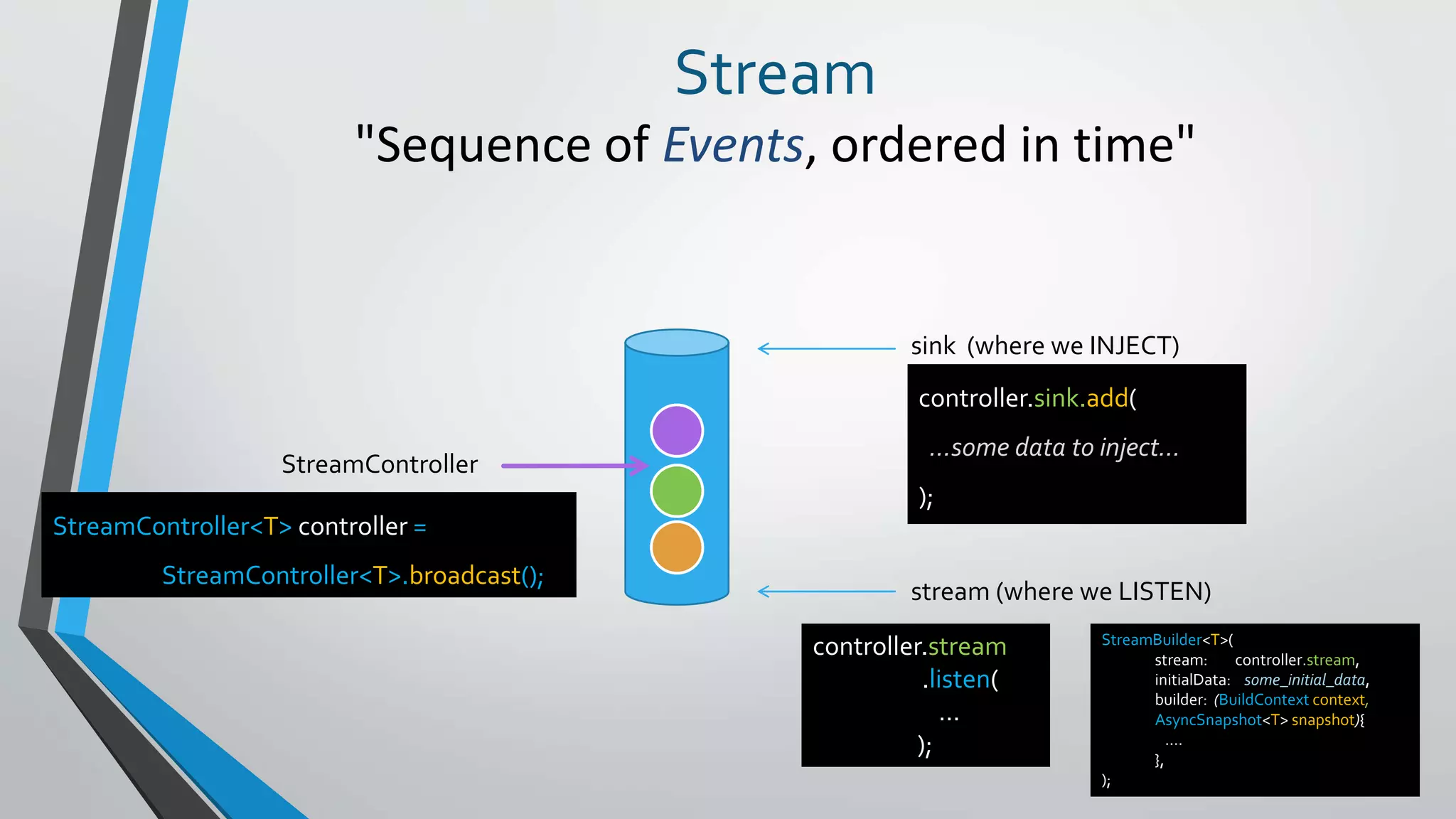
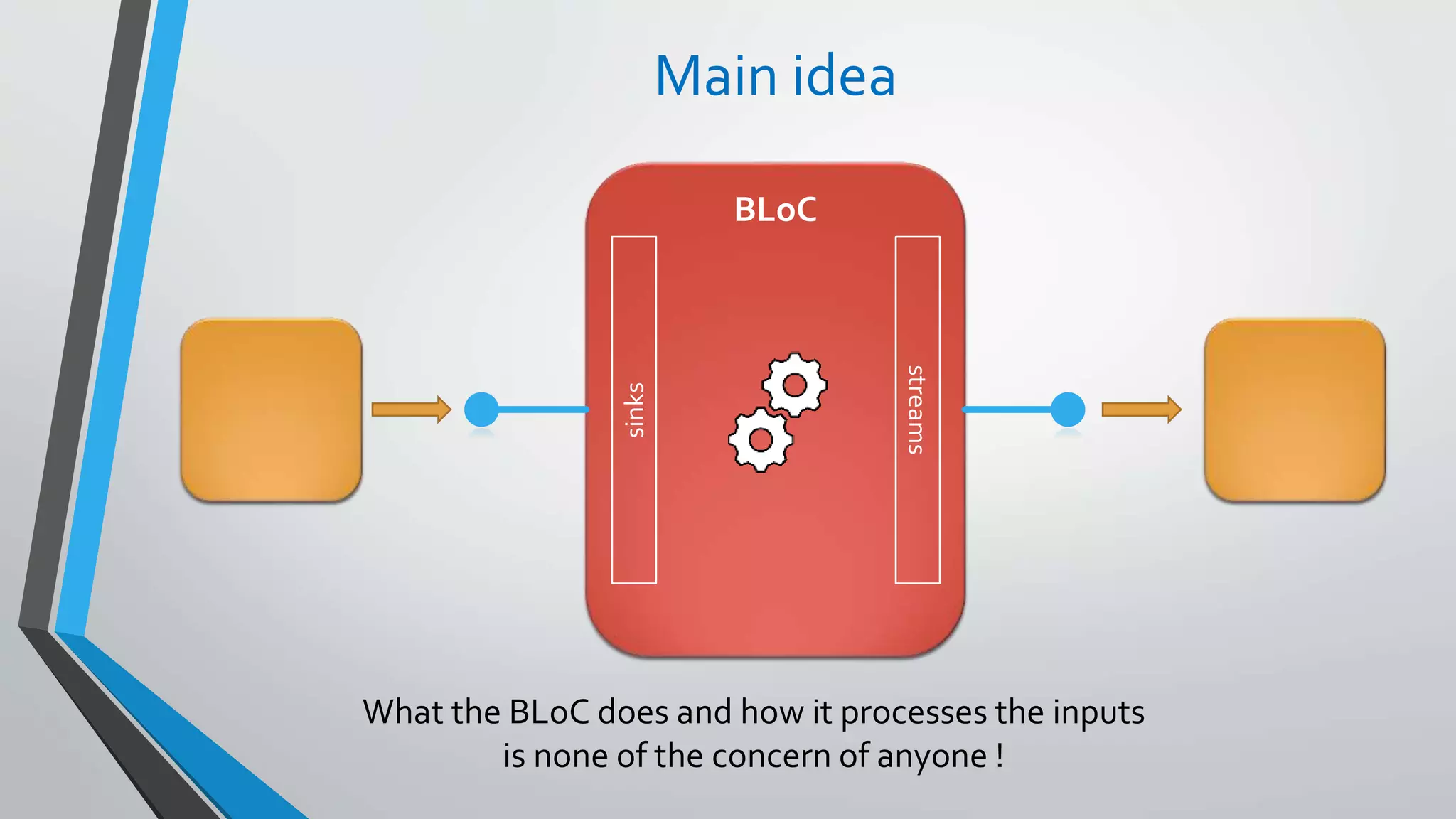
This document provides an introduction to reactive programming, specifically in the context of Flutter and the Bloc architecture. It explains the concepts of streams, the differences between single-subscription and broadcast streams, and the implementation of business logic components (Bloc) to handle data flow in applications. Practical examples are provided, demonstrating how Bloc manages application states, such as user authentication and music track playback, emphasizing its advantages like interchangeability and testability.












