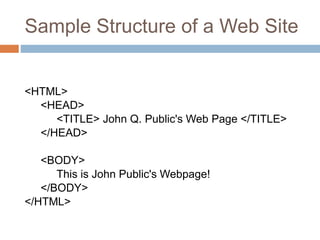
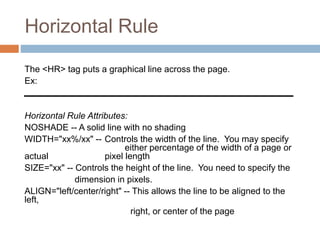
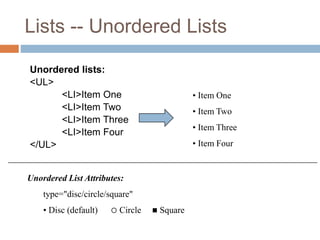
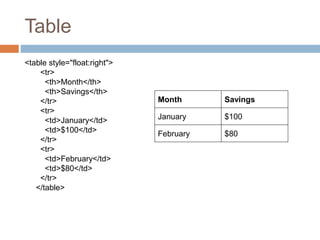
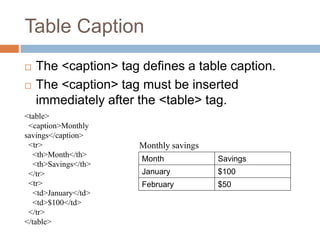
The document defines basic HTML tags for structuring web pages, including structural tags (<html>, <head>, <title>, <body>), header tags (<h1-h6>), paragraph tags (<p>), line break tags (<br>), and horizontal rule tags (<hr>). It also covers text formatting tags (<i>, <b>), lists (<ul>, <ol>, <li>), links (<a>), images (<img>), tables (<table>, <tr>, <td>, <th>), and block vs inline elements.