This document outlines topics covered in a lecture on object oriented JavaScript using the Prototype framework, including:
- Revision of object oriented JavaScript concepts like objects, prototypes, and classes
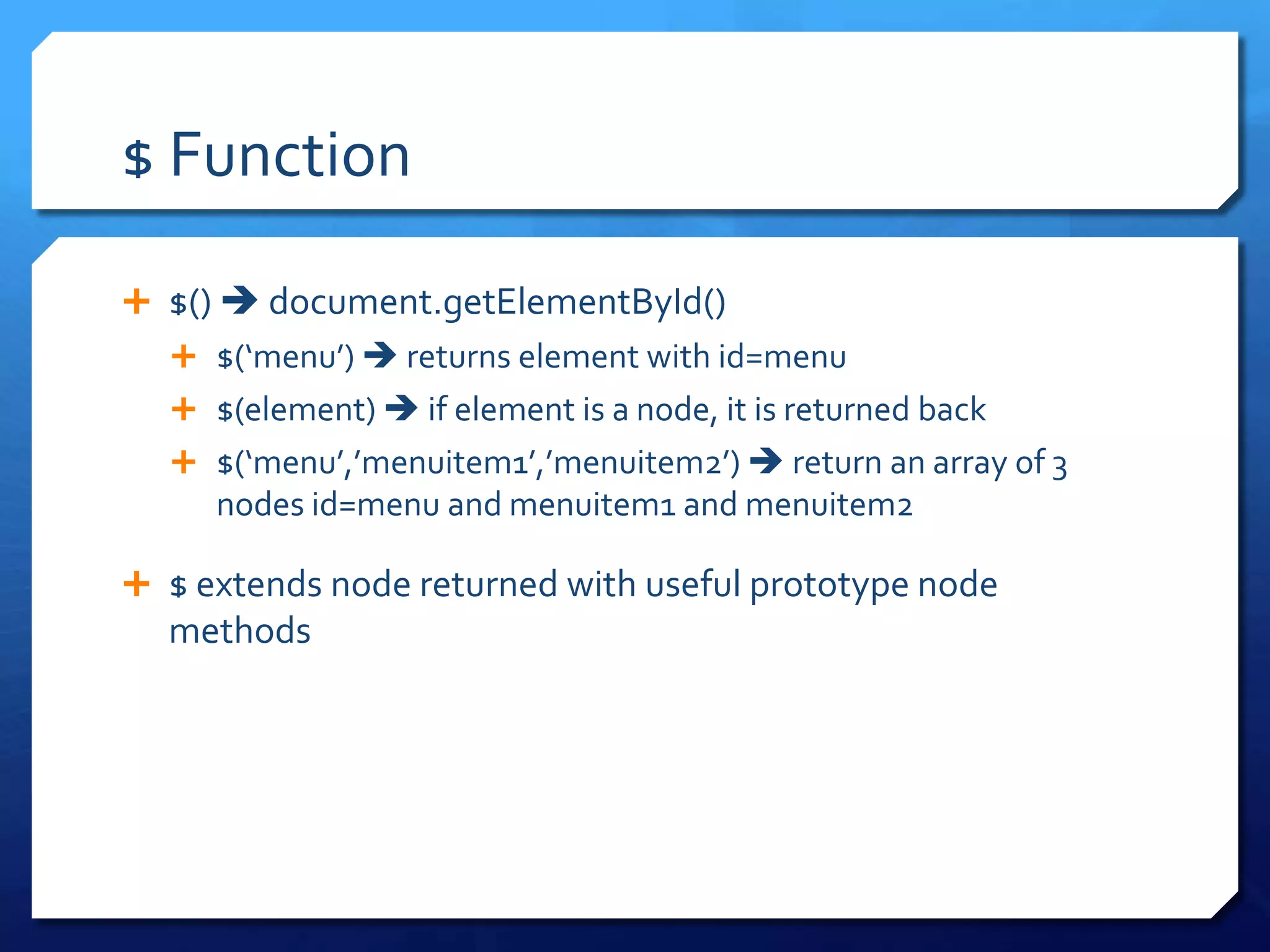
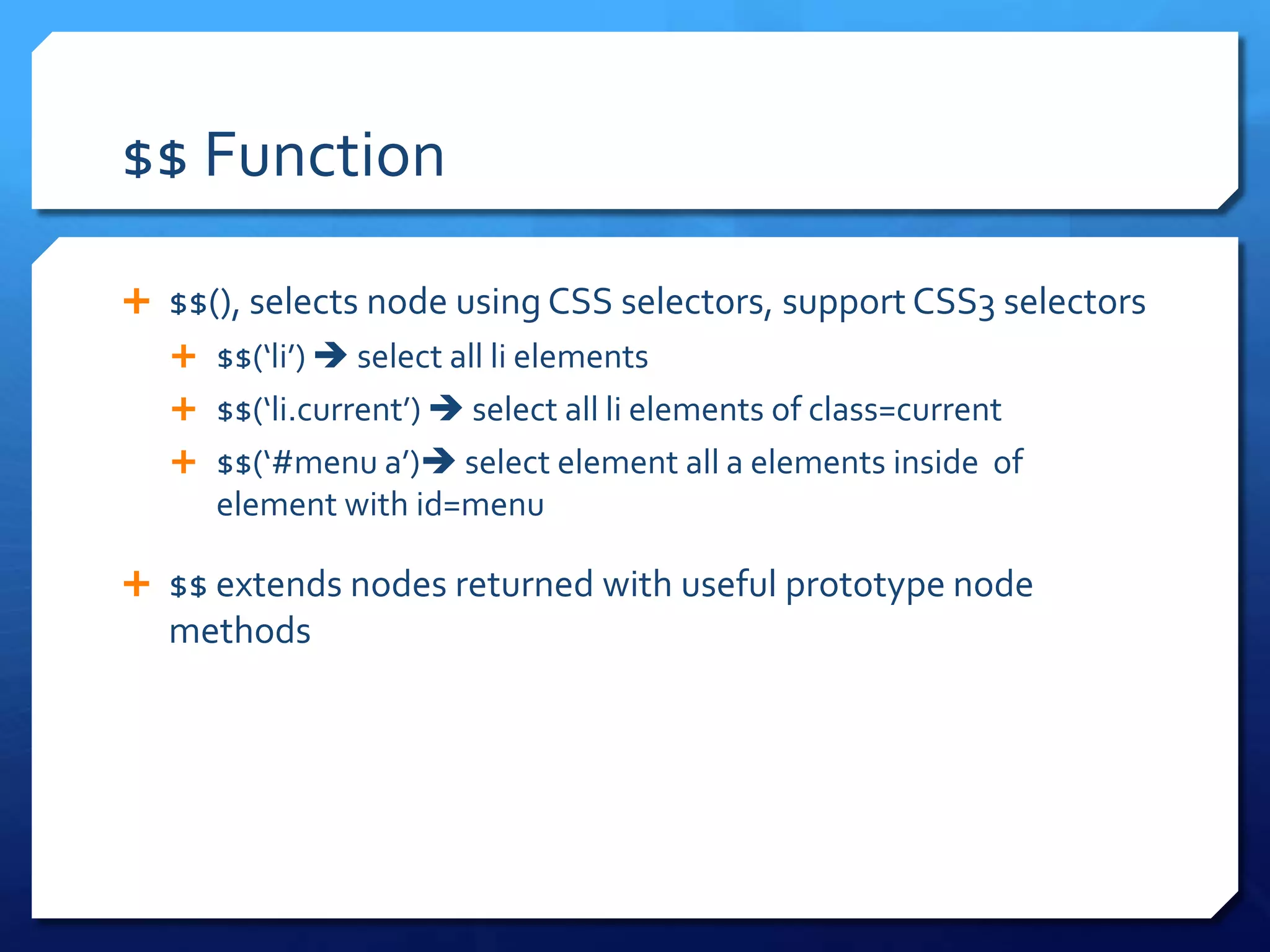
- Prototype framework utilities like $, $$ and Enumerable
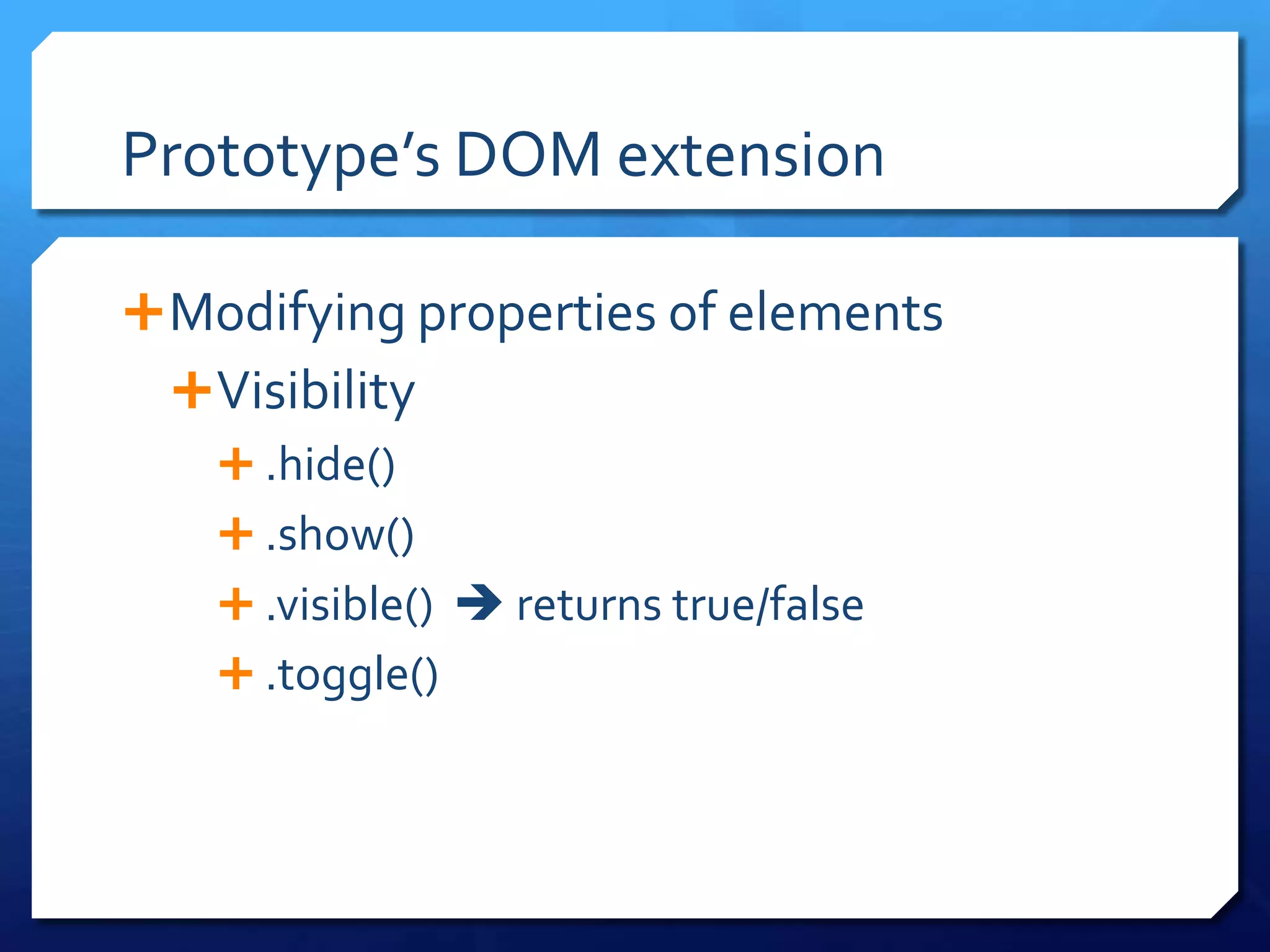
