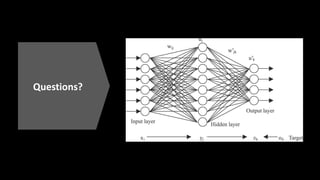
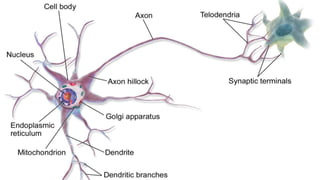
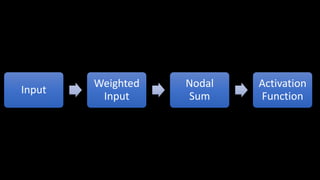
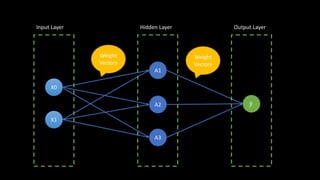
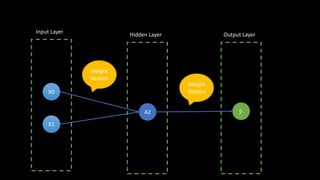
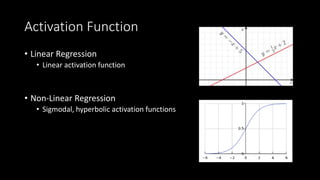
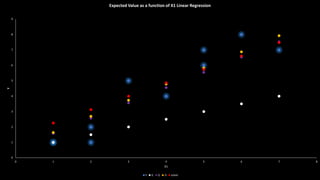
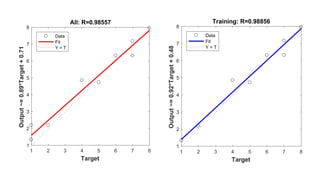
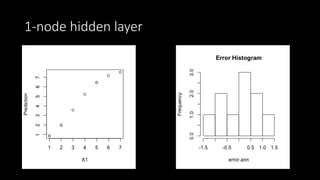
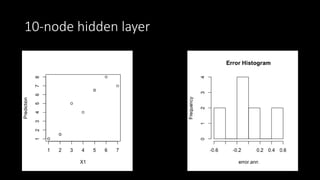
This document discusses neural networks and regression using artificial neural networks. It describes how neural networks mimic the human brain with networks of neurons and weighted connections. The document outlines the basic structure of a neural network with an input layer, hidden layers, and an output layer. It also discusses different activation functions that can be used for linear or nonlinear regression. The document provides an example of using an artificial neural network for regression with R code. It discusses concepts like forward and backward propagation, gradient descent, and minimizing a cost function.




![𝐸 =
1
2
( 𝑦 − 𝑦)2
𝐽1 =
𝒅𝑬
𝒅𝑾
=
𝑑𝑬
𝑑 𝑦
𝑑 𝑦
𝑑𝑧
𝑑𝑧
𝑑𝑾
= ( 𝑦 − 𝑦)
−𝑒−𝑧
1+𝑒−𝑧 2 [
𝜕𝑍
𝜕𝑊
(𝑥0 𝑤0 + 𝑥1 𝑤1 + 𝑥2 𝑤2)]
J2 =
𝒅𝑬
𝒅𝑾
=
𝑑𝑬
𝑑 𝑦
𝑑 𝑦
𝑑𝑧
𝑑𝑧
𝑑𝑾
= ( 𝑦 − 𝑦)[
𝜕𝑍
𝜕𝑊
(𝑥𝑖 𝑤𝑖 + 𝑥𝑗 𝑤𝑗 + 𝑥 𝑘 𝑤 𝑘)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170308231558/85/Artificial-Neural-Network-15-320.jpg)