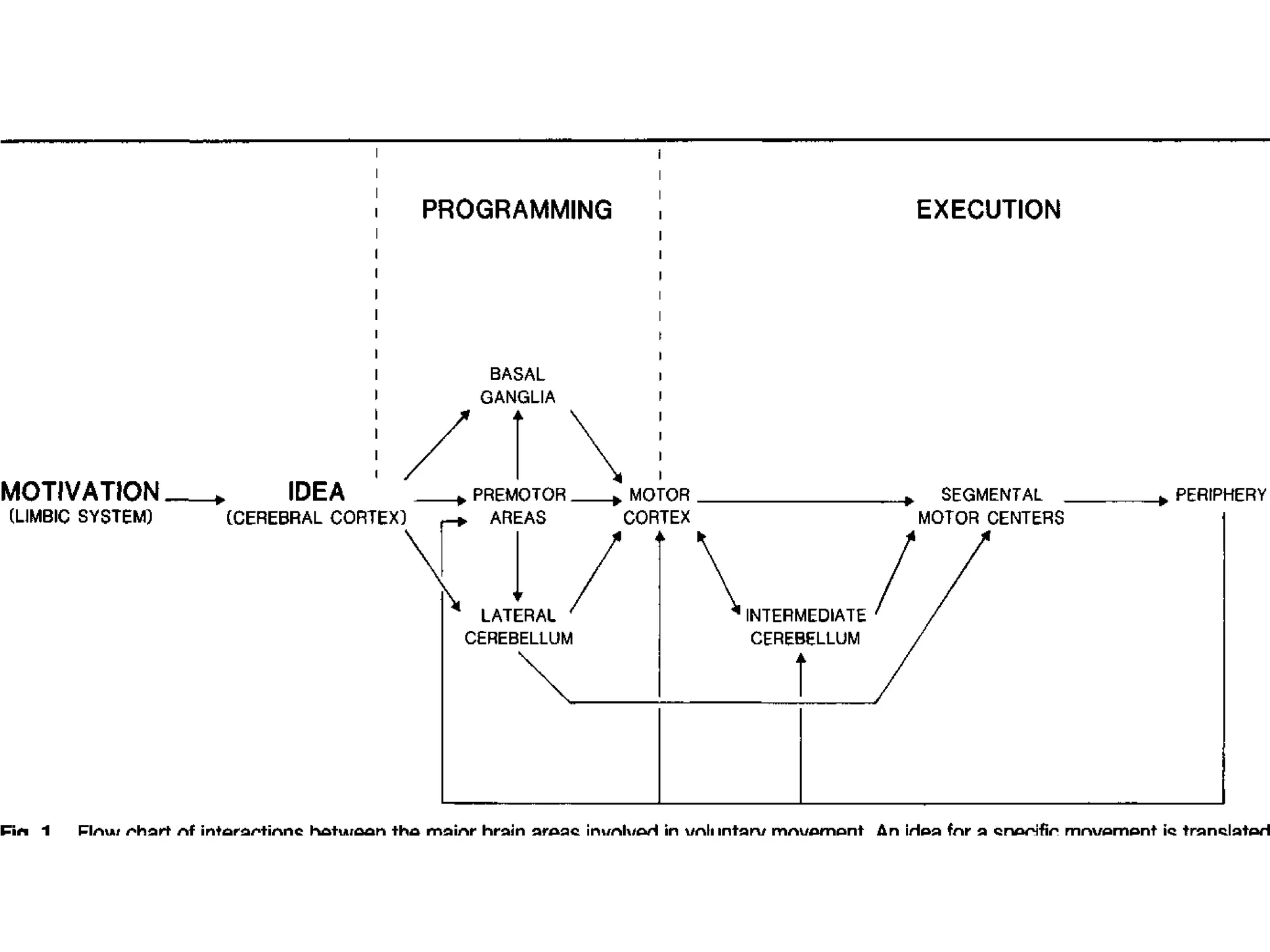
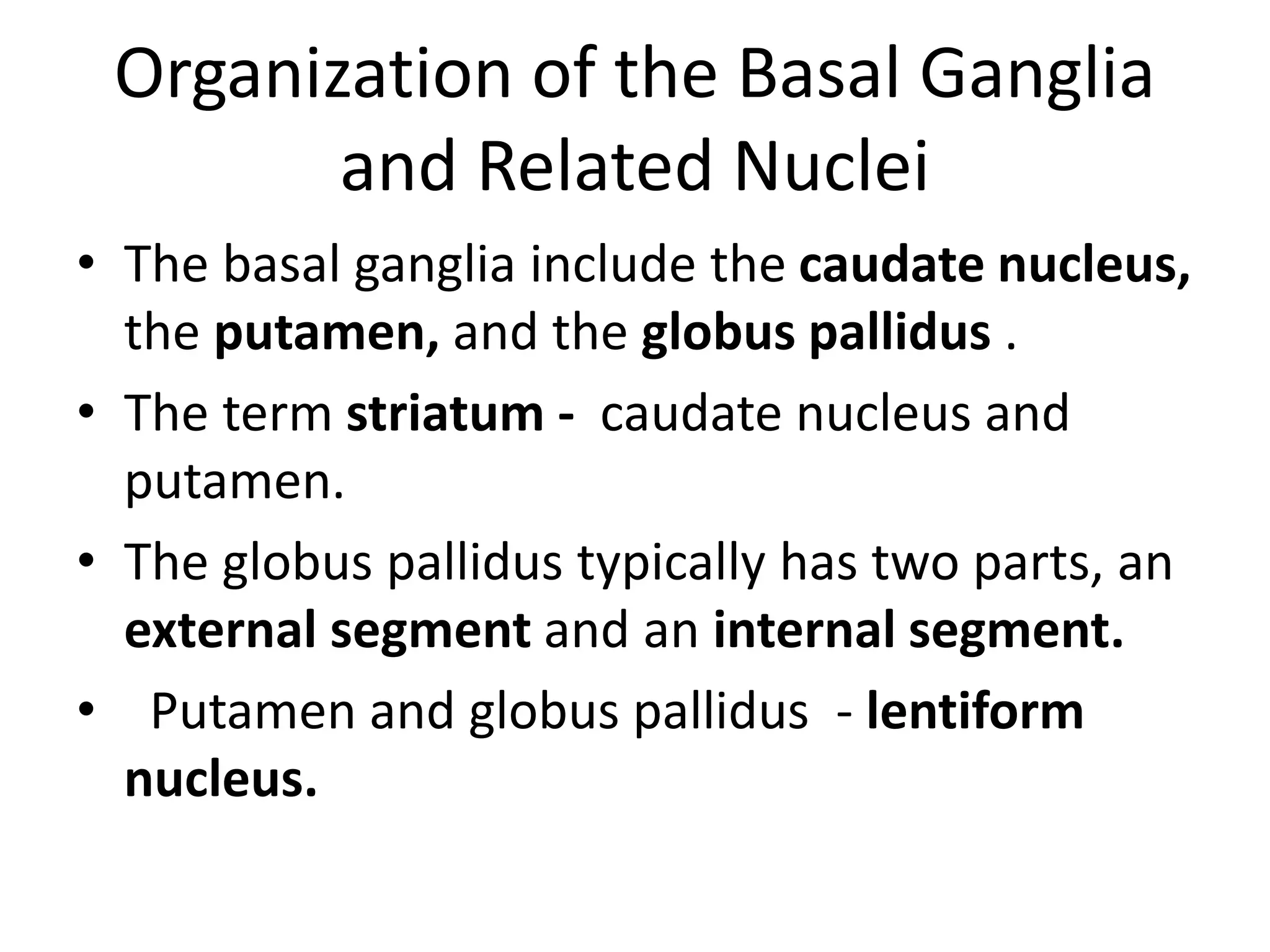
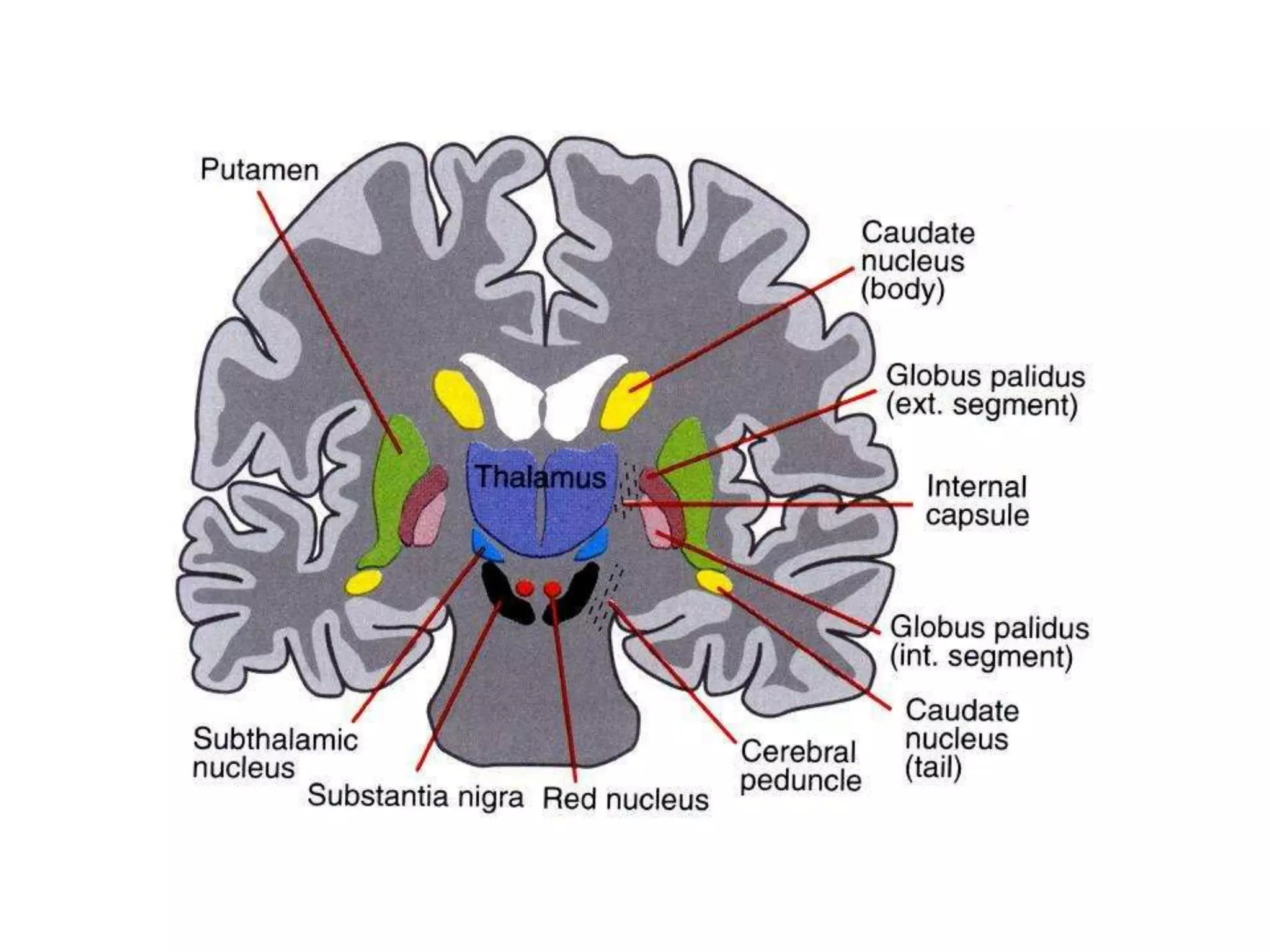