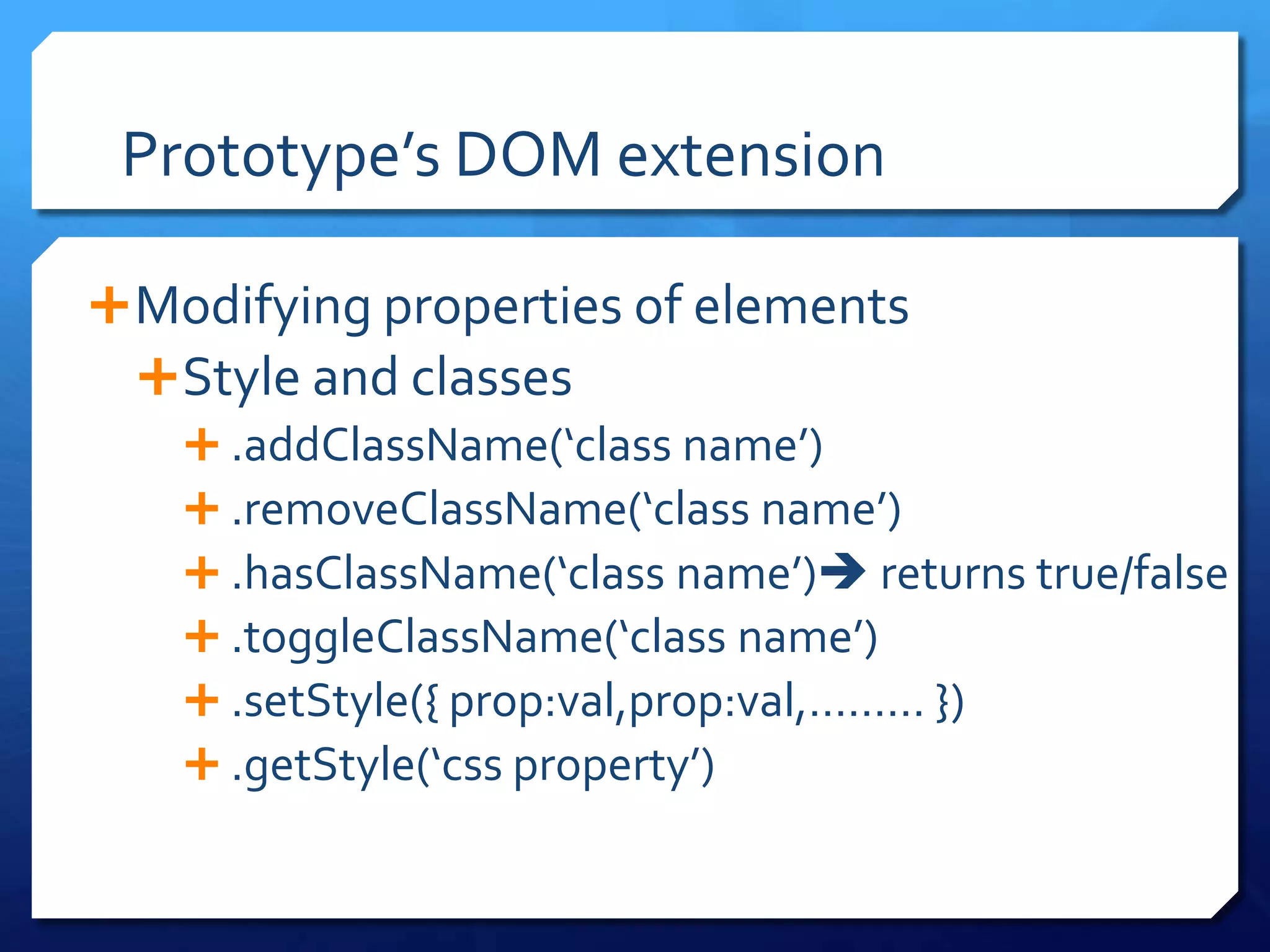
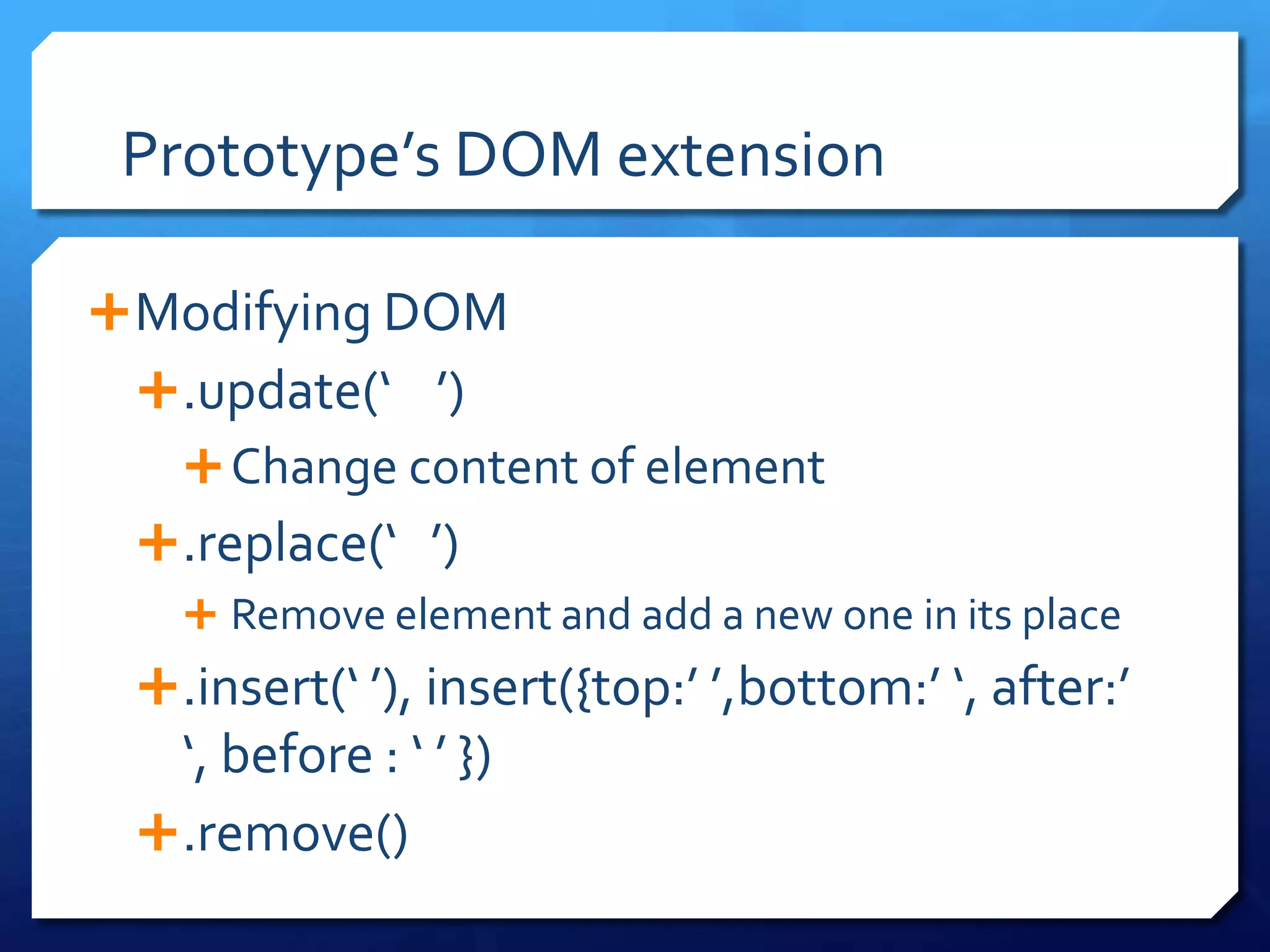
- Extending DOM elements using Prototype methods
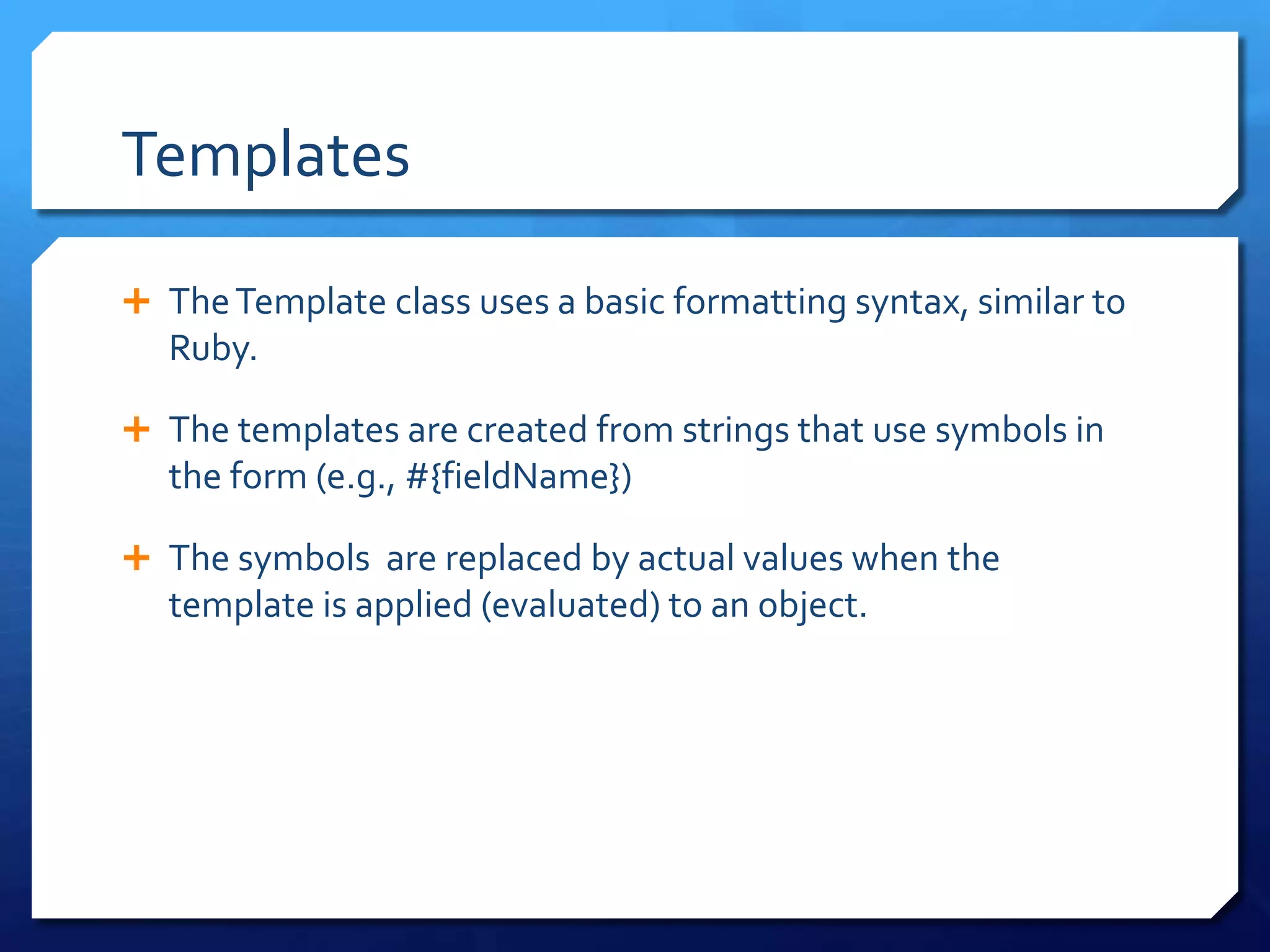
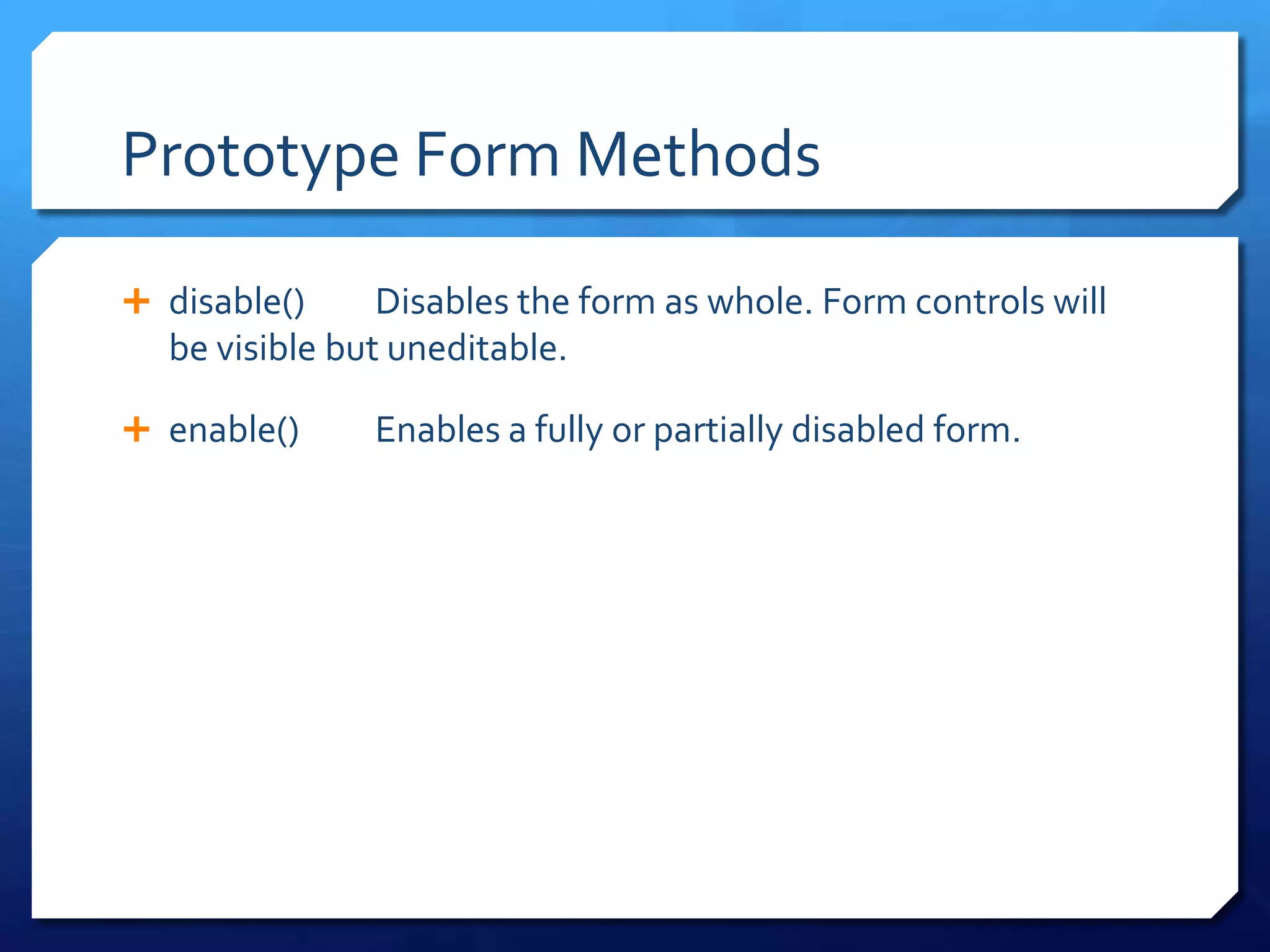
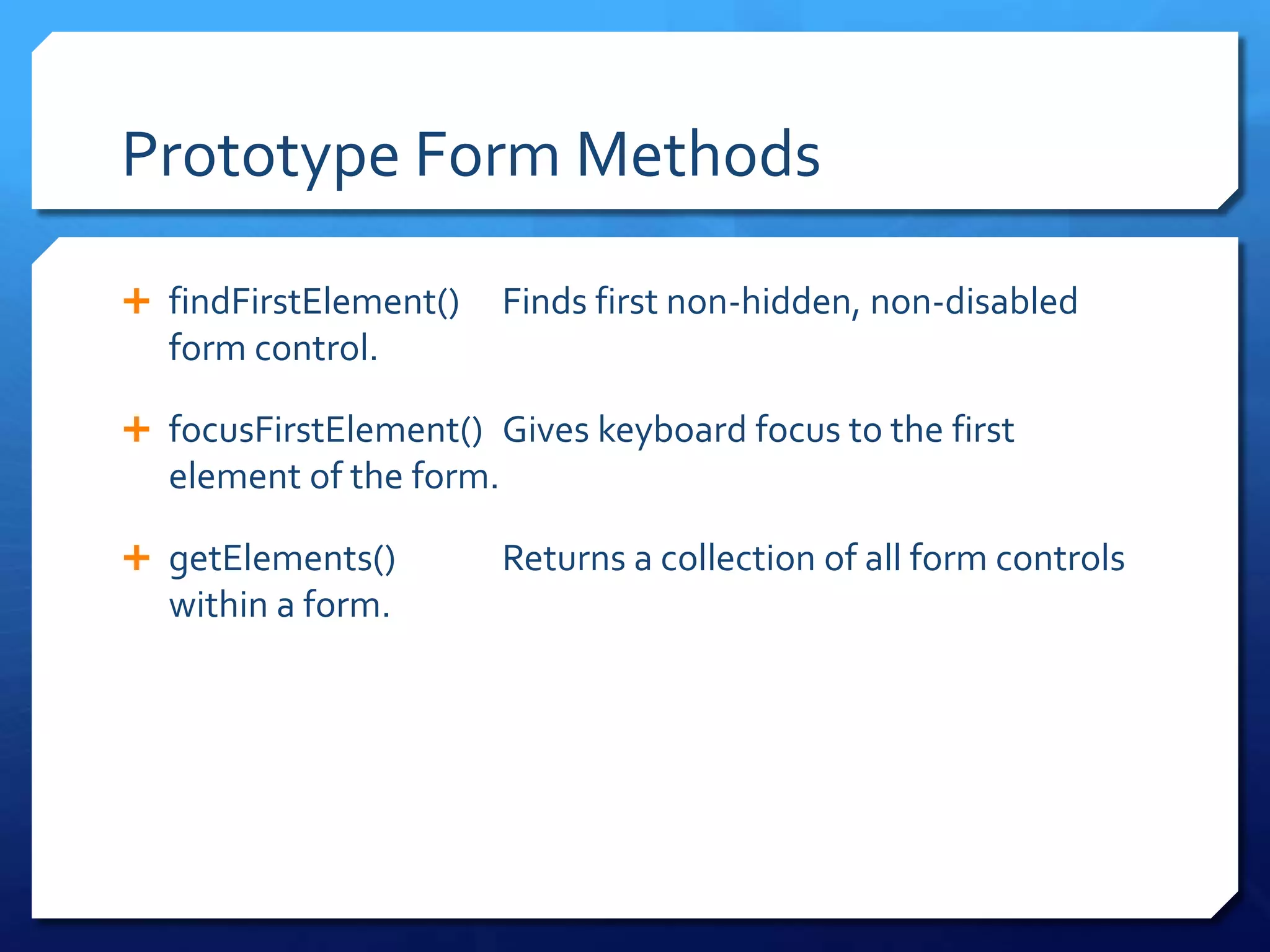
- Templates, form management, and getting element dimensions
- Event handling and classes/inheritance in Prototype
- JSON encoding/parsing
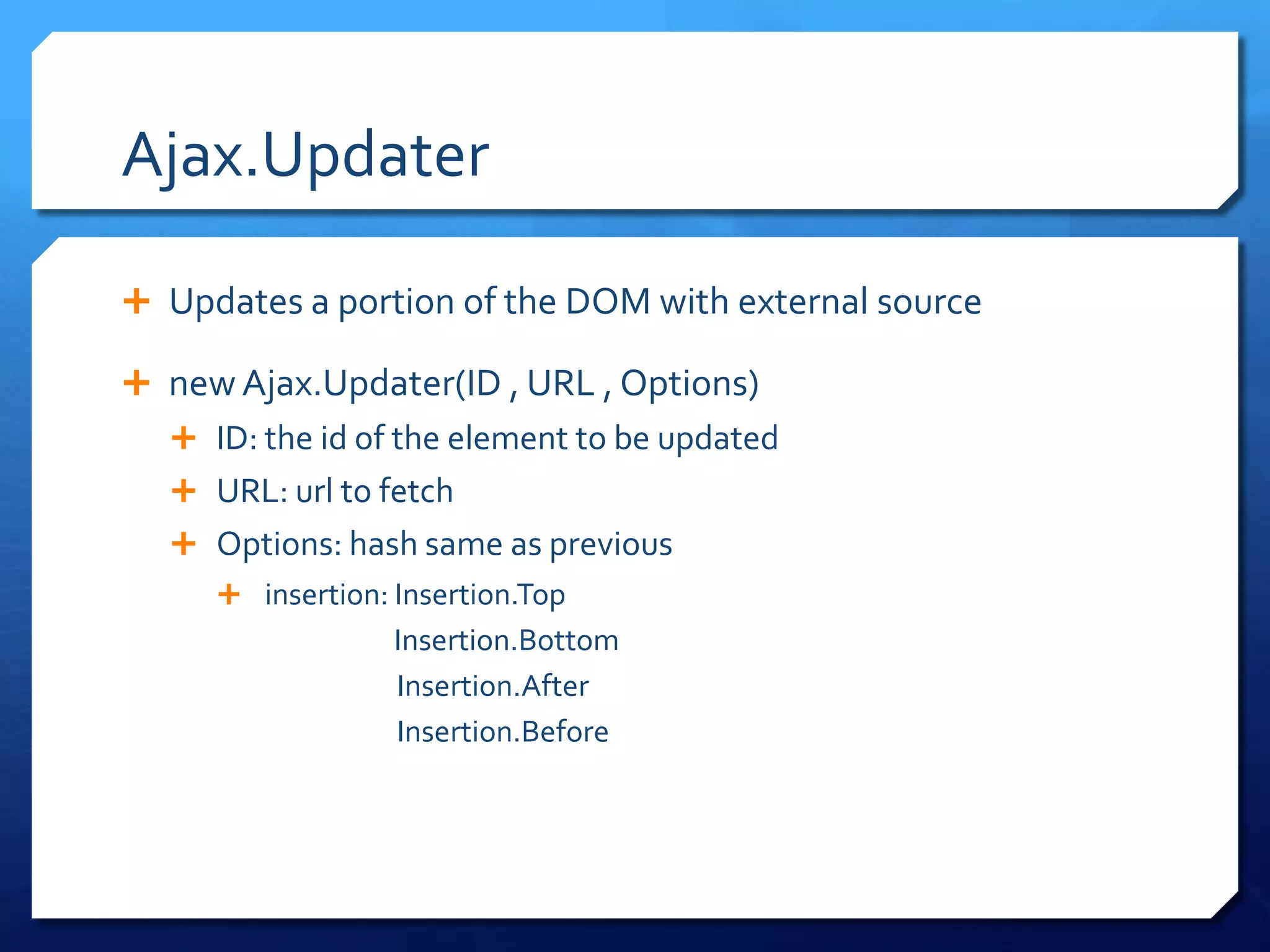
