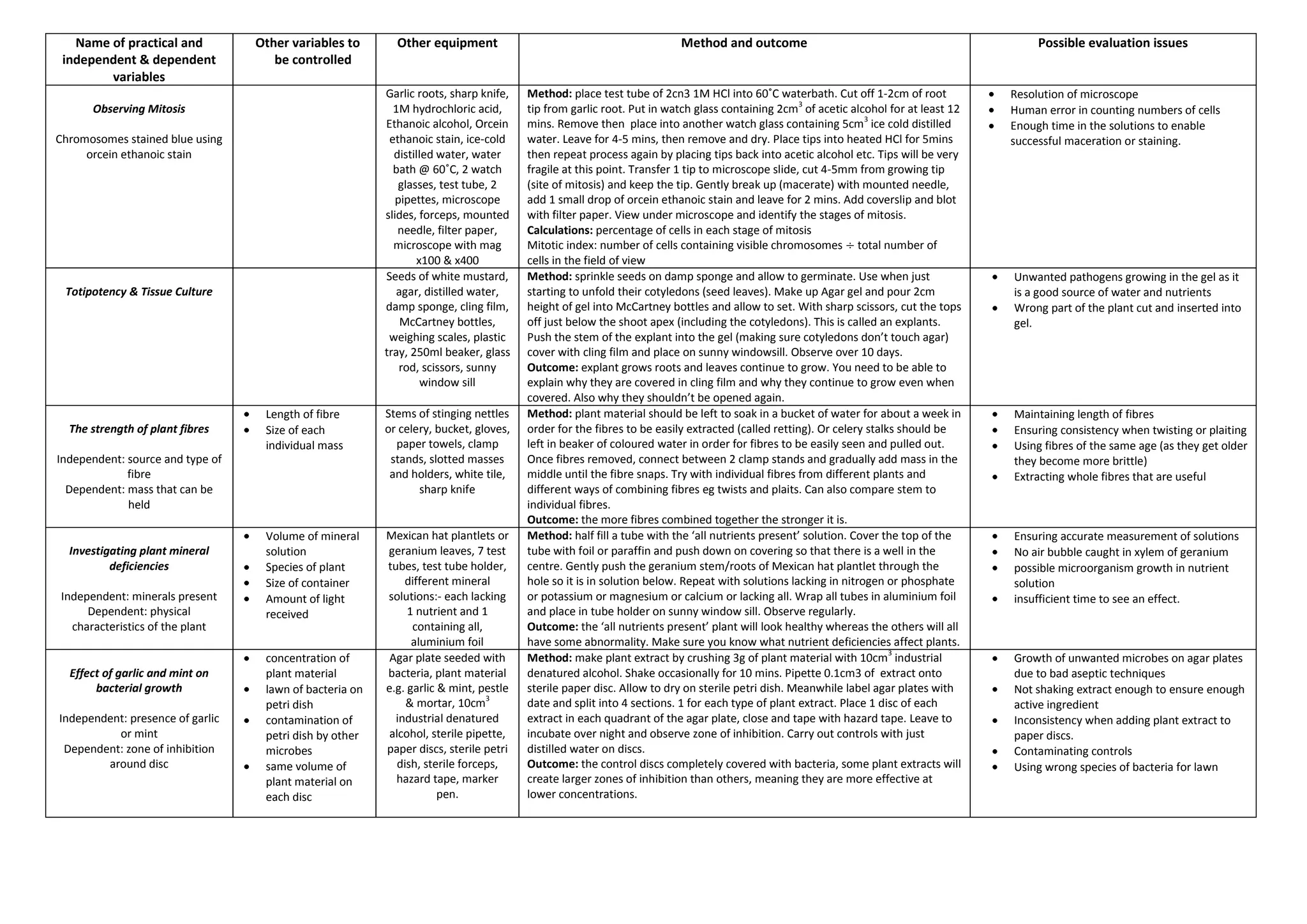
This document summarizes several biology practical experiments:
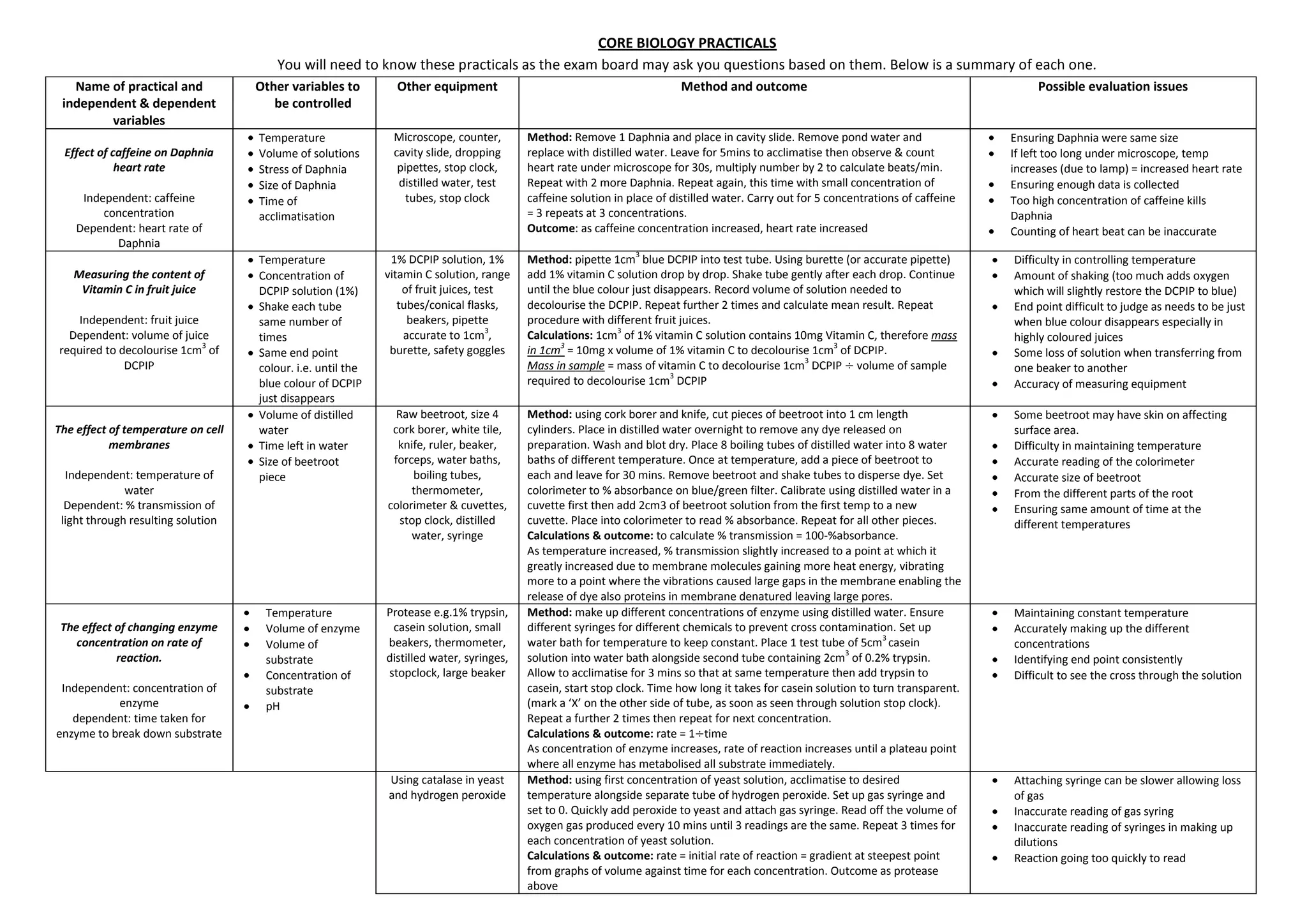
1. It describes an experiment measuring the effect of caffeine concentration on the heart rate of Daphnia, with caffeine concentration as the independent variable and heart rate as the dependent variable.
2. A experiment is outlined to measure the vitamin C content of different fruit juices by using the juices to decolorize a DCPIP solution, with fruit juice as the independent variable and volume needed to decolorize as the dependent variable.
3. An experiment is presented to examine the effect of temperature on cell membrane permeability in beetroot, with temperature as the independent variable and percentage transmission of light through the solution as the dependent variable.