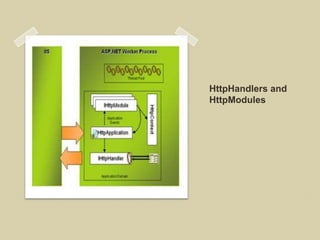
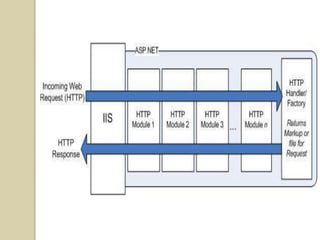
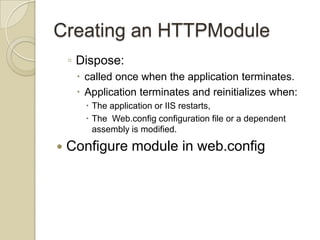
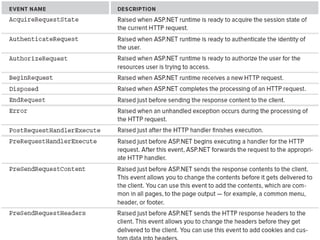
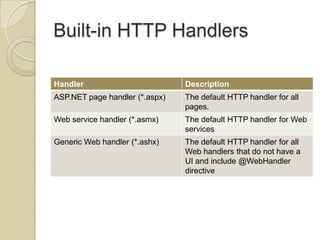
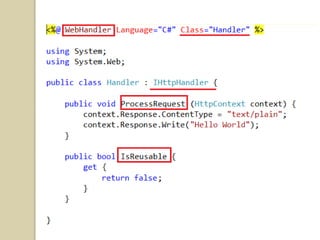
This document discusses ASP.NET handlers and modules. HttpModules are classes that plug into the request processing pipeline and respond to application events. They can store global state between requests and implement cross-cutting functionality. HttpHandlers process incoming HTTP requests and are mapped to file extensions. Common handlers include ASP.NET pages, web services, and generic handlers. The document demonstrates how to create custom HttpModules and HttpHandlers, and discusses deployment options such as publishing to local IIS.






















![REFERENCES
[1] Beginning ASP.NET 4 In C# 2010, Matthew
Macdonald, Apress
[2] Web Application Architecture
Principles, Protocols And Practices, Leon Shklar
And Richard Rosen, Wiley
[3] Professional AS P.NE T 4 In C# And VB, Bill
Evjen, Scott Hanselman And Devin Rader, Wiley
[4] Pro ASP.NET In C# 2010, Fourth
Edition,matthew Macdonald, Adam Freeman, And
Mario Szpuszta, Apress](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-net-lect8-130212121501-phpapp02/85/ASP-NET-lecture-8-32-320.jpg)