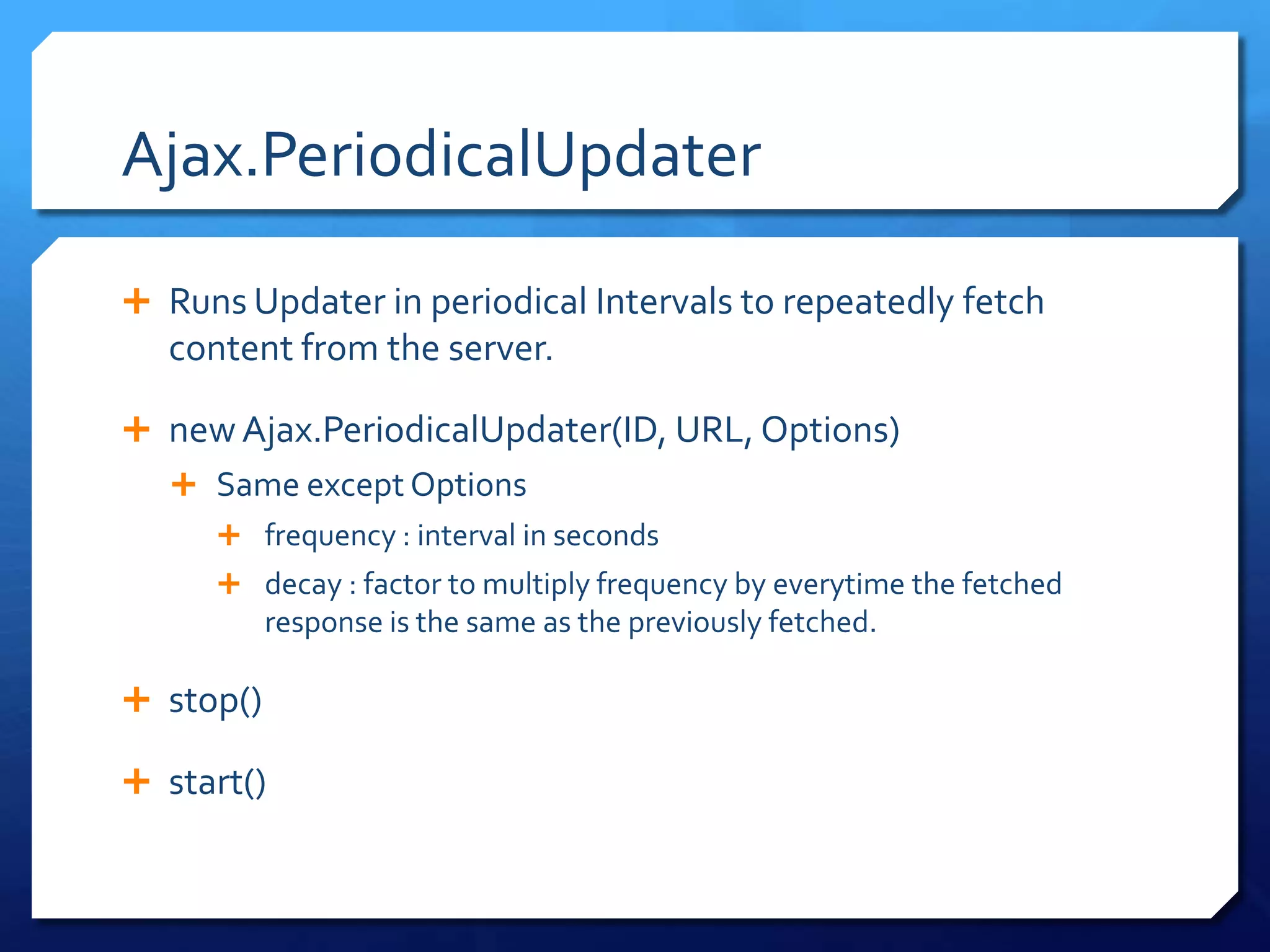
- Ajax utilities like Ajax.Request and Ajax.Updater







![each
elem.each(Visitor object)
Implements visitor on each element
Example:
[1,3,4,7,89,6,3,4,5].each(function(elem)
{
alert(elem);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prototype-130424095133-phpapp01/75/Prototype-Framework-12-2048.jpg)
![each
Implement continue using return
