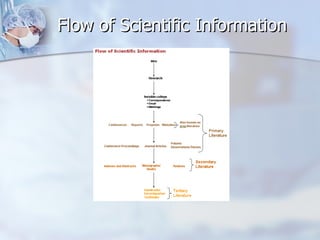
The document discusses various sources of information for biomedical engineers, including journals, conferences, databases, and other literature. It compares the scientific method process to the information retrieval process. Key sources mentioned include journals in specific biomedical engineering fields, conference proceedings, review journals, magazines, monographs, handbooks, and databases such as Scopus, IEEE, Medline, and SciFinder Scholar. The document outlines the flow of scientific information from experiments and research to publication and dissemination.








































![For Further Help Contact Bruce Slutsky Robert Van Houten Library [email_address] 973-642-4950 Reference desk at 973-596-3210](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biomedical-engineering-tutorial-spring-2012-120229120602-phpapp01/85/Biomedical-engineering-tutorial-spring-2012-42-320.jpg)