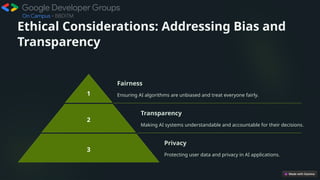
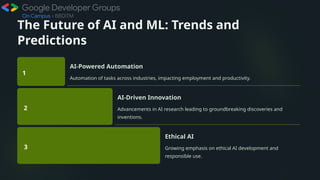
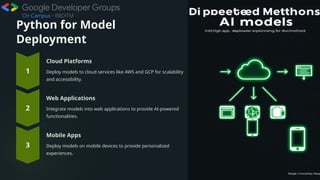
The document presents an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), detailing their definitions, evolution, algorithms, and significant applications across various industries such as healthcare and finance. It emphasizes the importance of data quality, ethical considerations like bias and transparency, and the necessity for skills development to adapt to an AI-driven world, notably through the use of Python programming. Lastly, the document explores the future potential of AI and ML, highlighting trends in automation, innovation, and responsible practices.