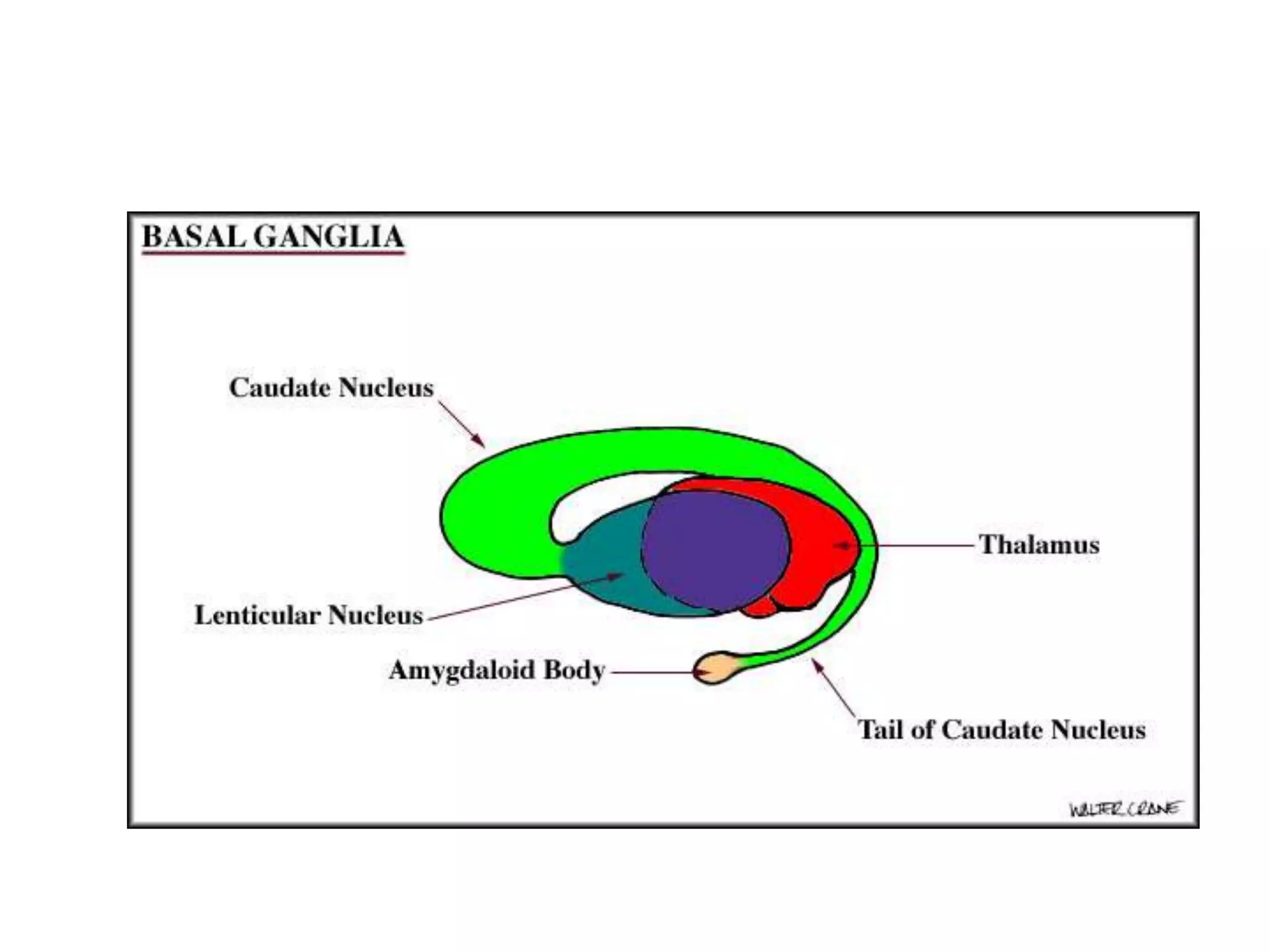
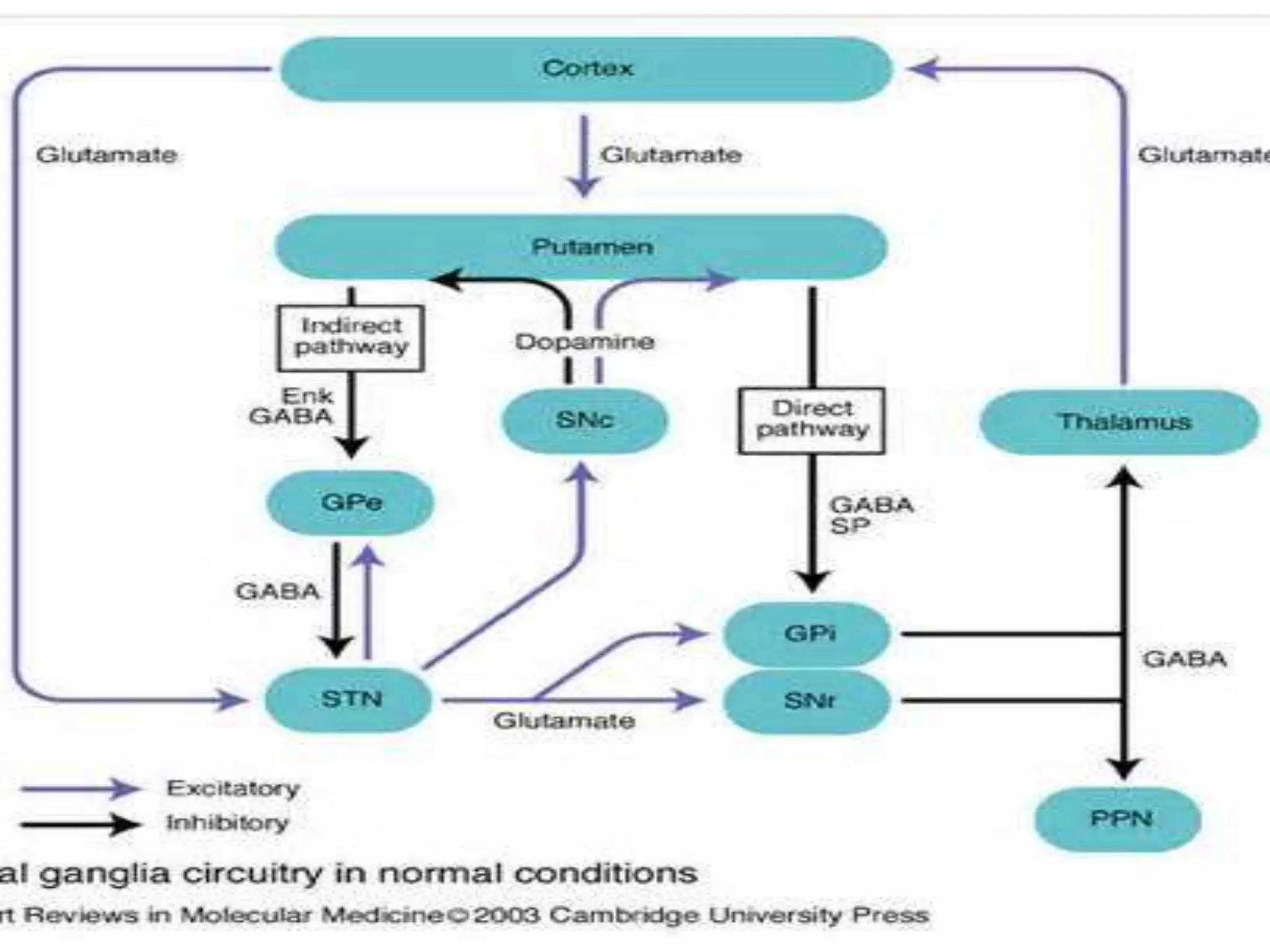
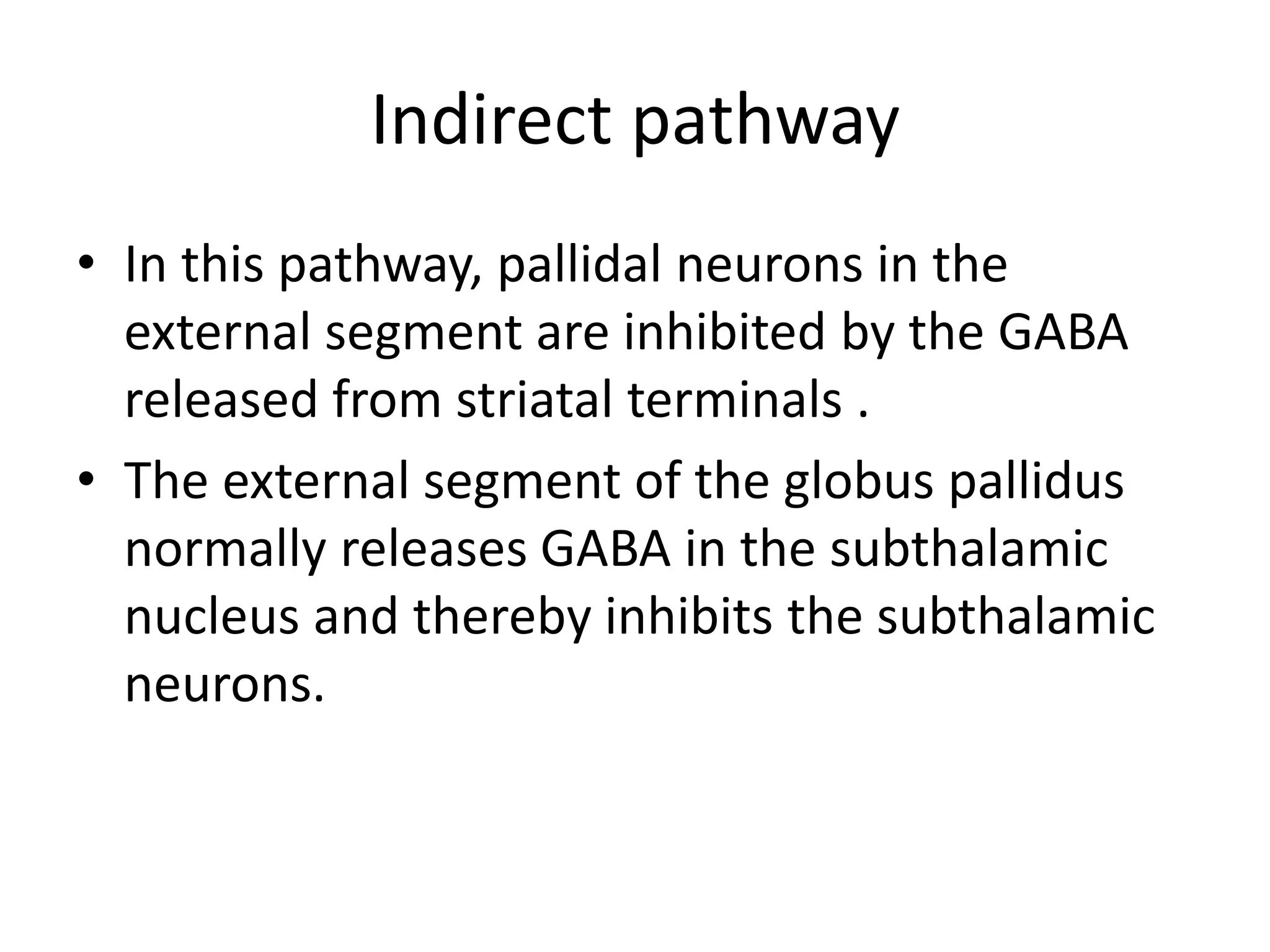
