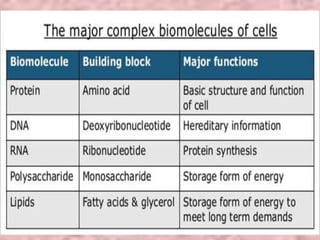
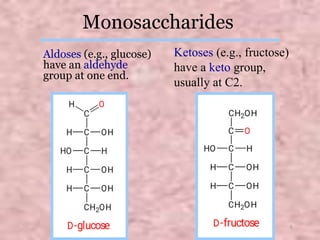
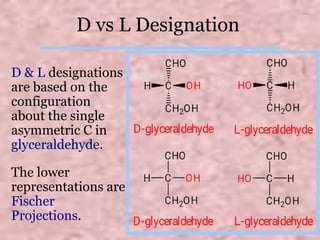
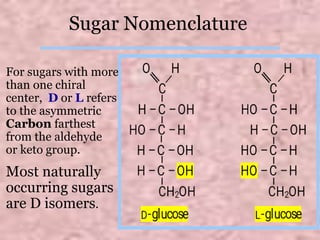
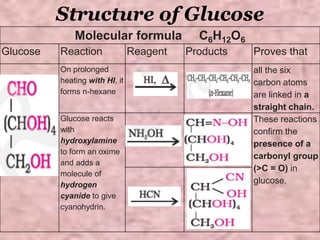
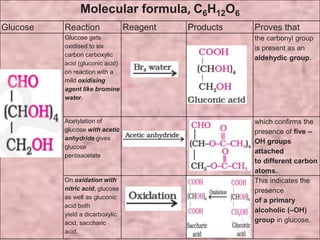
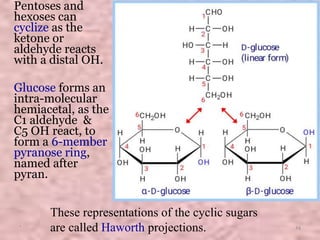
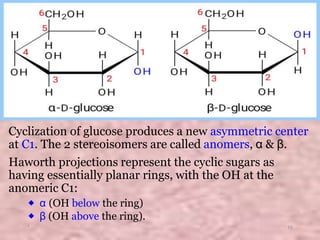
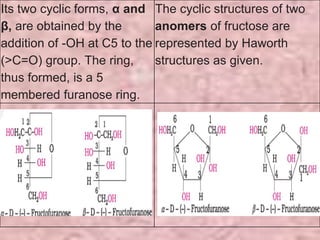
Carbohydrates are classified based on their structure and behavior during hydrolysis. Monosaccharides like glucose and fructose can further cyclize to form rings. Glucose forms a 6-membered pyranose ring while fructose forms a 5-membered furanose ring. Carbohydrates can also be classified as reducing or non-reducing based on whether their functional groups are free to participate in reduction reactions. Glucose and fructose both exist as cyclic structures with α and β anomers formed by the addition of the hydroxyl group to the carbonyl carbon. Their open chain forms do not fully explain properties like crystallization behavior and lack of reactivity of functional groups.