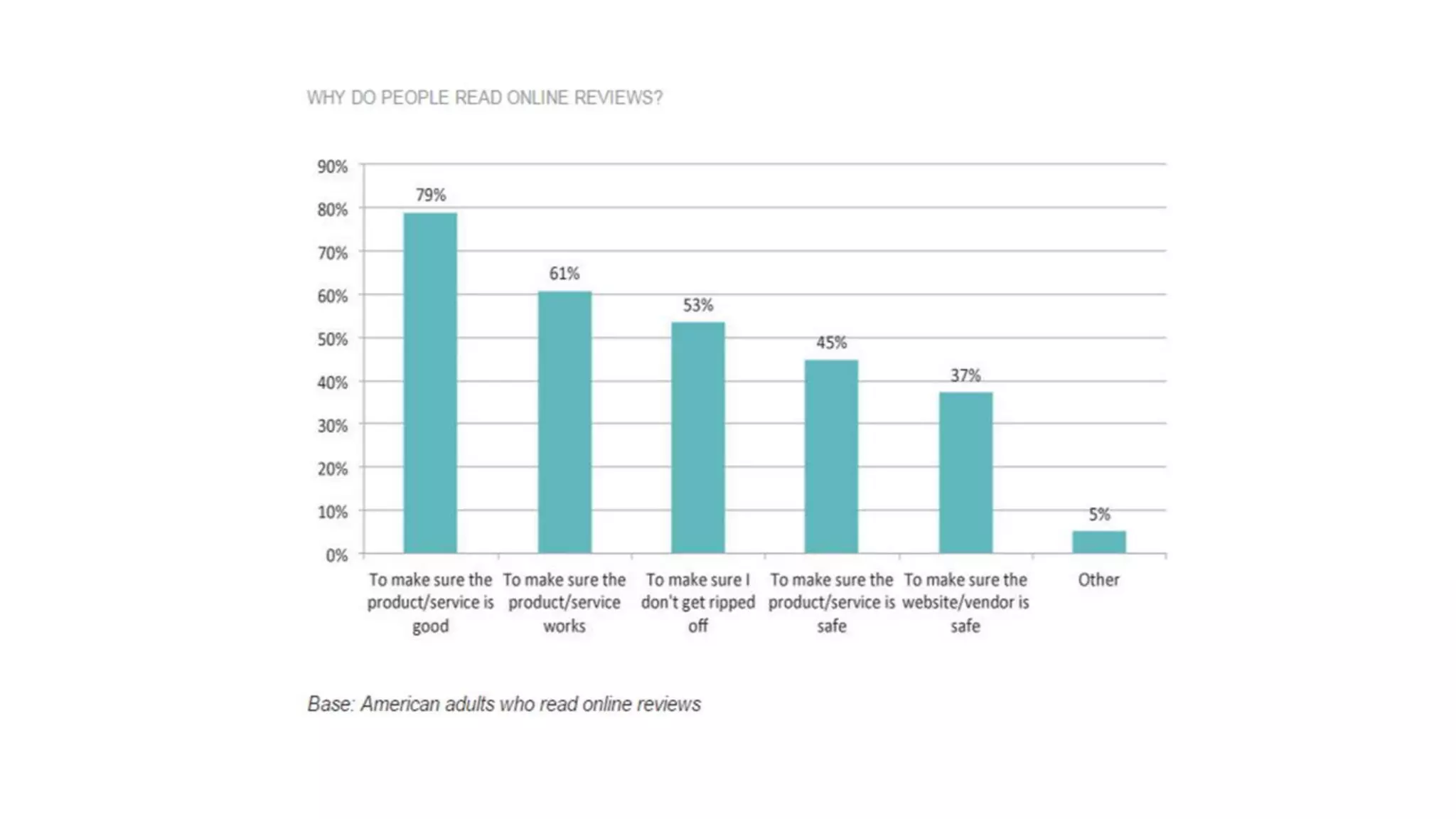
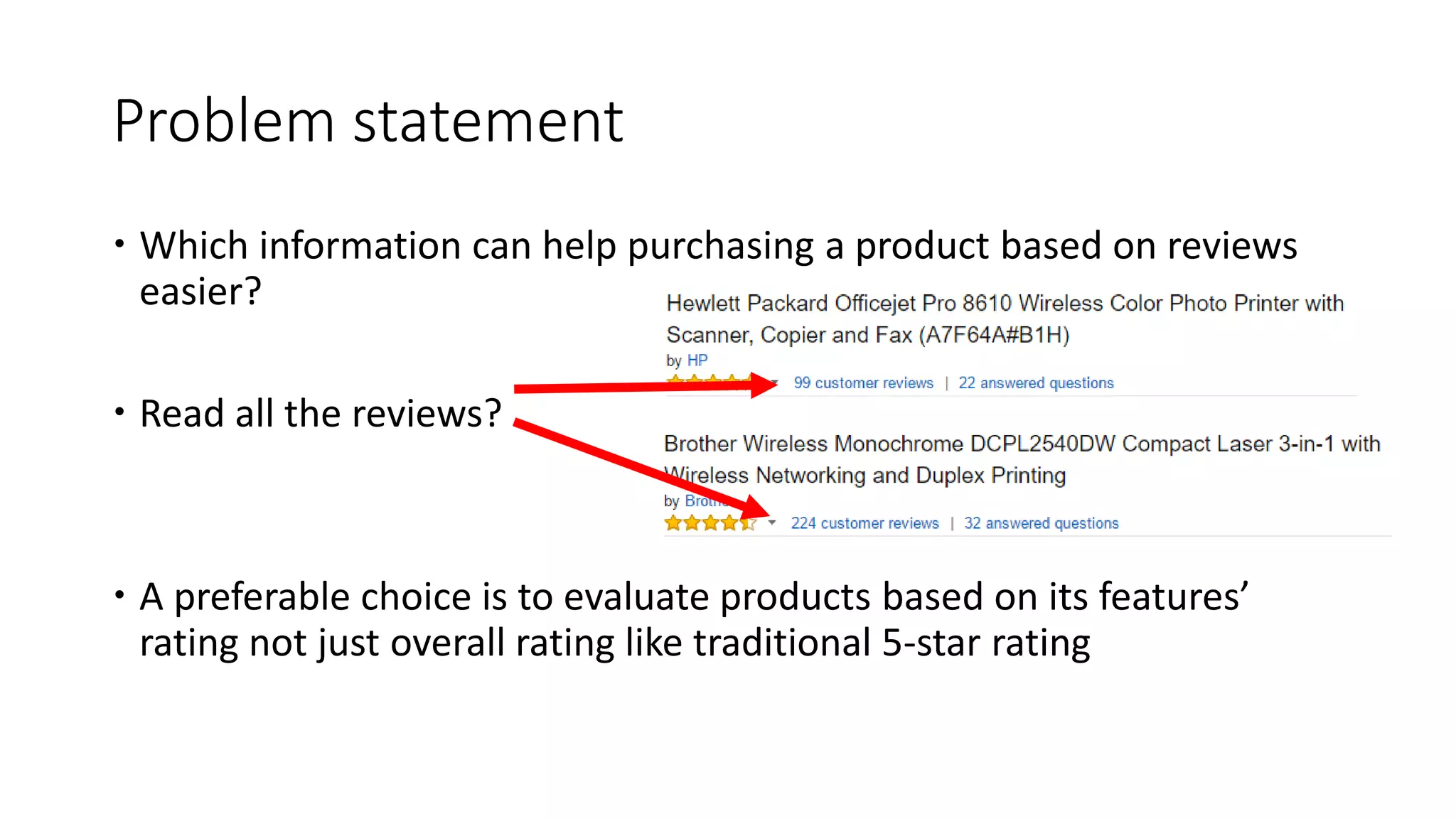
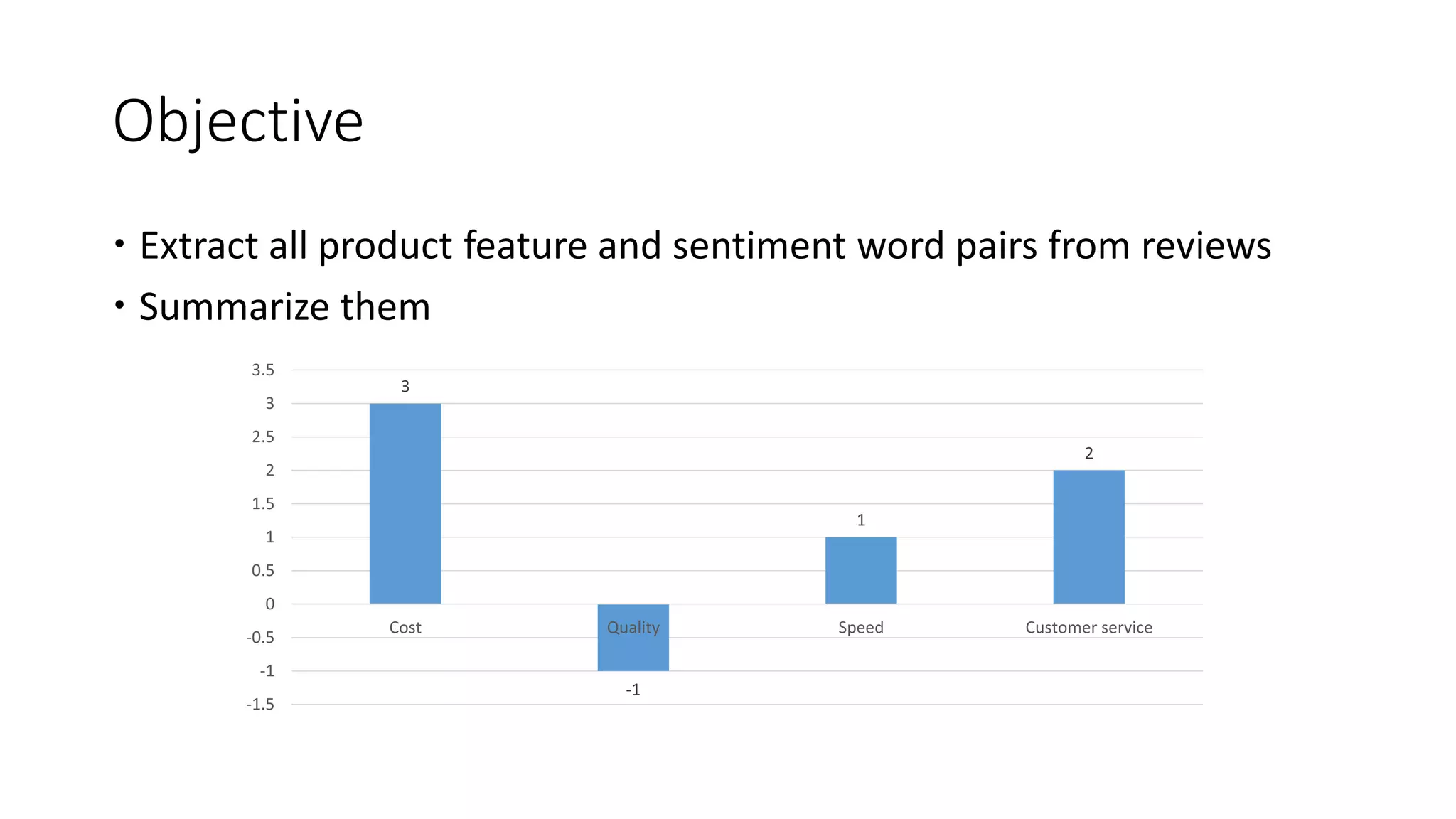
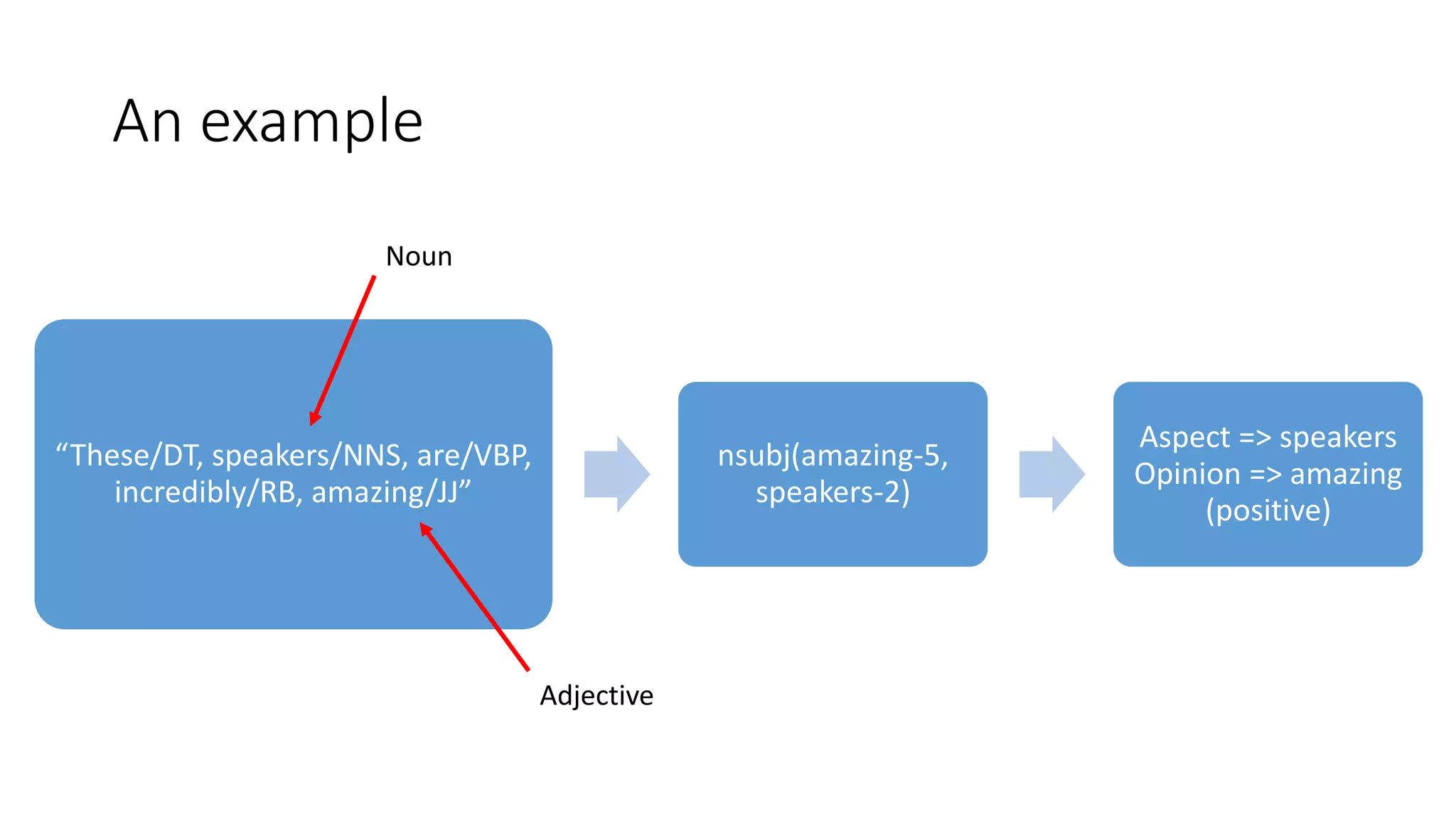
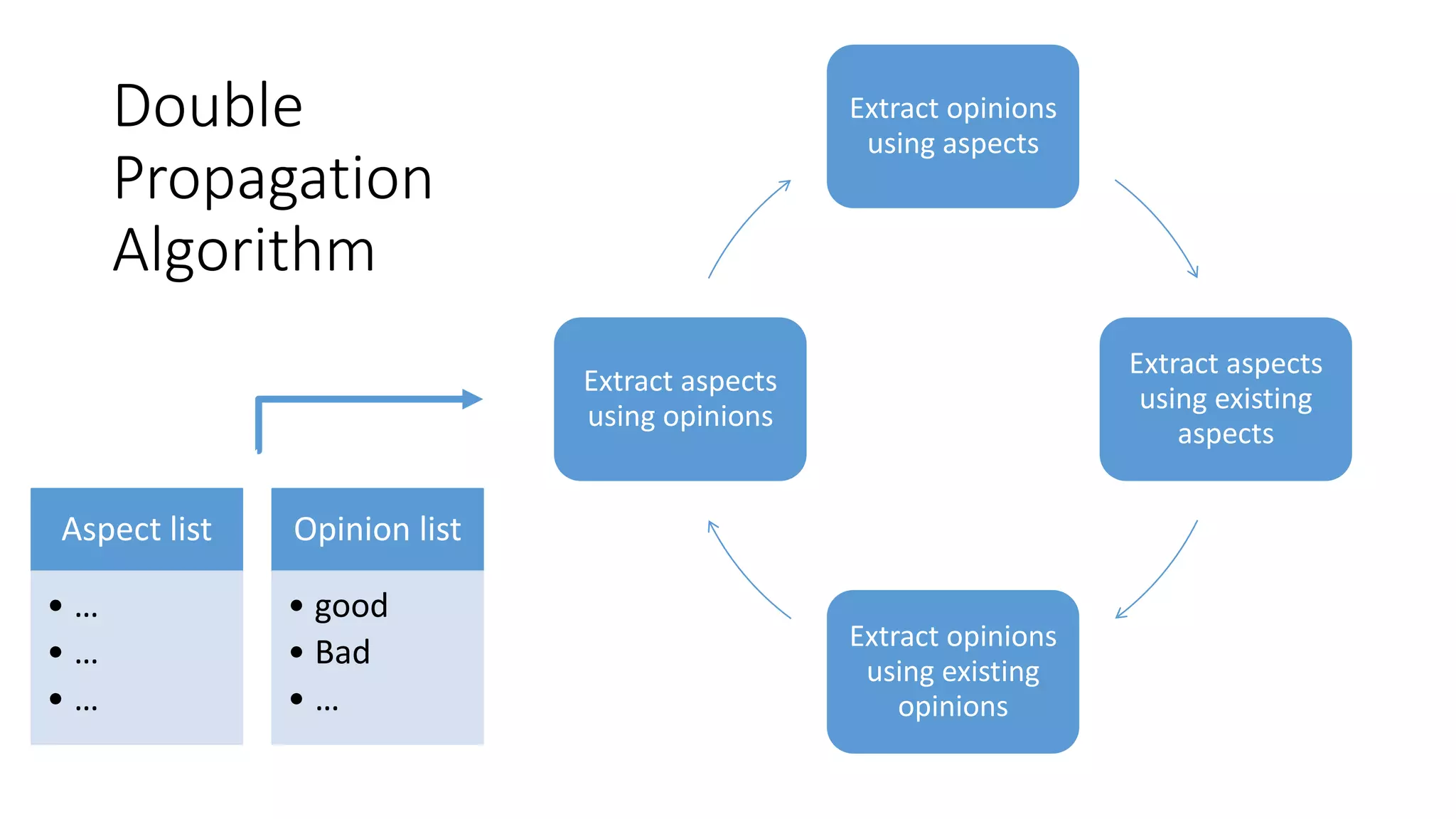