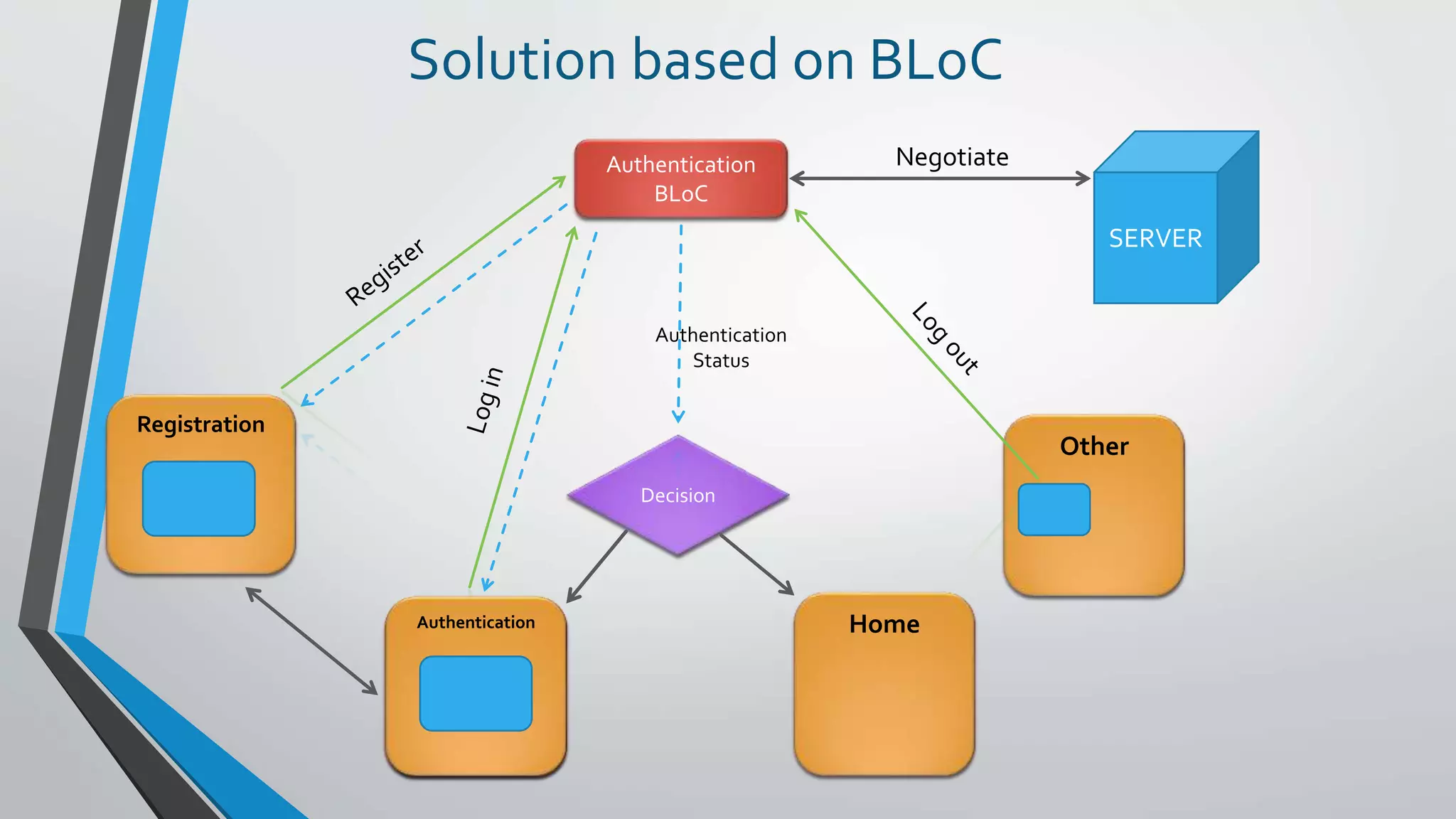
![How ?
