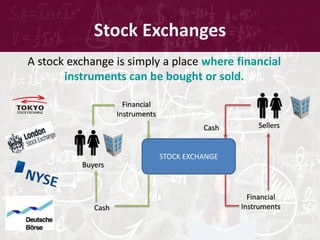
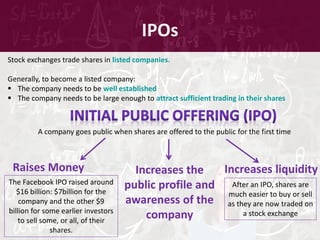
Stock exchanges began as physical meeting places for traders but have increasingly moved to electronic platforms. A stock exchange provides a marketplace for buyers and sellers to trade financial instruments like stocks. Major stock exchanges around the world include the New York Stock Exchange, London Stock Exchange, and Tokyo Stock Exchange. Most countries also have their own national stock exchange. Stock market indices track the performance of a basket of stocks to measure the overall health of the market.