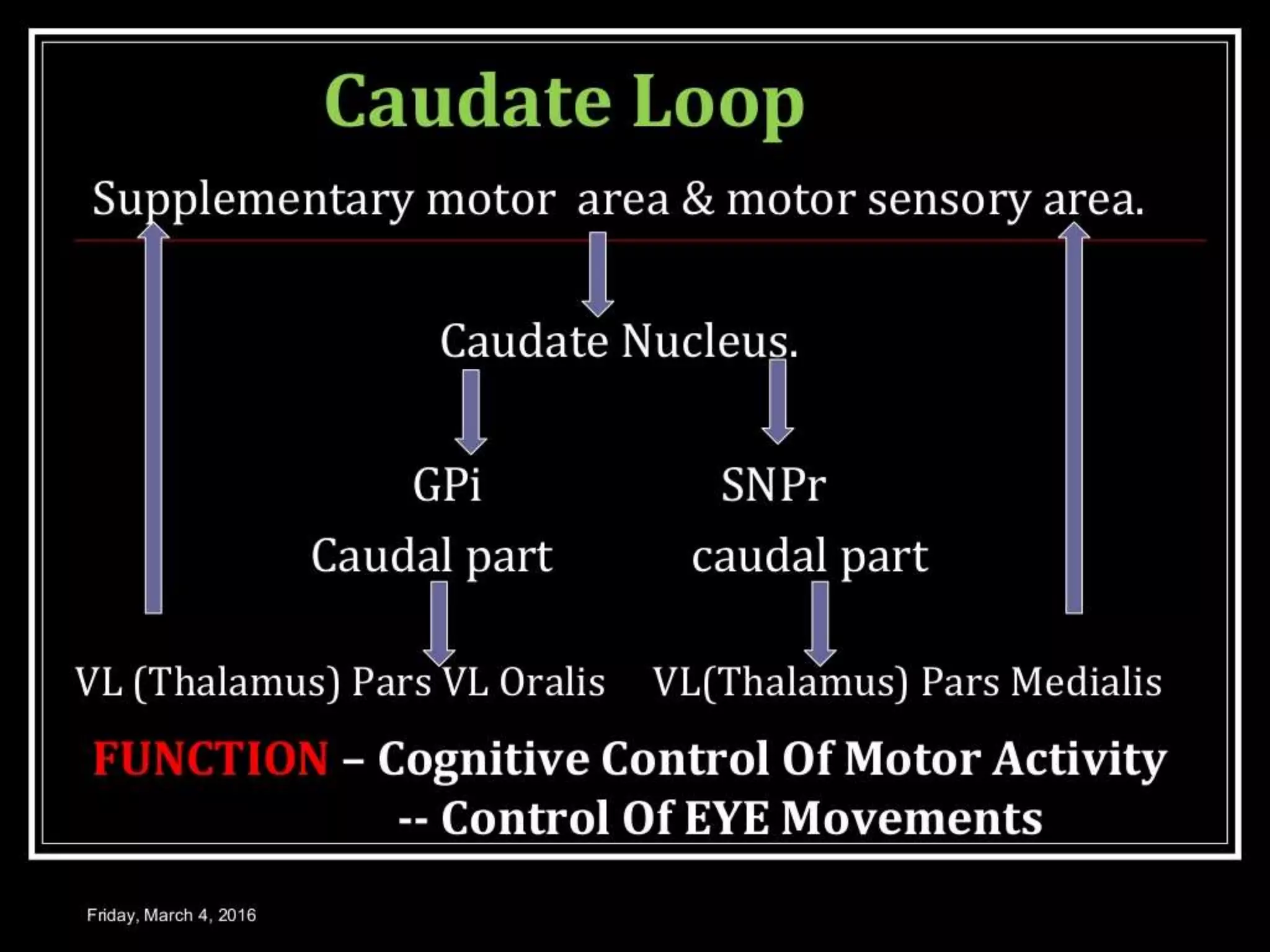
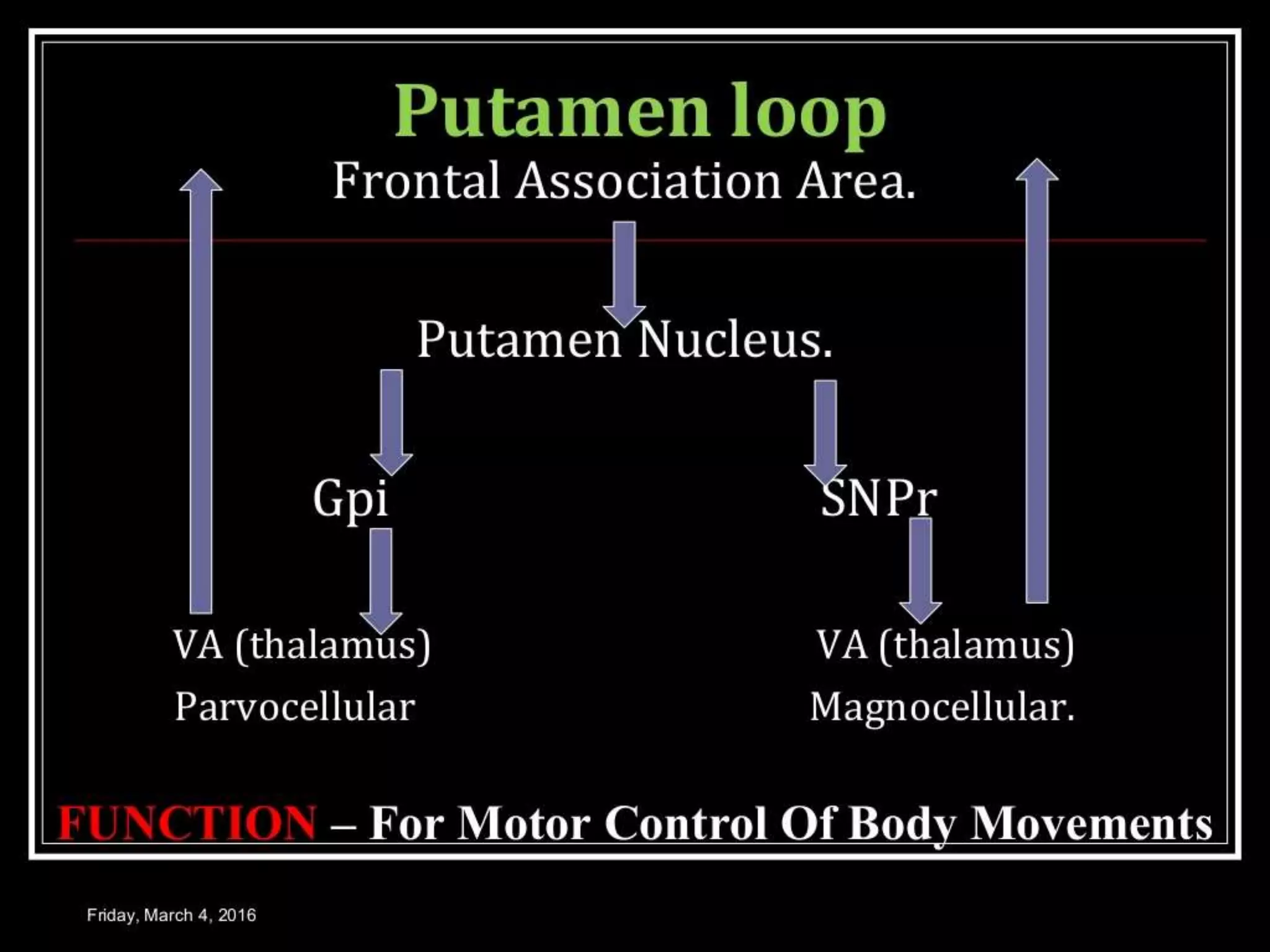
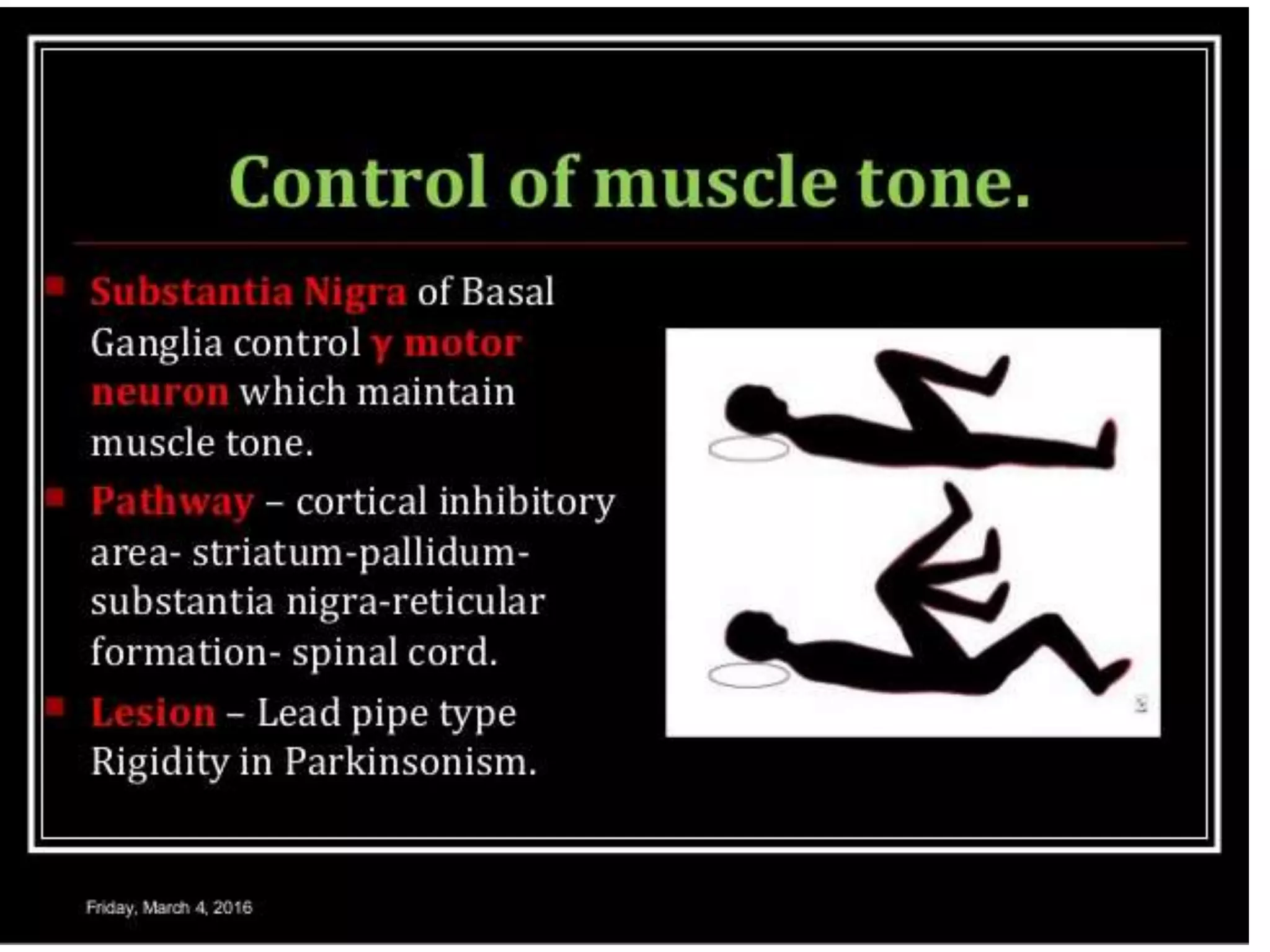