Authentication BLoC
Log In
Register
Log Out
Authentication Status
Action Status
Decision
Authentication
Registration
Other
Authentication
Registration
[ … ]
[ … ]
sinks
streams
SERVER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20190121-reactiveprogramming-flutterlondon-190123152754/75/Bloc-Pattern-Practical-Use-Cases-Flutter-London-21JAN2019-17-2048.jpg)




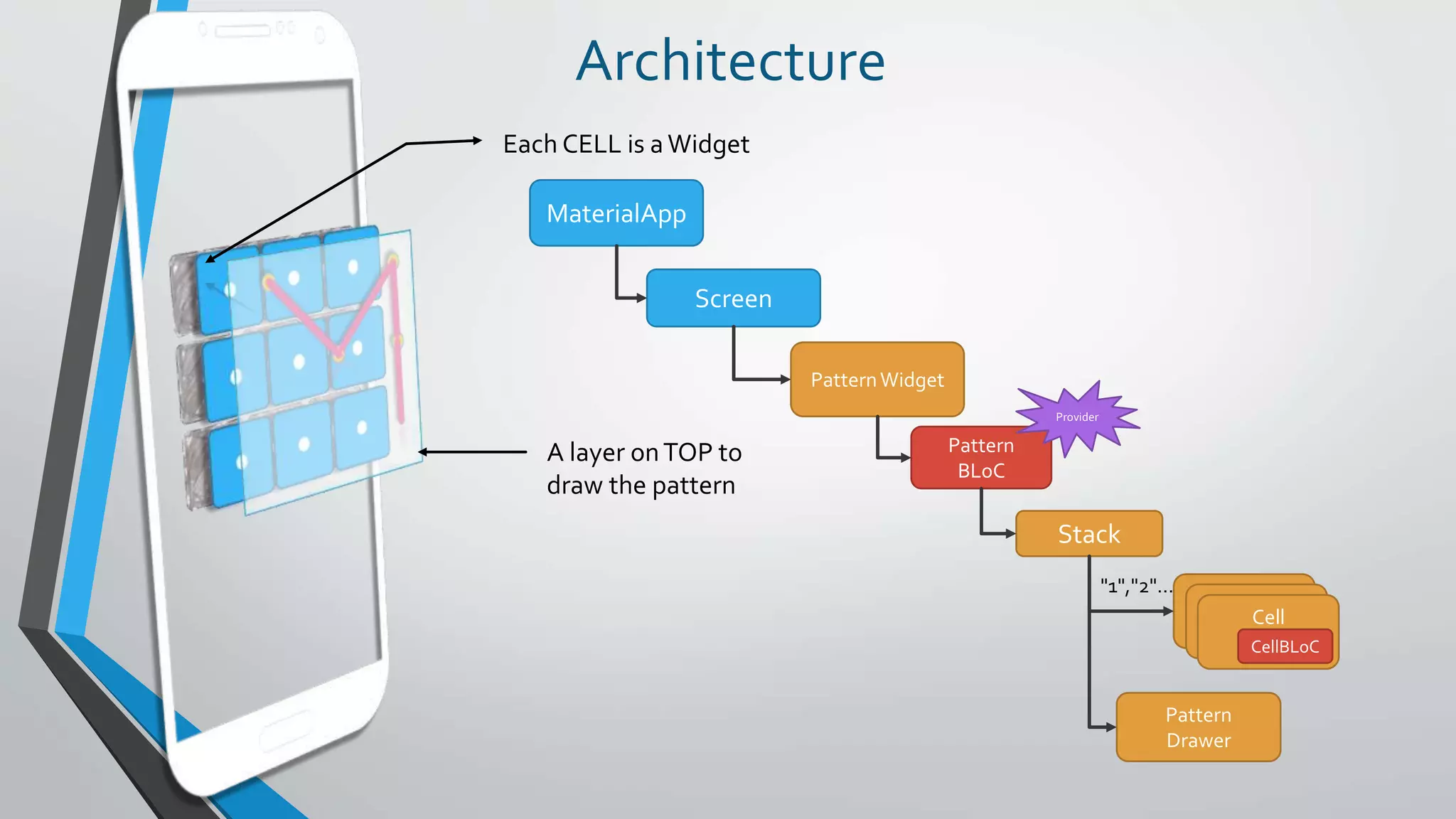
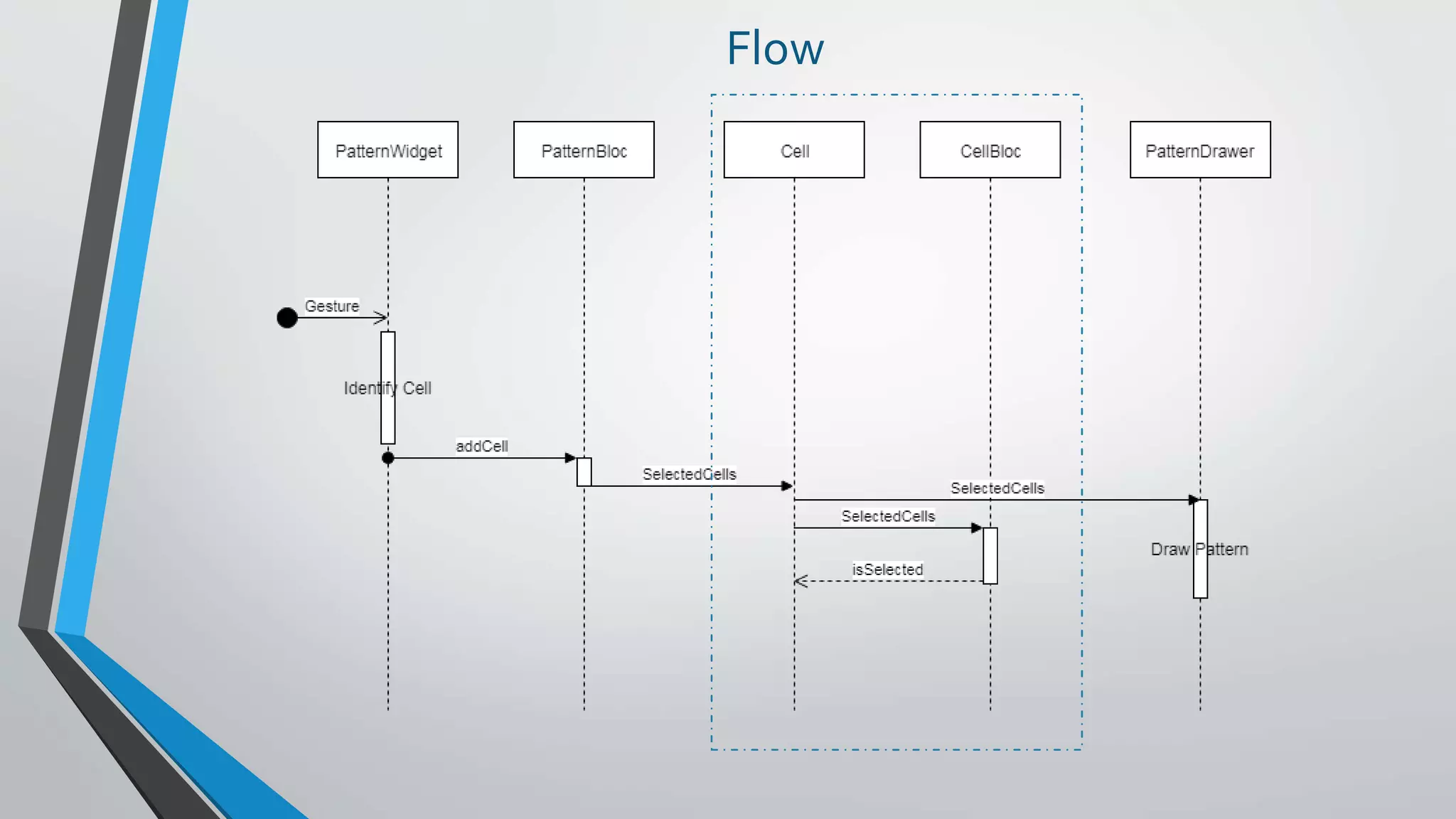
![Design
PatternBLoC
sinks
streams
SelectedCells[]addCell
Cell
CellBLoC
Each Cell only knows
• Its cell number
CellBloc tells Cell when
THAT Cell is part of the
pattern
When a Cell is part of
the pattern
it changes its center
color
PatternDrawer
Responsible for
drawing the pattern
based on the
Selected Cells.
PatternWidget
Responsible for
handling the
Gestures
CellBLoC
sinks
SelectedCells[]
streams
isSelected](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20190121-reactiveprogramming-flutterlondon-190123152754/75/Bloc-Pattern-Practical-Use-Cases-Flutter-London-21JAN2019-28-2048.jpg)