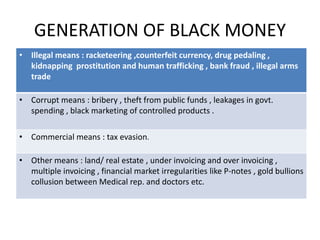
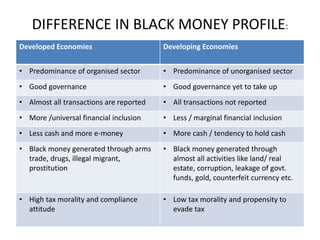
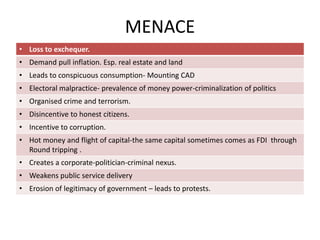
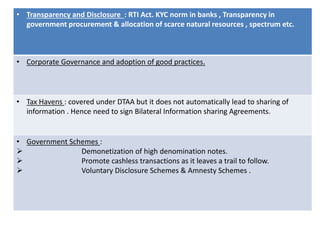
Black money refers to money earned through illegal or tax evading means that is hidden from the government. It is generated through various illegal activities like corruption, tax evasion, underreporting of incomes, and transfers of money to tax havens. The menace of black money includes loss of tax revenue, inflation, weakening of governance, and criminalization of politics. Steps to curb black money include strengthening laws and enforcement agencies, improving tax administration, fostering transparency, cooperation with international organizations, financial inclusion, and demonetization.