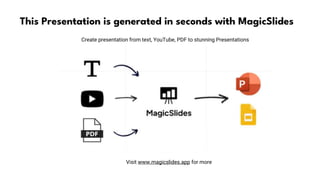
This document outlines the essential elements of biology, including vital processes of living organisms and the importance of understanding their interconnectedness. It provides guidance on selecting topics for biology projects, conducting literature reviews, designing experiments, analyzing data, and synthesizing findings. The document emphasizes the significance of experimental findings in advancing biological knowledge and suggests future research directions.