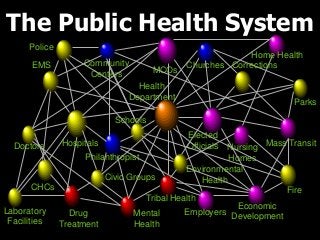
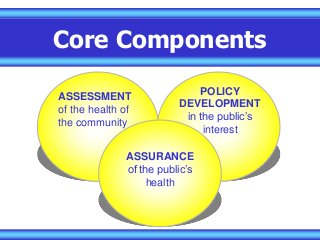
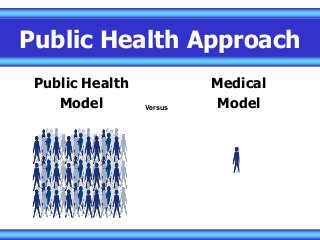
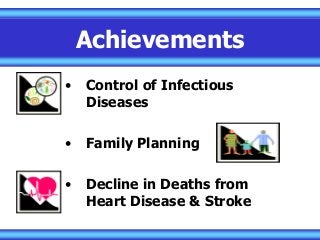
Basics on Public Health, Covers what types of essential services that are provided, defines areas simply and easily to understand. Perfect for an introductory lesson for a middle school health class. Covers Emergency services, core concepts, implementation, management, and how to apply it to practical use. Provides a solid foundation to expand on various concepts and topics. Great for new health teachers or physical education teachers who are establishing a core understanding of areas to focus more on with our students. Questions to be addressed:
What is public health?
What is a public health system?
Why take a public health approach?
Can public health make a difference?