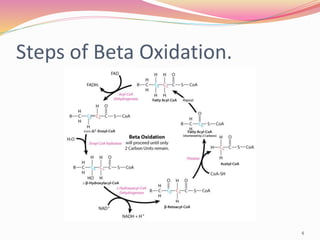
Beta oxidation is the process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA and energy in the form of NADH and FADH2. It occurs in four steps: dehydrogenation, hydration, oxidation, and thiolysis. Each cycle shortens the fatty acid chain by two carbons, producing one acetyl-CoA molecule, one FADH2, one NADH, and water. This yields 17 ATP molecules of energy per cycle, which are used to power cellular processes. Beta oxidation continues repeating until the fatty acid chain has been completely broken down into acetyl-CoA molecules.