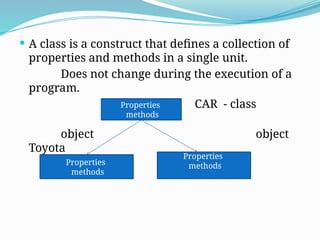
The document explains the concepts of classes and objects in object-oriented programming, detailing class definitions, attributes, access modifiers, and constructors. It distinguishes between default and parameterized constructors, and introduces destructors for resource management. Additionally, it emphasizes inheritance as a key feature for code reuse and easier application maintenance.

![ Syntax:
[ <attributelist> ] [ accessmodifier ]
[ Shadows ] [ MustInherit | NotInheritable ]
[ Partial ]
Class name [ ( Of typelist ) ]
[ Inherits classname ]
[ Implements interfacenames ]
[ statements ]
End Class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-250117074517-d0de7111/85/basic-concepts-of-object-oriented-programming-4-320.jpg)