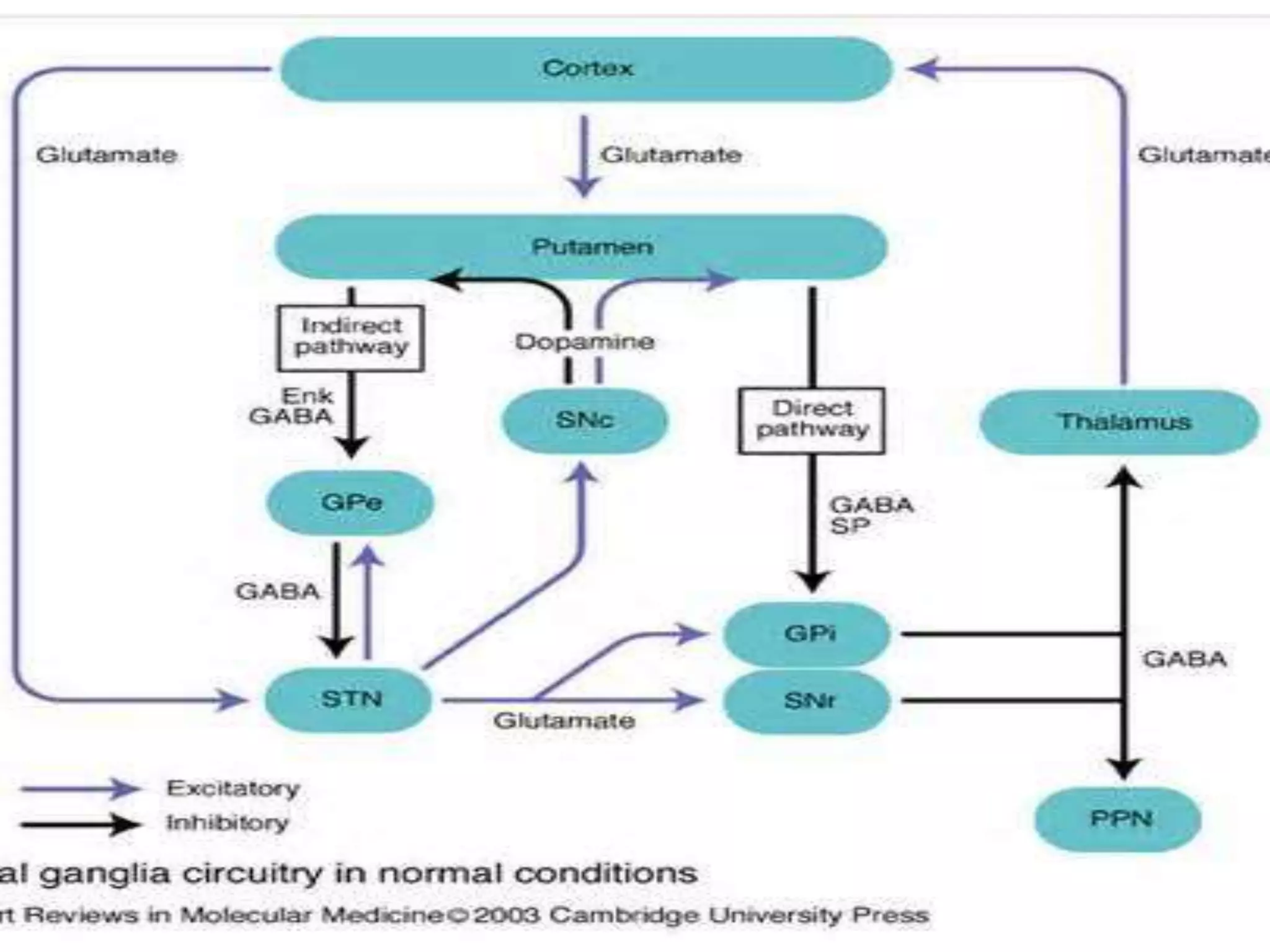
The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei that include the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus. They help translate ideas for movement into neural programs and provide feedback to correct movements. The basal ganglia have direct and indirect pathways that respectively decrease and increase inhibition of thalamic neurons. Diseases like Parkinson's and Huntington's result from basal ganglia dysfunction and cause hyperkinetic or hypokinetic movement abnormalities due to imbalances in dopaminergic, cholinergic, and GABAergic signaling.