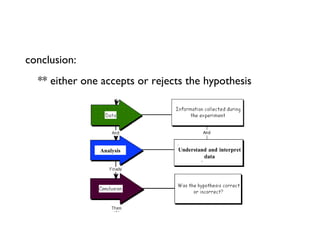
This document provides an overview of the course BIO 1 General Biology. It defines key scientific concepts like science, the scientific method, and theory. The scientific method is described as involving curiosity, evidence-based explanations, observation, hypothesis formation, experimentation, analysis, and sharing results. An example of applying the scientific method is given to test if bacteria from a mercury-contaminated river are mercury-resistant. The course will cover biology at the molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, and organism levels.