Embed presentation
Downloaded 39 times

![ Model: Is creating classes and writing the
business logic and can be connected to a
database.
View: Is the design [UI: User Interface].
Controller: Helps to communicate between
model from view.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-2-2048.jpg)
![ When we run the program , by default it
invokes Index method.
The Index method then invokes the
corresponding View.
Every View has the extension as .cshtml
[Combination of C# and HTML code].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-4-2048.jpg)

![ ViewData: Is used to store data as a key-value
pair. It stores a single data at a time.
Syntax:
ViewData["key"]=value;
where key is a unique name. It is user-
defined.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-6-2048.jpg)

![ The syntax used in view page is a
combination of C# code and HTML code is
called as Razor Syntax. ie: [C#,HTML ] or
[VB,HTML].
Extension of the file is .cshtml or .vbhtml.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-8-2048.jpg)




The document discusses the MVC framework, describing the model, view, and controller components. The model handles business logic and data access, the view handles the user interface, and the controller coordinates communication between the model and view. It also covers how data is passed between these components, the use of ViewData and ViewBag to store data, Razor syntax for combining C# and HTML in views, and how to create and call partial views.

![ Model: Is creating classes and writing the
business logic and can be connected to a
database.
View: Is the design [UI: User Interface].
Controller: Helps to communicate between
model from view.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-2-2048.jpg)

![ When we run the program , by default it
invokes Index method.
The Index method then invokes the
corresponding View.
Every View has the extension as .cshtml
[Combination of C# and HTML code].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-4-2048.jpg)

![ ViewData: Is used to store data as a key-value
pair. It stores a single data at a time.
Syntax:
ViewData["key"]=value;
where key is a unique name. It is user-
defined.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-6-2048.jpg)

![ The syntax used in view page is a
combination of C# code and HTML code is
called as Razor Syntax. ie: [C#,HTML ] or
[VB,HTML].
Extension of the file is .cshtml or .vbhtml.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-151126183717-lva1-app6892/75/ASP-NET-MVC-8-2048.jpg)




Presentation introduction by the author.
Explains the Model-View-Controller components: Model for business logic, View for UI design, and Controller for data communication.
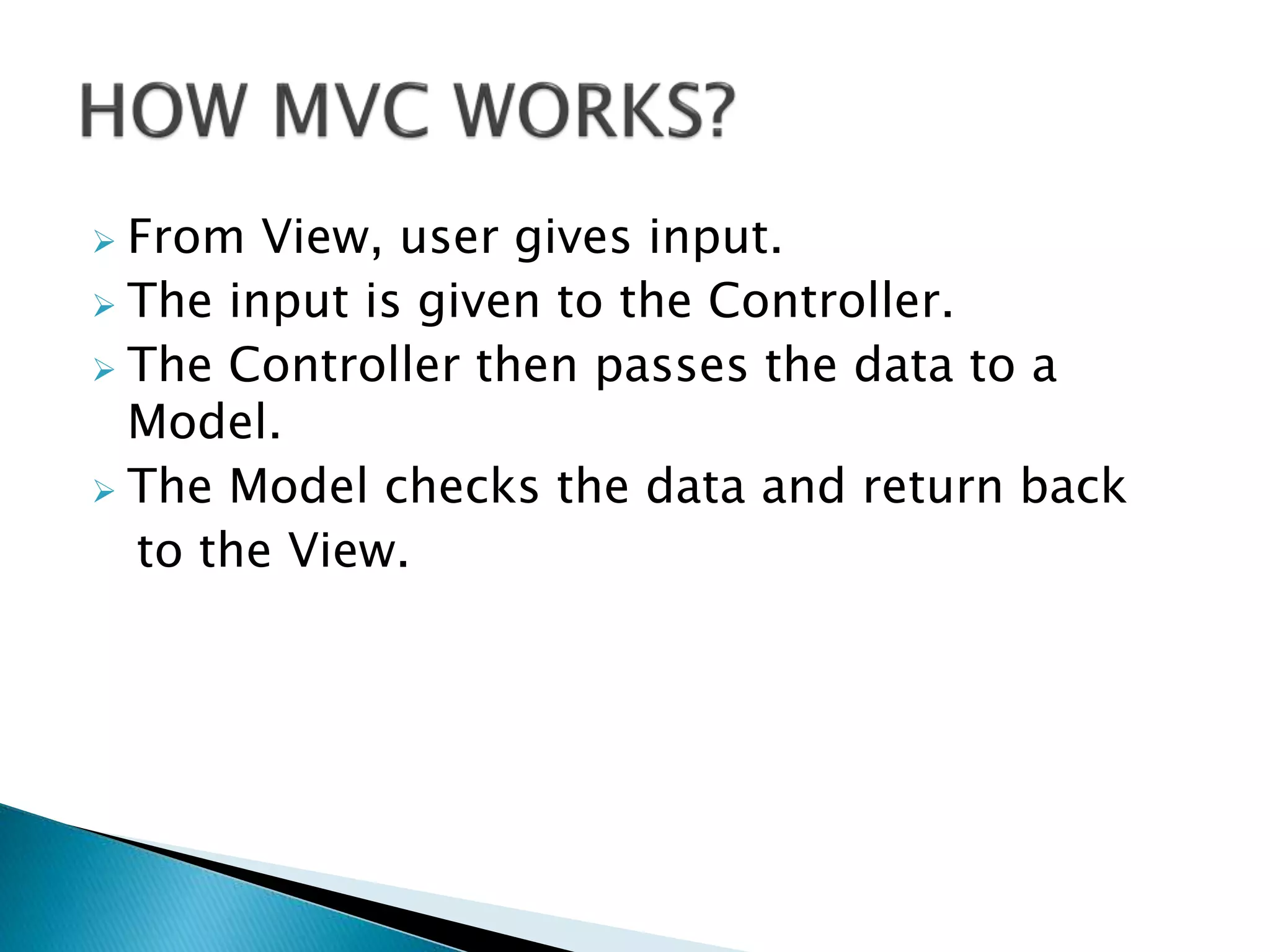
Describes the flow of data from View to Controller, and from Controller to Model, then back to View.
Details the program execution process, starting with Index method that calls the corresponding .cshtml View.
Indicates that every action method must link to a View, defaulting to matching names or using return view() if different.
Explains ViewData for one-time key-value pair data storage in MVC with provided syntax.
Details ViewBag for storing data with names, allowing multiple data storage with syntax.
Introduces Razor Syntax combining C# and HTML for views, file extensions are .cshtml or .vbhtml.
Specifications for using C# code in views: using @ character, case-sensitivity, string notation, and variable declaration.
Defines Partial Views for reusable code segments within shared folders, naming convention starts with '_'.
Instructions on creating Partial Views and how to call them in actual views using @Html.Partial.
Ends the presentation with a 'Thank You' note.