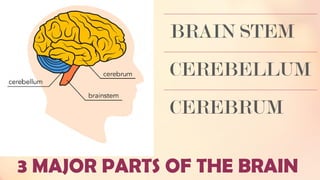
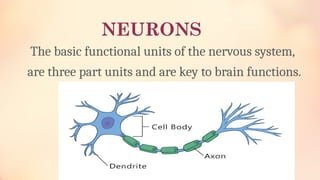
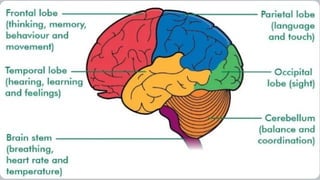
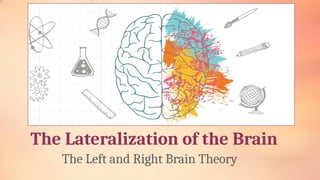
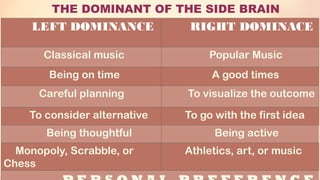
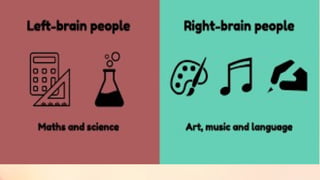
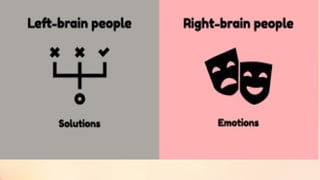
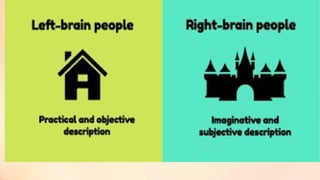
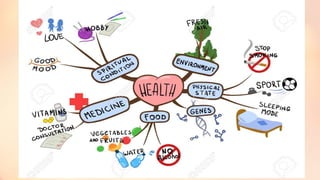
Chapter 6 discusses the functions of the brain and how understanding left and right brain dominance can enhance learning. It explores mind mapping techniques tailored to different thinking styles and highlights both the advantages and disadvantages of the left and right brain theory. Additionally, it covers the impact of various drugs on brain function and emphasizes the importance of adapting learning strategies to individual strengths.