Example:
[1,3,4,7,89,6,3,4,5].each(function(elem)
{
if(elem>10)
return;
alert(elem);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prototype-130424095133-phpapp01/75/Prototype-Framework-13-2048.jpg)
![each
Implement break by throw $break
Example:
[1,3,4,7,89,6,3,4,5].each(function(elem)
{
if(elem>10)
return;
if(elem==4)
throw $break;
alert(elem);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prototype-130424095133-phpapp01/75/Prototype-Framework-14-2048.jpg)
![detect
Takes function that returns true/false
Returns first element that returns true
If no match returns undefined
Examples:
[1,3,4,6,8,0,9].detect(function(elem)
{
return elem==0
}));
See also select, reject, partition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prototype-130424095133-phpapp01/75/Prototype-Framework-15-2048.jpg)
![map
Applies function on each element, pushes the
return into an array that is eventually returned
Example:
[2, 5, 7, 9,50].map(function(item)
{
return item*item;
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prototype-130424095133-phpapp01/75/Prototype-Framework-16-2048.jpg)



![Example
var records = [record1, record2, record3, record4 ];
// Now apply template to produce desired formatted output
records.each( function(conv)
{
$$('p')[0].insert( {bottom: "<div>Formatted Output : " +
myTemplate.evaluate(conv)+"</div>" });
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prototype-130424095133-phpapp01/75/Prototype-Framework-24-2048.jpg)









![Class.create([superclass][, methods...])
superclass (class): superclass to inherit from.
method (object): an object (mix-in) that will be mixed-in to my
new class. Multiple mixins can be used, later mixins take
precedence.
returns a constructor function that can be called using new
operator. It will invoke the initialize method.
The object mixin must contain ‘initialize’ method to be called
when new is called.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prototype-130424095133-phpapp01/75/Prototype-Framework-38-2048.jpg)