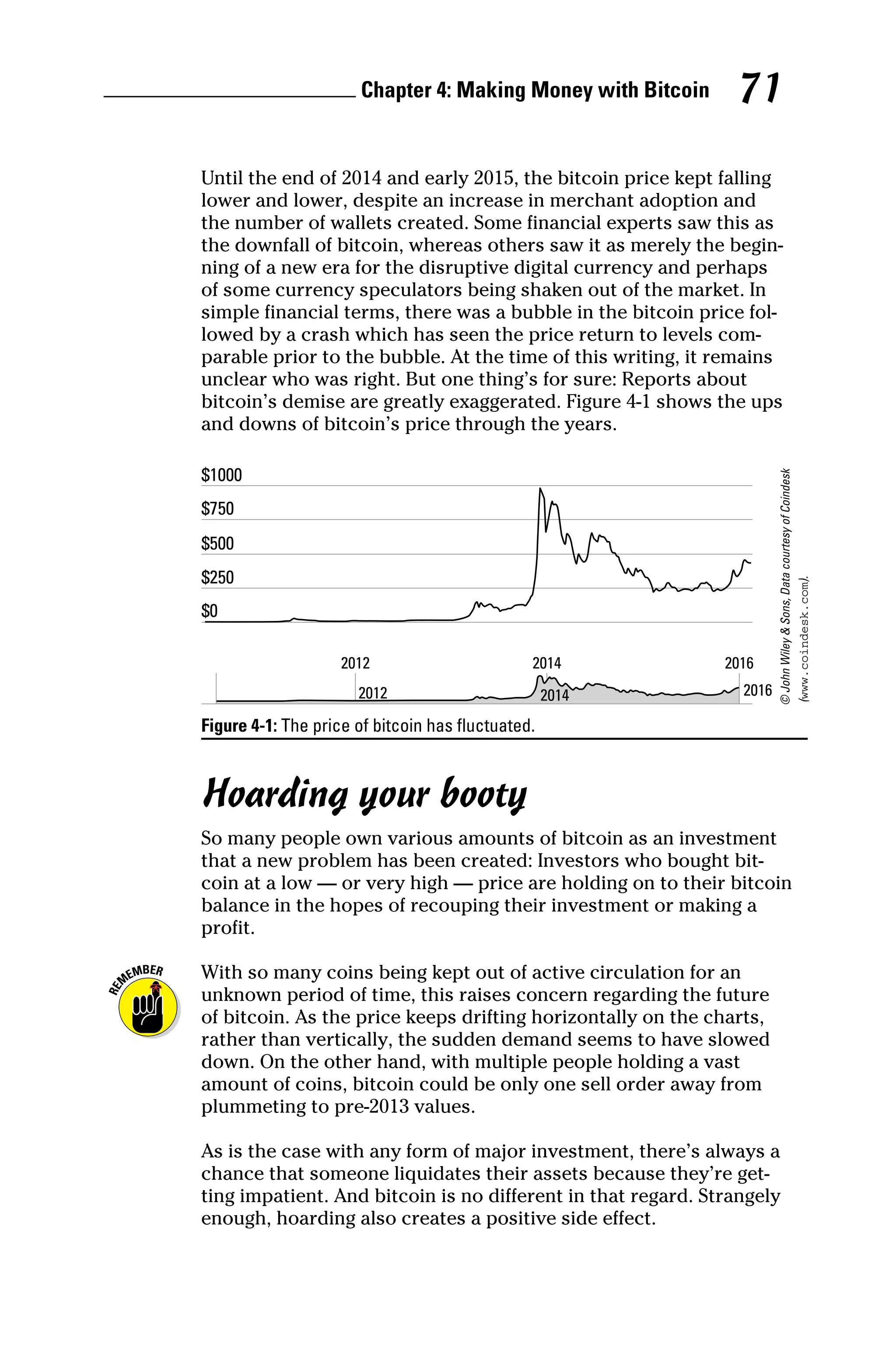
This document provides an introduction to the book "Bitcoin For Dummies" which aims to explain what bitcoin is, how it works, and how it can be used. The book covers bitcoin basics like how transactions are processed and stored on the blockchain. It also discusses how to obtain, store and spend bitcoins safely. Readers will learn about mining, trading and investing in bitcoins as well as regulatory issues around bitcoin. The book provides resources for readers to continue learning about bitcoin and engaging with the online community.