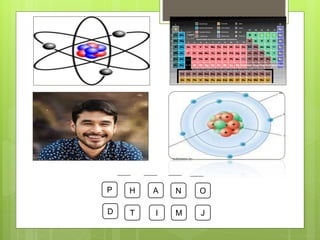
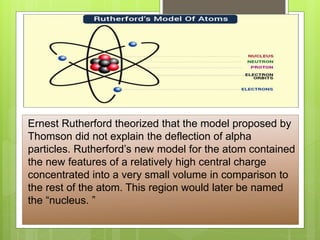
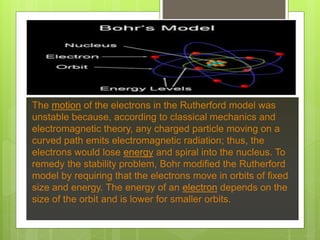
J.J. Thomson proposed the plum pudding model of the atom in 1904 to account for the electron. This model depicted the atom as electrons surrounded by a uniform positively charged background, like plums in pudding. However, Rutherford's experiments in 1911 showed that Thomson's model was incorrect and most of an atom's mass and positive charge must be concentrated in a small nucleus. In 1913, Bohr proposed his quantized shell model to explain the stability of electron orbits, which required that electrons orbit in fixed shells of discrete energy levels.