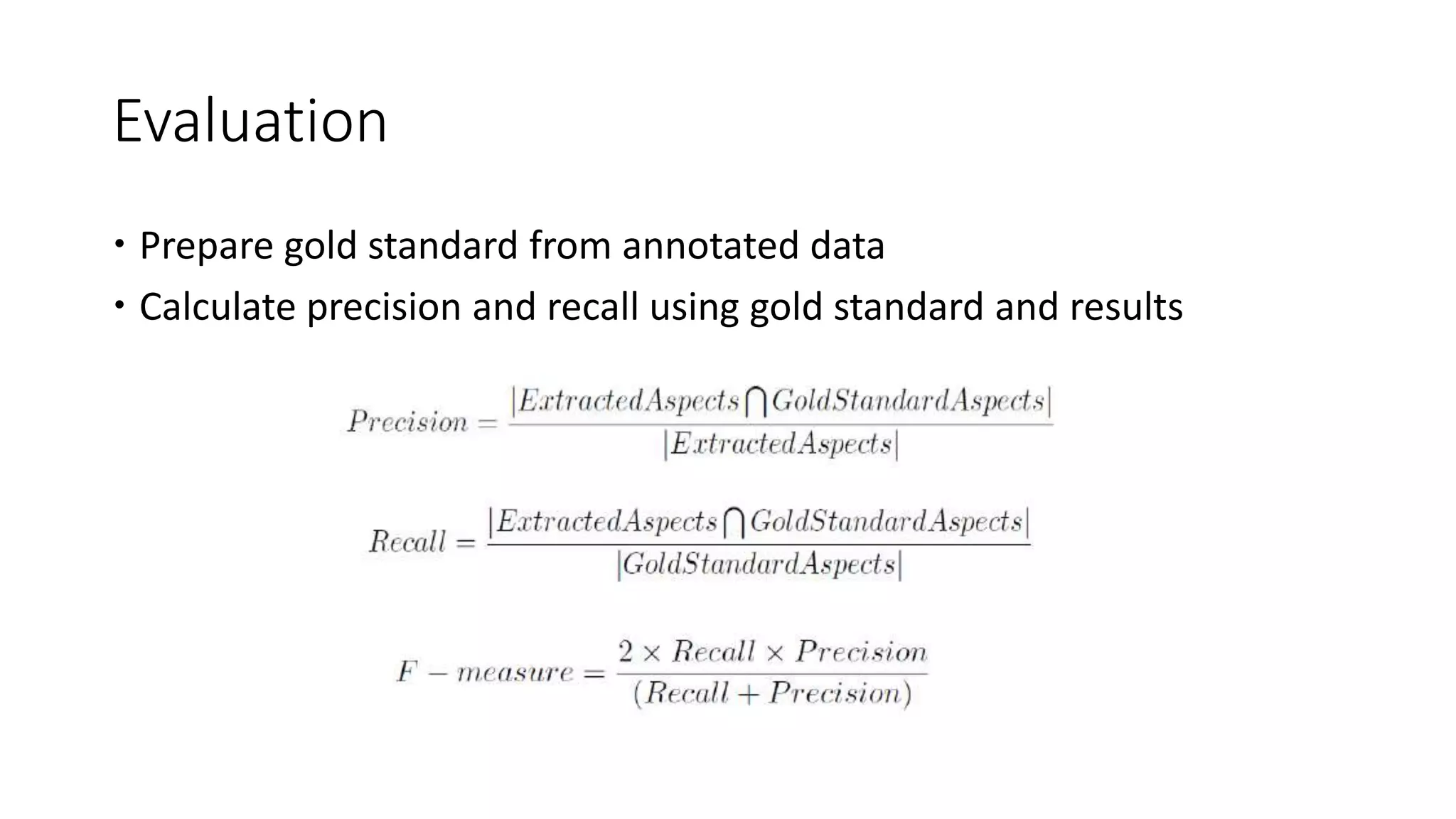
The document discusses Hardik Dalal's research on aspect-level sentiment analysis of customer reviews, used to extract product feature and sentiment word pairs. It highlights the importance of customer reviews in purchasing decisions and details methods such as the double propagation algorithm for analyzing sentiments based on grammatical relations. The work concludes with the effectiveness of the proposed approach and its potential applications in text mining.










![References
Liu, Q., Liu, B., (2015). Annotated: More Customer Review Datasets (3
products) [Dataset]. Retrieved from
www.cs.uic.edu/~liub/FBS/CustomerReviews-3-domains.rar.
Garcıa-Pablos, A., Cuadros, M., Gaines, S., & Rigau, G. (2014). V3:
Unsupervised Generation of Domain Aspect Terms for Aspect Based
Sentiment Analysis. In SemEval 2014, 833.
SentiWordNet, from http://sentiwordnet.isti.cnr.it/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-copy-160609032841/75/Aspect-level-sentiment-analysis-of-customer-reviews-using-Double-Propagation-17-2048.jpg)
