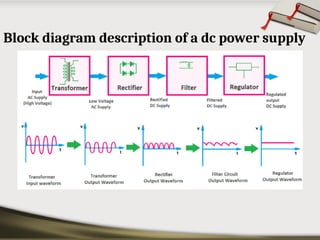
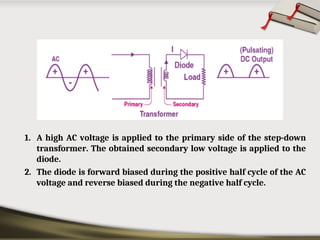
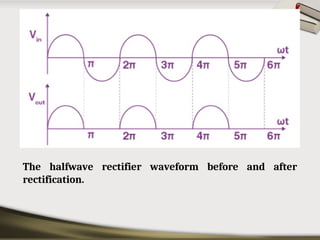
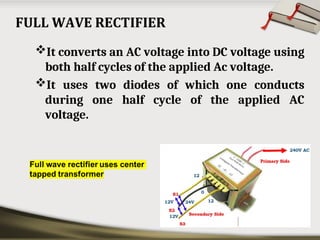
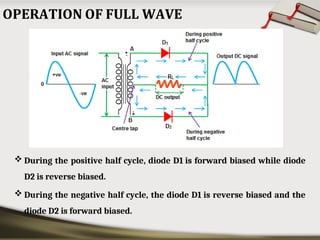
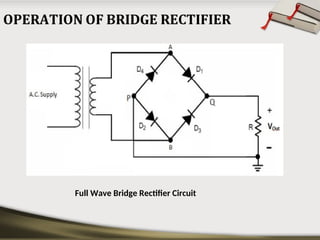
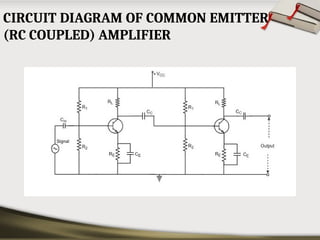
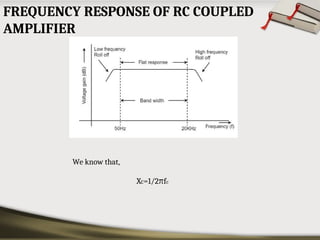
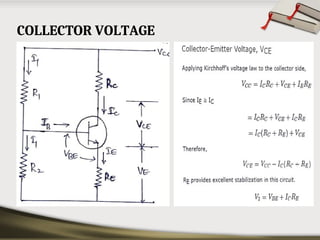
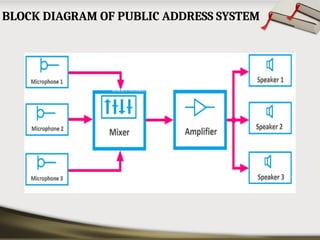
The document provides an overview of basic electronic circuits and instrumentation, detailing components like transformers, rectifiers, filters, and regulators within a DC power supply system. It explains the function and types of rectifiers, including half-wave and full-wave bridge rectifiers, as well as the operation of common emitter amplifiers and public address system components. Additionally, it covers the principles of electronic instrumentation systems, focusing on the roles of sensors, variable conversion, data transmission, and presentation elements.
![Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Part – B
Unit 2 – BASIC ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS &
INSTRUMENTATION
By
Dr.S.A.Sivakumar [Dean-Academics, ASKW]
Mr.B.Naga Rajesh(Ph.D) [AP-ECE, ASKW]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beee-partb-unit2slides-240917111414-79746257/85/Basic-Elec-EE-Part-B-Unit-2-slides-ppt-1-320.jpg)