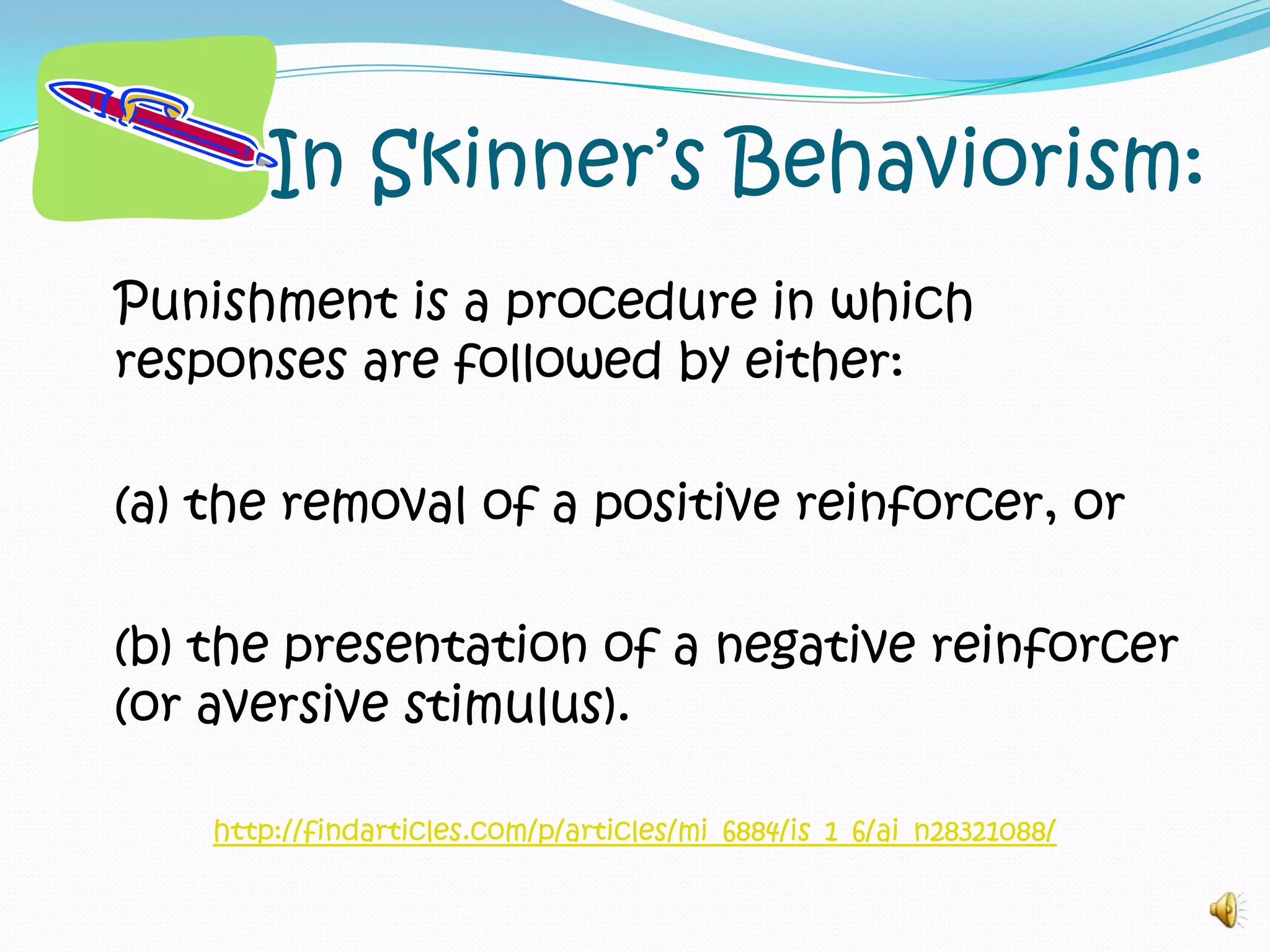
The document summarizes key concepts of operant conditioning including reinforcement schedules and types of reinforcement and punishment. It provides definitions and examples of positive and negative reinforcement as well as links to additional resources on topics like reinforcement schedules and Skinner's views on punishment. Videos are referenced to illustrate examples of reinforcement and help determine behaviors discussed in relation to conditioning principles.