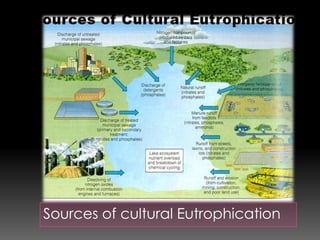
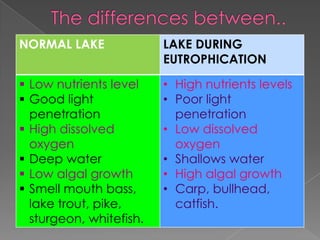
The fertilizer spreads on land and is washed into lakes by rain and underground water. This causes overgrowth of algae and aquatic plants in the lake. The algae blocks sunlight from reaching lower parts of the lake and dies. Bacteria decompose the algae, using up all the oxygen and making the lake anoxic. All organisms in the lake then die, due to eutrophication caused by excess nutrients entering the lake. Eutrophication decreases diversity and changes dominant species, increasing plant and animal biomass while reducing oxygen and water clarity.