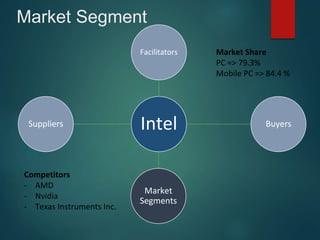
Intel dominates the microprocessor market, holding 79.3% of the PC market and 84.4% of the mobile PC market. Its product mix includes processors for mobile devices, networking products, chipsets, and server products. Intel has established market dominance through innovative new products like the 4004, 8086, 80286 and 80386 processors and strategic marketing campaigns like "Intel Inside" that associated Intel with top computer brands. While once pursuing a sole-source strategy, AMD and others now compete through products like the Athlon. Intel's success comes through balancing technological leadership with responses to economic, ecological, technological and other macro-environmental factors.