1) A class is a logical entity that defines the structure and behavior of objects. It contains data members, constructors, methods and blocks but does not allocate memory itself.
2) An object is a physical entity that is instantiated from a class. Memory is allocated when an object is created using the 'new' keyword. An object is an instance of a class.
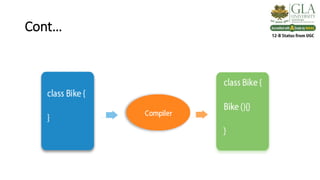
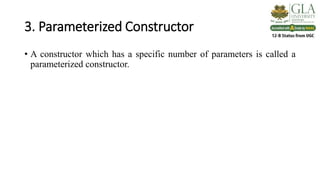
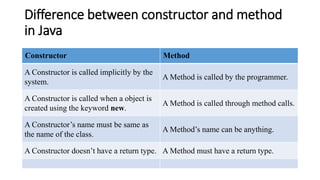
3) Constructors are used to initialize objects. They are called when an object is created and allocate memory for the object. They can be default, no-argument, or parameterized based on whether they take arguments or not.








![Example
class Student
{
int id;
public static void main(String a[])
{
Student s1=new Student();
System.out.println(s1.id);
}
}
Output: 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcaclassandobject-230820074534-4c861f19/85/BCA-Class-and-Object-pptx-12-320.jpg)

![Example
class Bike
{
Bike()
{
System.out.println("Bike is created");
}
public static void main(String a[])
{
Bike b=new Bike();
}
}
Output: Bike is created](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcaclassandobject-230820074534-4c861f19/85/BCA-Class-and-Object-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Example
class Student
{
int id;
String name;
Student(int i, String n)
{
id = i;
name = n;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
}
public static void main(String a[])
{
Student s1 = new Student(111,"Karan");
s1.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcaclassandobject-230820074534-4c861f19/85/BCA-Class-and-Object-pptx-16-320.jpg)



![Example
class Student
{
int id;
public static void main(String a[])
{
Student s1= new Student();
s1.id=101;
System.out.println(s1.id);
}
}
Output
101](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcaclassandobject-230820074534-4c861f19/85/BCA-Class-and-Object-pptx-21-320.jpg)

![Example
class Student
{
int id;
void display(int n)
{
id = n;
System.out.println(id);
}
public static void main(String a[])
{
Student s1=new Student();
s1.display(101);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcaclassandobject-230820074534-4c861f19/85/BCA-Class-and-Object-pptx-23-320.jpg)


![Example
class Student
{
int id;
Student(int i)
{
id = i;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(id);
}
public static void main(String a[])
{
Student s1 = new Student(101);
s1.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcaclassandobject-230820074534-4c861f19/85/BCA-Class-and-Object-pptx-26-320.jpg)
