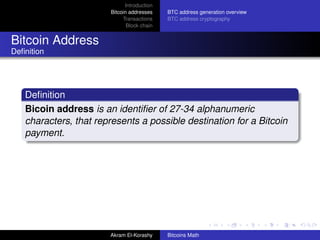
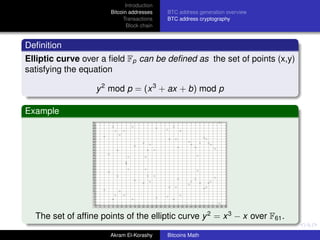
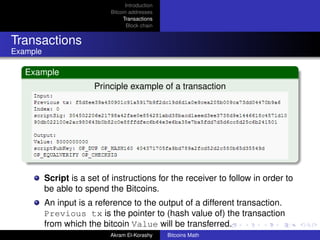
The document provides an overview of bitcoin, focusing on its network properties, address generation, and transaction mechanisms. It explains how bitcoin addresses are formed, the cryptographic principles behind transactions, and the role of the blockchain in maintaining security and preventing double spending. Key concepts such as elliptic curve cryptography, the transaction process, and the structure of blocks in the blockchain are also discussed.